Abstract
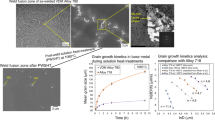
In the present work, an investigation is conducted into the effects of heat treatment (700, 800, 900 and 1000 °C) on the microstructure, mechanical properties and fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM). According to the results of microstructure analysis, compared with the Ti-6Al-4V alloy under the initial SLM condition, the sample shows a completely different microstructure after heat treatment. With the increase in heat treatment temperature, the dominant acicular α' martensite in Ti-6Al-4V alloy is decomposed into fine (α + β) lamellae, and the microstructure is significantly coarsened. When the heat treatment temperature exceeds 800 °C, the heat treatment sample develops a finer (α + β) dual-phase matrix microstructure. As revealed by the test of mechanical properties, the samples heat treatment at 900 °C exhibits higher yield strength, higher tensile strength, finer microstructure and greater elongation at break. To be specific, the tensile strength, yield strength and elongation are 921 Mpa, 819 MPa and 16.1%, respectively. According to the results of high cycle fatigue test, the fatigue performance of SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloy is significantly improved by conducting stress relief heat treatment at 900 °C for 107 cycles, with the fatigue strength reaching 190 MPa.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Rezvanian, R. Daza, P.A. Lopez, M. Ramos, D. Gonzaleznieto, M. Elices and J. Perezrigueiro, Enhanced Biological Response of AVS-Functionalized Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Through Covalent Immobilization of Collagen, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, p 3337. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21685-3
C.J. Todaro, M.A. Easton, D. Qiu, D. Zhang, M.J. Bermingham, E.W. Lui, M. Brandt, D.H. StJohn and M. Qian, Grain Structure Control During Metal 3D Printing by High-intensity Ultrasound, Nat. Commun., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13874-z
Y. Xiong, W. Wang, R. Gao, H. Zhang, L. Dong, J. Qin, B. Wang, W. Jia and X. Li, Fatigue Behavior and Osseointegration of Porous Ti-6Al-4V Scaffolds with Dense Core for Dental Application, Mater. Des., 2020, 195, p 108994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108994
S. Cao, Q. Hu, A. Huang, Z. Chen, M. Sun, J. Zhang, C. Fu, Q. Jia, C.V.S. Lim, R.R. Boyer, Y. Yang and X. Wu, Static Coarsening Behaviour of Lamellar Microstructure in Selective Laser Melted Ti- 6Al-4V, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35, p 1578–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.04.008
L. Zhao, J.G.S. Macías, A. Dolimont, A. Simar and E.R. Lorphèvre, Comparison of Residual Stresses Obtained by the Crack Compliance Method for Parts Produced by Different Metal Additive Manufacturing Techniques and After Friction Stir Processing, Addit. Manuf., 2020, 36, p 101499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101499
X.P. Ren, H.Q. Li, H. Guo, F.L. Shen, C.X. Qin, E.T. Zhao and X.Y. Fang, A Comparative Study on Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Processed by Additive Manufacturing vs. Traditional Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 817, p 141384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141384
C.J. Huang, X.C. Yan, L. Zhao, M. Liu, W.Y. Ma, W.B. Wang, J. Soete and A. Simar, Ductilization of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 755, p 85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.133
A. Hemmasian Ettefagh, C. Zeng, S. Guo and J. Raush, Corrosion Behavior of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Parts and the Effect of Post Annealing, Addit. Manuf., 2019, 28, p 252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.05.011
W. Zhang, M. Tong and N.M. Harrison, Scanning Strategies Effect on Temperature, Residual Stress and Deformation by Multi-laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion Manufacturing, Addit. Manuf., 2020, 36, p 101507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101507
M. Asherloo, Z.H. Wu, M.H. Delpazir, E. Ghebreiesus, S. Fryzlewicz, R.B. Jiang, B. Gould, M. Heim, D. Nelson, M. Marucci, M. Paliwal, A.D. Rollett and A. Mostafaei, Laser-beam Powder Bed Fusion of Cost-effective Non-spherical Hydride-dehydride Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Addit. Manuf., 2022, 56, p 102875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2022.102875
C. Qiu, N.J.E. Adkins and M.M. Attallah, Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Selectively Laser-melted and of HIPed Laser-melted Ti-6Al-4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 578, p 230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.04.099
D. Gu, Y.-C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, G. Meng, R.J.S. Batista, K. Wissenbach and R. Poprawe, Densification Behavior, Microstructure Evolution, and Wear Performance of Selective Laser Melting Processed Commercially Pure Titanium, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(9), p 3849–3860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.04.006
C. Yuan, B. Liu, Y. Liu and Y. Liu, Processing Map and Hot Deformation Behavior of Ta-particle Reinforced TiAl Composite, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2020, 30, p 657–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65240-2
W. Yang, X. He, H. Li, J. Dong, W. Chen, H. Xin and Z. Jin, A Tribological Investigation of SLM Fabricated TC4 Titanium Alloy with Carburization Pre-treatment, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, p 3043–3050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.004
Q. Yan, B. Chen, N. Kang, X. Lin, S. Lv, K. Kondoh, S. Li and J.S. Li, Comparison Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloys Fabricated by Powder-based Selective-laser-Melting and Sintering Methods, Mater Charact, 2020, 164, p 110358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110358
Y. Xu, D. Zhang, Y. Guo, S. Hu, X. Wu and Y. Jiang, Microstructural Tailoring of As-Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V Alloy for High Mechanical Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 816, p 152536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152536
W. Sun, Y. Ma, W. Huang, W. Zhang and X. Qian, Effects of Build Direction on Tensile and Fatigue Performance of Selective Laser Melting Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2020, 130, p 105260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105260
W. Xu, M. Brandt, S. Sun, J. Elambasseril, Q. Liu, K. Latham, K. Xia and M. Qian, Additive Manufacturing of Strong and Ductile Ti-6Al-4V by Selective Laser Melting via in situ Martensite Decomposition, Acta Mater., 2015, 85, p 74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.11.028
H. Ali, L. Ma, H. Ghadbeigi and K. Mumtaz, In-situ Residual Stress Reduction, Martensitic Decomposition and Mechanical Properties Enhancement through High Temperature Powder Bed Pre-heating of Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 695, p 211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.033
H. Li, Z. Yang, D. Cai, D. Jia and Y. Zhou, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Melted Bulk-form Titanium Matrix Nanocomposites with Minor B4C Additions, Mater. Des., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108245
B.K. Nagesha, S. Anand Kumar, K. Vinodh, A. Pathania and S. Barad, A Thermo–Mechanical Modelling Approach on the Residual Stress Prediction of SLM Processed HPNGV Aeroengine Part, Mater. Today Proc., 2021, 44, p 4990–4996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.940
M. Frkan, R. Konecna, G. Nicoletto and L. Kunz, Microstructure and Fatigue Performance of SLM-fabricated Ti6Al4V Alloy After Different Stress-relief Heat Treatments, Transp. Res. Procedia., 2019, 40, p 24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2019.07.005
S.G. Chen, Y.D. Zhang, Q. Wu, H.J. Gao, Z.H. Gao and X. Li, Effect of Solid-state Phase Transformation on Residual Stress of Selective Laser Melting Ti-6Al-4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 819, p 141299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141299
J.W. Pegues, M.A. Melia, R. Puckett, S.R. Whetten, N. Argibay and A.B. Kustas, Exploring Additive Manufacturing as a High-throughput Screening Tool for Multiphase High Entropy Alloys, Addit. Manuf., 2021, 37, p 101598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101598
A. Azarniya, X.G. Colera, M.J. Mirzaali, S. Sovizi, F. Bartolomeu, S. Weglowski, W.W. Wits, C.Y. Yap, J. Ahn, G. Miranda, F.S. Silva, H.R.M. Hosseini, S. Ramakrishna and A.A. Zadpoor, Additive Manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V Parts Through Laser Metal Deposition (LMD): Process, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 804, p 163–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.255
B. Vrancken, L. Thijs, J.-P. Kruth and J. Van Humbeeck, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Novel β Titanium Metallic Composite by Selective Laser Melting, Acta Mater., 2014, 68, p 150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.01.018
L. Emanuelli, A. Molinari, L. Facchini, E. Sbettega, S. Carmignato, M. Bandini and M. Benedetti, Effect of Heat Treatment Temperature and Turning Residual Stresses on the Plain and Notch Fatigue Strength of Ti-6Al-4V Additively Manufactured via Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Int. J. Fatigue, 2022, 162, p 107009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107009
S. Leuders, M. Thöne, A. Riemer, T. Niendorf, T. Tröster, H.A. Richard and H.J. Maier, On the Mechanical Behaviour of Titanium Alloy TiAl6V4 Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting: Fatigue Resistance and Crack Growth Performance, Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, 48, p 300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.11.011
E. Pessard, M. Lavialle, P. Laheurte, P. Didier and M. Brochu, High-cycle Fatigue Behavior of a Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Titanium: Effect of Pores and Tested Volume Size, Int. J. Fatigue, 2021, 149, p 106206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106206
B. Ellyson, M. Brochu and M. Brochu, Characterization of Bending Vibration Fatigue of SLM Fabricated Ti-6Al-4V, Int. J. Fatigue, 2017, 99, p 25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.02.005
F. Cao, T. Zhang, M.A. Ryder and D.A. Lados, A Review of the Fatigue Properties of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V, JOM, 2018, 70, p 349–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2728-5
S.A. Etesami, B. Fotovvati and E. Asadi, Heat Treatment of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Manufactured by Laser-based Powder-bed Fusion: Process, Microstructures, and Mechanical Properties Correlations, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 895, p 162618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162618
Q. Chao, P.D. Hodgson and H. Beladi, Ultrafine Grain Formation in a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Thermomechanical Processing of a Martensitic Microstructure, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45, p 2659–2671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2205-5
M. Paghandeh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H.R. Abedi and Y. Vahidshad, The Enhanced Warm Temperature Ductility of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Through Strain Induced Martensite Reversion and Recrystallization, Mater. Lett., 2021, 302, p 130405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130405
N. Jin, Z. Yan, Y. Wang, H. Cheng and H. Zhang, Effects of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Lattice Materials, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2021, 190, p 106042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106042
H. Galarraga, R.J. Warren, D.A. Lados, R.R. Dehoff, M.M. Kirka and P. Nandwana, Effects of Heat Treatments on Microstructure and Properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI Alloy Fabricated by Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 685, p 417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.01.019
D. Agius, K.I. Kourousis, C. Wallbrink and T. Song, Cyclic Plasticity and Microstructure of As-built SLM Ti-6Al-4V: The Effect of Build Orientation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 701, p 85–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.06.069
L. Thijs, F. Verhaeghe, T. Craeghs, J.V. Humbeeck and J.-P. Kruth, A Study of the Microstructural Evolution During Selective Laser Melting of Ti-6Al-4V, Acta Mater., 2010, 58, p 3303–3312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.02.004
A. Zafari, M.R. Barati and K. Xia, Controlling Martensitic Decomposition During Selective Laser Melting to Achieve Best Ductility in High Strength Ti-6Al-4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 744, p 445–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.12.047
C. Chang, J. Huang, X. Yan, Q. Li, M. Liu, S. Deng, J. Gardan, R. Bolot, M. Chemkhi and H. Liao, Microstructure and Mechanical Deformation Behavior of Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V ELI Alloy Porous Structures, Mater. Lett., 2020, 277, p 128366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128366
C. Qiu, M.A. Kindi, A.S. Aladawi et al., A Comprehensive Study on Microstructure and Tensile Behaviour of a Selectively Laser Melted Stainless Steel, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, p 7785. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26136-7
J. Haubrich, J. Gussone, P. Barriobero-Vila, P. Kürnsteiner, E.A. Jägle, D. Raabe, N. Schell and G. Requena, The Role of Lattice Defects, Element Partitioning and Intrinsic Heat Effects on the Microstructure in Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V, Acta Mater., 2019, 167, p 136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.01.039
P. Krakhmalev, G. Fredriksson, I. Yadroitsava, N. Kazantseva, A.D. Plessis and I. Yadroitsev, Deformation Behavior and Microstructure of Ti6Al4V Manufactured by SLM, Phys. Procedia, 2016, 83, p 778–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2016.08.080
W. Shi Feng, L. Shuai, W. Qingsong, C. Yan, Z. Sheng and S. Yusheng, Effect of Molten Pool Boundaries on the Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Melting Parts, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, 214, p 2660–2667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.06.002
A. Maenosono, M. Koyama, Y. Tanaka, S. Ri, Q. Wang and H. Noguchi, Crystallographic Selection Rule for the Propagation Mode of Microstructurally Small Fatigue Crack in a Laminated Ti-6Al-4V Alloy: Roles of Basal and Pyramidal Slips, Int. J. Fatigue, 2019, 128, p 105200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.105200
J. Liu, K. Zhang, J. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Yang, L. Yan, X. Tian, Y. Zhu and A. Huang, Investigation of Fatigue Behavior of Laser Powder Bed Fusion Ti-6Al-4V: Roles of Heat Treatment and Microstructure, Int. J. Fatigue, 2023, 176, p 107839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107839
P. Åkerfeldt, R. Pederson and M.-L. Antti, A Fractographic Study Exploring the Relationship Between the Low Cycle Fatigue and Metallurgical Properties of Laser Metal Wire Deposited Ti-6Al-4V, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 87, p 245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2016.02.011
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Class III Peak Discipline of Shanghai—Materials Science and Engineering (High-Energy Beam Intelligent Processing and Green Manufacturing) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M7010380) for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Minghui Wang and Hua Yan helped in conceptualization, data analysis, writing—original draft and methodology. Hua Yan helped in conceptualization, data analysis and methodology. Peilei Zhang helped in data verification and investigation. Qing Hua Lu worked in investigation and methodology. Kaiwei Liu worked in investigation and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Yan, H., Lu, Q. et al. Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Alloy after Post-Heat Treatments: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Fatigue Behavior. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09504-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09504-5