Abstract
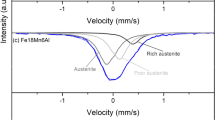
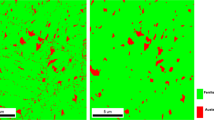
In the present study, strain-induced martensitic transformation has been used to estimate plastic strain resulting from grit-blasting in 18Ni(300) maraging steel. Overaged samples having high volume fraction of γ-austenite phase were blasted at two different blasting angles (at 45° and 75°), keeping constant all the other process variables. The kinetics of martensitic transformation induced by grit-blasting was treated as a function of the strain, according to the Ludwigson–Berger model, and the Kp value was adopted as an indicator of the mechanical stability of γ-austenite. The model was parametrized through the stretching of tensile testing specimens, at specific deformation levels. The increase on the dislocation density (ρ) resulting from blasting could also be determined by the Williamson–Hall method. The volume fraction of γ-austenite (Vγ) was quantified in both blasted and stretched samples by ex situ XRD analyses. It was found that γ-austenite to α′-martensite phase transformation occurred in blasted and stretched samples, after certain stress levels, despite their strain rate differences. For the process parameters employed, the resulting plastic true strain on the steel surface was in the order of 0.031 and 0.047 for blasting angles of 45° and 75°, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Rohrbach and M. Schmidt, Maraging steels, in Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High-Performance Alloys, ASM International, 1990, p 793–800.
A.G. dos Reis, D.A.P. Reis, A.J. Abdalla, and J. Otubo, High-Temperature Creep Resistance and Effects on the Austenite Reversion and Precipitation of 18 Ni (300) Maraging Steel, Mater Charact, 2015, 107, p 350–357.
W. Sha, A. Cerezo, and G.D.W. Smith, Phase Chemistry and Precipitation Reactions in Maraging Steels: Part I. Introduction and Study of Co-Containing C-300 Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1993, 24(6), p 1221–1232.
A.M. Hall and C.J. Slunder, The Metallurgy, Behavior and Application of the 18-Percent Nickel Maraging Steels, SP-5051, NASA (Washington, DC), 1968.
F. Habiby, A. ul Haq, and A.Q. Khan, The Properties and Applications of 18% Nickel Maraging Steels, Mater. Technol., 1994, 9(11–12), p 246–252.
R.F. Decker, J.T. Eash, and A.J. Goldman, 18% Nickel Maraging Steel, Trans. ASM, 1962, 55, p 58.
S. Floreen, The Physical Metallurgy of Maraging Steels, Metall. Rev., 1968, 13(1), p 115–128.
R. Schnitzer, G.A. Zickler, E. Lach, H. Clemens, S. Zinner, T. Lippmann, and H. Leitner, Influence of Reverted Austenite on Static and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of a PH 13-8 Mo Maraging Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(7–8), p 2065–2070.
U.K. Viswanathan, G.K. Dey, and V. Sethumadhavan, Effects of Austenite Reversion During Overageing on the Mechanical Properties of 18 Ni (350) Maraging Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 398(1–2), p 367–372.
M. Ahmed, A. Ali, S.K. Hasnain, F.H. Hashmi, and A.Q. Khan, Magnetic Properties of Maraging Steel in Relation to Deformation and Structural Phase Transformations, Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, 42(3), p 631–638.
M. Farooque, H. Ayub, A. Ul Haq, and A.Q. Khan, The Formation of Reverted Austenite in 18% Ni 350 Grade Maraging Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 1998, 33(11), p 2927–2930.
A. Markfeld and A. Rosen, The Effect of Reverted Austenite on the Plastic Deformation of Maraging Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1980, 46(2), p 151–157.
H. Springer, M. Belde, and D. Raabe, Bulk Combinatorial Design of Ductile Martensitic Stainless Steels through Confined Martensite-to-Austenite Reversion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 582, p 235–244.
F. Habiby, A. ul Haq, and A.Q. Khan, Influence of Austenite on the Coercive Force, Electrical Resistivity and Hardness of 18% Ni Maraging Steels, Mater. Des., 1992, 13(5), p 259–264.
F. Qian, J. Sharp, and W.M. Rainforth, Microstructural Evolution of Mn-Based Maraging Steels and Their Influences on Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 674, p 286–298.
S.S.M. Tavares, M.R. da Silva, J.M. Neto, M. Pardal, C. Fonseca, and H.F. Abreu, Magnetic Properties of a Ni–Co–Mo–Ti Maraging 350 Steel, J. Alloys Compd., 2004, 373(1–2), p 304–311.
C. Celada-Casero, H. Kooiker, M. Groen, J. Post, and D. San-Martin, In-Situ Investigation of Strain-Induced Martensitic Transformation Kinetics in an Austenitic Stainless Steel by Inductive Measurements, Metals (Basel), 2017, 7(7), p 271.
W. Sha, H. Leitner, Z. Guo, and W. Xu, Phase transformations in maraging steels, Phase Transformations in Steels. E. Pereloma, S. Edmonds Ed., Elsevier, 2012, p 332–362
L. Yuan, D. Ponge, J. Wittig, P. Choi, J.A. Jiménez, and D. Raabe, Nanoscale Austenite Reversion through Partitioning, Segregation and Kinetic Freezing: Example of a Ductile 2 GPa Fe-Cr-C Steel, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(6–7), p 2790–2804.
M. Ahmed, I. Nasim, H. Ayub, F.H. Hashmi, and A.Q. Khan, Mechanical Stability and Magnetic Properties of Austenite, J. Mater. Sci., 1995, 30(24), p 6257–6266.
Y. Katz, H. Mathias, and S. Nadiv, The Mechanical Stability of Austenite in Maraging Steels, Metall. Trans. A, 1983, 14(4), p 801–808.
S. Hossein Nedjad, S. Meimandi, A. Mahmoudi, T. Abedi, S. Yazdani, H. Shirazi, and M. Nili Ahmadabadi, Effect of Aging on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Fe–Ni–Mn–Cr Maraging Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 501(1–2), p 182–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.09.062
S. Ebnesajjad and A.H. Landrock, Material Surface Preparation Techniques, Adhesives Technology Handbook, S. Ebnesajjad and A.H.B.T.-A.T.H. (Third E. Landrock, Eds., (Boston), Elsevier, 2015, p 35–66.
K. Tosha, J. Lu, B. Guelorget, and E. Nagashima, Shot Peening and Grit Blasting-Effects on Surface Integrity, Icsp9 Shot Peen, Citeseer, 2005, 16, p 400–405.
H. Sato, T. Nishiura, E. Miura-Fujiwara, and Y. Watanabe, Phase Transformation in Fe Alloys Induced by Surface Treatment, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2014, 2012(706–709), p 1996–2001.
A. Eres-Castellanos, C. Garcia-Mateo, and F.G. Caballero, Future Trends on Displacive Stress and Strain Induced Transformations in Steels, Metals (Basel), 2021, 11(2), p 299.
E.S. Perdahcioglu, H.J.M. Geijselaers, and M. Groen, Influence of Plastic Strain on Deformation-Induced Martensitic Transformations, Scr. Mater., 2008, 58(11), p 947–950.
D. Fahr, Stress- and Strain-Induced Formation of Martensite and Its Effects on Strength and Ductility of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels, Metall. Trans., 1971, 2(7), p 1883–1892.
M. Kobayashi, K. Ueno, A. Kamada, and T. Nakane, Transformation-Induced Plastic Behaviour of 18%Ni Maraging Steels, Met. Technol., 1981, 8(1), p 27–32.
A. Das, P.C. Chakraborti, S. Tarafder, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Analysis of Deformation Induced Martensitic Transformation in Stainless Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, 27(1), p 366–370.
M.J. Sohrabi, M. Naghizadeh, and H. Mirzadeh, Deformation-Induced Martensite in Austenitic Stainless Steels: A Review, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2020, 20(4), p 124.
K. Spencer, J.D. Embury, K.T. Conlon, M. Véron, and Y. Bréchet, Strengthening via the Formation of Strain-Induced Martensite in Stainless Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 387–389(1–2 SPEC. ISS.), p 873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.11.084
B. He, On the Factors Governing Austenite Stability: Intrinsic versus Extrinsic, Materials (Basel), 2020, 13(15), p 3440.
J. Talonen, H. Hänninen, P. Nenonen, and G. Pape, Effect of Strain Rate on the Strain-Induced γ → Α′-Martensite Transformation and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36(2), p 421–432.
S.S. Hecker, M.G. Stout, K.P. Staudhammer, and J.L. Smith, Effects of Strain State and Strain Rate on Deformation-Induced Transformation in 304 Stainless Steel: Part I. Magnetic Measurements and Mechanical Behavior, Metall. Trans. A, 1982, 13(4), p 619–626.
A.W. Momber and Y.C. Wong, Overblasting Effects on Surface Properties of Low-Carbon Steel, J. Coatings Technol. Res., 2005, 2(6), p 453–461.
S.K. Asl and M.H. Sohi, Effect of Grit-Blasting Parameters on the Surface Roughness and Adhesion Strength of Sprayed Coating, Surf. Interface Anal., 2010, 42(6–7), p 551–554.
W. Czepułkowska, E. Wołowiec-Korecka, and L. Klimek, The Condition of Ni-Cr Alloy Surface After Abrasive Blasting with Various Parameters, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(3), p 1439–1444.
T. Ghara, S. Paul, and P.P. Bandyopadhyay, Effect of Grit Blasting Parameters on Surface and Near-Surface Properties of Different Metal Alloys, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2021, 30(1–2), p 251–269.
G.D. Byrne, L. O’Neill, B. Twomey, and D.P. Dowling, Comparison between Shot Peening and Abrasive Blasting Processes as Deposition Methods for Hydroxyapatite Coatings onto a Titanium Alloy, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2013, 216, p 224–231.
S.A. Meguid, G. Shagal, and J.C. Stranart, Finite Element Modelling of Shot-Peening Residual Stresses, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1999, 92–93, p 401–404.
K. Schiffner and C. Droste, Simulation of Residual Stresses by Shot Peening, Comput. Struct., 1999, 72(1), p 329–340.
K. Poorna Chander, M. Vashista, K. Sabiruddin, S. Paul, and P.P. Bandyopadhyay, Effects of Grit Blasting on Surface Properties of Steel Substrates, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(8), p 2895–2902.
M. Umemoto, Y. Todaka, and K. Tsuchiya, Formation of Nanocrystalline Structure in Steels by Air Blast Shot Peening, Mater. Trans., 2003, 44(7), p 1488–1493.
J.L. Liu, M. Umemoto, Y. Todaka, and K. Tsuchiya, Formation of a Nanocrystalline Surface Layer on Steels by Air Blast Shot Peening, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42(18), p 7716–7720.
X.Y. Wang and D.Y. Li, Mechanical, Electrochemical and Tribological Properties of Nano-Crystalline Surface of 304 Stainless Steel, Wear, 2003, 255(7), p 836–845.
M. Multigner, S. Ferreira-Barragáns, E. Frutos, M. Jaafar, J. Ibáñez, P. Marín, M.T. Pérez-Prado, G. González-Doncel, A. Asenjo, and J.L. González-Carrasco, Superficial Severe Plastic Deformation of 316 LVM Stainless Steel through Grit Blasting: Effects on Its Microstructure and Subsurface Mechanical Properties, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2010, 205(7), p 1830–1837.
A. Lara, M. Roca, S. Parareda, N. Cuadrado, J. Calvo, and D. Casellas, Effect of Sandblasting on Low and High-Cycle Fatigue Behaviour after Mechanical Cutting of a Twinning-Induced Plasticity Steel, MATEC Web Conf., 2018, 165, p 4–11.
B. Arifvianto, M. Mahardika, U.A. Salim, and S. Suyitno, Comparison of Surface Characteristics of Medical-Grade 316L Stainless Steel Processed by Sand-Blasting, Slag Ball-Blasting and Shot-Blasting Treatments, J. Eng. Technol. Sci., 2020, 52(1), p 1.
D.J. Buchanan and R. John, Residual Stress Redistribution in Shot Peened Samples Subject to Mechanical Loading, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 615, p 70–78.
P.S. Prevéy, The Effect of Cold Work on the Thermal Stability of Residual Compression in Surface Enhanced IN718, ASM Proc. Heat Treat., 2000, 1, p 426–434.
P.S. Prevéy, Residual Stress in Design, Process and Materials Selection, Ed. WB Young, Am. Soc. Met., Met. Park. Ohio, 1987, p 11–19.
P.S. Prevéy, The Measurement of Subsurface Residual Stress and Cold Work Distributions in Nickel Base Alloys, Residual Stress Des. Process. Mater. Sel., 1987, p 11–19.
T. Kim, H. Lee, S. Jung, and J.H. Lee, A 3D FE Model with Plastic Shot for Evaluation of Equi-Biaxial Peening Residual Stress Due to Multi-Impacts, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2012, 206(13), p 3125–3136.
K.A. Soady, B.G. Mellor, G.D. West, G. Harrison, A. Morris, and P.A.S. Reed, Evaluating Surface Deformation and near Surface Strain Hardening Resulting from Shot Peening a Tempered Martensitic Steel and Application to Low Cycle Fatigue, Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, 54, p 106–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2013.03.019
J.R. Cahoon, W.H. Broughton, and A.R. Kutzak, The Determination of Yield Strength from Hardness Measurements, Metall. Trans., 1971, 2(7), p 1979–1983.
E.J. Pavlina and C.J. Van Tyne, Correlation of Yield Strength and Tensile Strength with Hardness for Steels, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2008, 17(6), p 888–893.
D.C. Ludwigson and J.A. Berger, Plastic Behaviour of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels, J Iron Steel Inst, 1969, 207(1), p 63–69.
T. Narutani, Effect of Deformation-Induced Martensitic Transformation on the Plastic Behavior of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Trans. JIM, 1989, 30(1), p 33–45.
G.K. Williamson and R.E. Smallman, Dislocation Densities in Some Annealed and Cold-Worked Metals from Measurements on the X-Ray Debye-Scherrer Spectrum, Philos. Mag., 1956, 1(1), p 34–46.
H. Guechichi and L. Castex, Fatigue Limits Prediction of Shot Peened Materials, Fatigue Fract. Steels, 2006, 172, p 221–228.
P. Rozenak, L. Zevin, and D. Eliezer, Hydrogen Effects on Phase Transformations in Austenitic Stainless Steels, J. Mater. Sci., 1984, 19(2), p 567–573.
M. Morawiec and A. Grajcar, Some Aspects of the Determination of Retained Austenite Using the Rietveld Refinement, J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng., 2017, 1(80), p 11–17. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0010.1442
J.M. Pardal, S.S.M. Tavares, M.P. CindraFonseca, H.F.G. Abreu, and J.J.M. Silva, Study of the Austenite Quantification by X-Ray Diffraction in the 18Ni-Co-Mo-Ti Maraging 300 Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41(8), p 2301–2307.
O. Matsumura, Y. Sakuma, and H. Takechi, Trip and Its Kinetic Aspects in Austempered 0.4C–1.5Si-0.8Mn Steel, Scr. Metall., 1987, 21(10), p 1301–1306.
R.E. Smallman and K.H. Westmacott, Stacking Faults in Face-Centred Cubic Metals and Alloys, Philos. Mag., 1957, 2(17), p 669–683.
A. Sharma, A. Agarwal, M. Acharya, and S.C. Sharma, Optimization of Aging Cycle of Stainless Maraging Steel Using Dilatometric and Differential Scanning Calorimetric Analysis to Improve Its Strength, 2015, 831, p 147–150.
A.G. Reis, D.A.P. Reis, A.J. Abdalla, J. Otubo, and H.R.Z. Sandim, A Dilatometric Study of the Continuous Heating Transformations in Maraging 300 Steel, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2015, 97(1).
J. Post, “On the Constitutive Behaviour of Sandvik Nanoflex: Modelling, Experiments and Multi-Stage Forming,” University of Twente, 2004, https://ris.utwente.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/6087584/thesis_Post.pdf.
Z.H. Cai, H. Ding, R.D.K. Misra, and H. Kong, Unique Serrated Flow Dependence of Critical Stress in a Hot-Rolled Fe–Mn–Al–C Steel, Scr. Mater., 2014, 71, p 5–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.09.009
V. Govindaraj, P. Hodgson, R.P. Singh, and H. Beladi, The Effect of Austenite Reversion on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 828(9), p 142097.
S. Shamsdini, M.H. Ghoncheh, M. Sanjari, H. Pirgazi, B.S. Amirkhiz, L. Kestens, and M. Mohammadi, Plastic Deformation throughout Strain-Induced Phase Transformation in Additively Manufactured Maraging Steels, Mater. Des., 2021, 198, p 109289.
G.A. Zickler, R. Schnitzer, R. Hochfellner, T. Lippmann, S. Zinner, and H. Leitner, Transformation of Reverted Austenite in a Maraging Steel under External Loading: An In-Situ X-Ray Diffraction Study Using High-Energy Synchrotron Radiation, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2009, 100(11), p 1566–1573.
Y. Ye, J. Li, X. Lv, and L. Liu, Study on Failure Mechanism and Phase Transformation of 304 Stainless Steel during Erosion Wear, Metals (Basel), 2020, 10(11), p 1427.
T. Ghara, S. Paul, and P.P. Bandyopadhyay, Influence of Grit Blasting on Residual Stress Depth Profile and Dislocation Density in Different Metallic Substrates, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2021, 52(1), p 65–81.
P.J. Ferreira, J.B. VanderSande, M.A. Fortes, and A. Kyrolainen, Microstructure Development during High-Velocity Deformation, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35(10), p 3091–3101.
M. Multigner, E. Frutos, J.L. González-Carrasco, J.A. Jiménez, P. Marín, and J. Ibáñez, Influence of the Sandblasting on the Subsurface Microstructure of 316LVM Stainless Steel: Implications on the Magnetic and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2009, 29(4), p 1357–1360.
B.J. Griffiths, D.T. Gawne, and G. Dong, The Erosion of Steel Surfaces by Grit-Blasting as a Preparation for Plasma Spraying, Wear, 1996, 194(1–2), p 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(95)06798-1
S. Geng, J. Sun, and L. Guo, Effect of Sandblasting and Subsequent Acid Pickling and Passivation on the Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of 316L Stainless Steel, Mater. Des., 2015, 88, p 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.08.113
M. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Zhu, L. Zhang, and P. Jin, Ex-Situ EBSD Analysis of Hot Deformation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Mg–1Al–6Y Alloy via Uniaxial Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 775, 138978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.138978
J. Chiang, B. Lawrence, J.D. Boyd, and A.K. Pilkey, Effect of Microstructure on Retained Austenite Stability and Work Hardening of TRIP Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(13–14), p 4516–4521.
F.F. Conde, J.D. Escobar, J.P. Oliveira, A.L. Jardini, W.W. Bose Filho, and J.A. Avila, Austenite Reversion Kinetics and Stability during Tempering of an Additively Manufactured Maraging 300 Steel, Addit. Manuf., 2019, 29(October 2018), p 100804.
S.A. Meguid, G. Shagal, and J.C. Stranart, 3D FE Analysis of Peening of Strain-Rate Sensitive Materials Using Multiple Impingement Model, Int. J. Impact Eng, 2002, 27(2), p 119–134.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Instituto Tecnológico de Aeronáutica (ITA), in special to Professor A.S. Antunes and to the MSc. Filipe Caldatto Dalan for the FEG-SEM analysis, to the Instituto de Estudos Avançados (IEAv) in special to DSc. Davi Neves, for the XRD analysis, for the Institute de Aeronáutia e Espaço (IAE) for the metallographic preparation, and for the Núcleo de Apoio à Pesquisa em Ciência e Engenharia de Materiais (NAPCEM) of the Federal University of São Paulo for the XRD, Dilatometry and SEM analysis
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Palau, J.C.F., Travessa, D.N. The Use of Strain-Induced Martensitic Transformation Phenomena to Estimate the Surface Plastic Strain Produced by Grit Blasting on Overaged 18Ni Maraging Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09176-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09176-1