Abstract
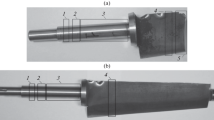
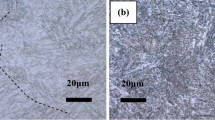
The high-pressure bypass valve stem of an ultra-supercritical unit has undergone a fatal fracture after running for more than 10,000 h. We analyzed the causes and types of the fracture by applying a series of tests: macroscopic and metallographic observation, chemical analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), microhardness, and high-temperature tensile tests. The results show that the leading reasons for fracture are inadequate chemical composition of the material, unreasonable structural design, insufficient high-temperature strength, vibration, and corrosion. Furthermore, the two ends of the dowel hole represent the crack source, and crack propagation and transient fracture zones could be observed. Based on these characteristics, it is concluded that the fracture of the valve stem belongs to fatigue fracture.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.C. Jung, T.H. Lee, M.T. Kim, Failure analysis of isolation valve stems in steam generator blow down system. Eng. Fail. Anal. 32, 98–105 (2013)
M. Ipohorski, M.I. Luppo, R. Castillo-Guerra, J. Ovejero-GarcIa, Failure analysis of a steam valve stem. Mater. Charact. 50, 23–30 (2003)
L. Yang, S. Li, X. Ziliu et al., Mo对双相钢过冷奥氏体连续冷却转变的影响 (Effect of Mo on continuous transformation of overcooled austenite for dual phase(DP) steel). Hebei Metall. 5, p8-13 (2021). ((in Chinese))
D. Leyi, W. Xiaoxiang, 马氏体时效不锈钢组织和性能的影响(Effect of Mo content on microstructure and properties of 00Ce12Ni9Mo(x)Cu2Ti maraging stainless steel). J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2, p235-238 (2013). ((in Chinese))
J. Wenna, J. Hui, Q. Dongxu et al., Effects of Mo on microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe2Ni2CrMox eutectic high entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 260, 1–8 (2021)
S. Yang Zhuoyue, C.J. Jie, X. Jianxin, C_Cr_Ni和Mn含量对304不锈钢变形诱发马氏体相变的影响 (Effect of C, Cr, Ni and Mn content on deformation-induced martensite transformation in 304 austenitic stainless steel). Iron Steel. 5, p61-64 (2007). ((in Chinese))
S. Zhenxue, L. Shizhong, Z. Jinqian, C含量对一种单晶高温合金组织和持久性能的影响 (Effect of C content on microstructures and stress rupture properties of a single crystal superalloy). Nonferrous Metal Mater. Eng. 5, p1-6 (2018). ((in Chinese))
Y. Bingyan, Z. Jiancang, X20CrMoV121钢焊接接头力学性能的试验研究 (Experimental study on mechanical properties of X20CrMoV121 Steel Welded Joint). Weld. Technol. 6, p1-4 (1996). ((in Chinese))
A. Jalali, A.A. Delouei, Failure analysis in a steam turbine stop valve of a thermal power plant. Eng. Fail. Anal. 105, 1131–1140 (2019)
O.G. Kwon, M.S. Han, Failure analysis of the exhaust valve steam from a Waukesha P9390 GSI gas engine. Eng. Fail. Anal. 11, 439–447 (2004)
Y. Ding, B. Wenbing, Li. Runquan, 碳含量对微合金化铸钢组织与性能的影响 (Effect of carbon content on microstructure and properties of microalloyed cast steel). Res. Explor. 5, p156-158 (2018). ((in Chinese))
M. Qikun, 不锈钢马氏体转变的影响因素研究 (Research of the influence factors of stainless martensitic transformation). Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 8, p124-125 (2015). ((in Chinese))
L. Du, Mo含量对1RK91马氏体时效不锈钢组织与性能的影响(Effect of Mo content on structure and properties of 1RK91 Maraging stainless steel), ZheJiang University, Master Thesis. 2012 (in Chinese).
Z. Weigang, Z. Yun, L. Shaozun, Li. Yong, W. Chunxu, Mo与Co含量对18Ni马氏体时效钢性能的影响 (Effects of Mo and Co content on properties of 18Ni maraging steel). Heat Treat. Met. 4, p48-52 (2018). ((in Chinese))
T. Liu, Effects of Mo contents on microstructure and properties of a microalloyed cast steel, China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House. 2016.
L. Ge, 热生长氧化层的生长机制及其力学性能表征分析 (Growth Mechanism of Thermal Growth Oxide Layer and Characterization of Its Mechanical Properties), Xiangtan University, Master Thesis. 2019(in Chinese).
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Project HNKJ19-H25 (Research and application of the Key technologies of controlled spalling and pre-separation of oxide peel in online detection of super (ultra) critical unit) of the China Huaneng Group. The authors are grateful for this support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C.L., Yan, A.J., Wei, X. et al. Fracture Failure Analysis of a High-Pressure Bypass Valve Stem. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 23, 1038–1045 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-023-01647-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-023-01647-2