Abstract
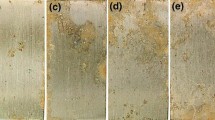
In this study, the atmosphere corrosion behavior of stainless steels (SSs) 201 and 304 was investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-disperse spectroscopy (EDS) and electrochemical measurements. The result shows that the steels undergo the atmosphere corrosion under the help of water in air, and the general corrosion degree of the steels increases with time. The corrosion degree of SS201 is more serious than that of SS304, and local corrosion occurs around grain boundaries. The results are simultaneously confirmed by icorr and Rp of the steels. The lower Ni content, the high MnS inclusion and the chloride-containing ingredient could be the main reasons for the high corrosion activity of SS201.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data will be made available on request.
References
A.I. Shcherbakov, Theory of Dissolution of Binary Alloys and the Tamman Rule, Prot. Met., 2005, 41, p 30–35.
T.L.S.L. Wijesinghe and D.J. Blackwood, Characterisation of Passive Films on 300 Series Stainless Steels, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 253, p 1006–1009.
R.-H. Jung, H. Tsuchiya, and S. Fujimoto, XPS Characterization of Passive Films Formed on Type 304 Stainless Steel in Humid Atmosphere, Corros. Sci., 2012, 58, p 62–68.
C. García, F. Martín, P. de Tiedra, and L.G. Cambronero, Pitting Corrosion Behaviour of PM Austenitic Stainless Steels Sintered in Nitrogen–Hydrogen Atmosphere, Corros. Sci., 2007, 49, p 1718–1736.
A. Fattah-alhosseini, M.A. Golozar, A. Saatchi, and K. Raeissi, Effect of Solution Concentration on Semiconducting Properties of Passive Films Formed on Austenitic Stainless Steels, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 205–209.
R.T. Loto, Pitting Corrosion Evaluation of Austenitic Stainless Steel Type 304 in Acid Chloride Media, J. Mater. Environ. Sci., 2013, 4, p 448–459.
Z.Y. Chen, F. Cui, and R.G. Kelly, Calculations of the Cathodic Current Delivery Capacity and Stability of Crevice Corrosion under Atmospheric Environments, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155, p 360–368.
U.K. Mudali and M.G. Pujar, Pitting Corrosion of Austenitic Stainless Steels and Their Weldments, Corrosion of Austenitic Stainless Steels. H.S. Khatak, B. Raj Ed., Woodhead Publishing, 2002, p 74–105
F.G. Wilson, Mechanism of Intergranular Corrosion of Austenitic Stainless Steels—Literature Review, Br. Corros. J., 2013, 6, p 100–108.
D.-H. Xia, S. Song, Z. Qin, W. Hu, and Y. Behnamian, Review—Electrochemical Probes and Sensors Designed for Time-Dependent Atmospheric Corrosion Monitoring: Fundamentals, Progress, and Challenges, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167, p 1–10.
Y.K. Cai, Y. Zhao, X.B. Ma, K. Zhou, and Y. Chen, Influence of Environmental Factors on Atmospheric Corrosion in Dynamic Environment, Corros. Sci., 2018, 137, p 163–175.
D.-H. Xia, C. Ma, S. Song, and L. Xu, Detection of Atmospheric Corrosion of Aluminum Alloys by Electrochemical Probes: Theoretical Analysis and Experimental Tests, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166, p 1000–1009.
Y. Zhu, T. Hu, Y. Li, J. Hao, B. Han, and Q. Yuan, Pitting Corrosion of 2A12 Aluminum Alloy Long-Scale Specimen in Simulated Seawater Splash Zone, Dynamic Waterline Zone and Full Immersion Zone, Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2023, 70, p 101–107.
D.-H. Xia, Z. Qin, S. Song, D. Macdonald, and J.-L. Luo, Combating Marine Corrosion on Engineered Oxide Surface by Repelling, Blocking and Capturing Cl-: A Mini Review, Corros. Commun., 2021, 2, p 1–7.
Y. Tsutsumi, A. Nishikata, and T. Tsuru, Monitoring of Rusting of Stainless Steels in Marine Atmospheres using Electrochemical Impedance Technique, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2006, 153, p 278–282.
M. Kouřil, P. Novák, and M. Bojko, Threshold Chloride Concentration for Stainless Steels Activation in Concrete Pore Solutions, Cem. Concr. Res., 2010, 40, p 431–436.
J. Hu, J. Deng, P. Deng, and G. Wang, Corrosion Monitoring Method of 304 Stainless Steel in a Simulated Marine-Industrial Atmospheric Environment: Electrochemical Noise Method, Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2022, 69, p 629–635.
H.E. Button and D.W. Simm, The Influence of Particulate Matter on the Corrosion Behaviour of Type 316 Stainless Steel, Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 1985, 32, p 8–10.
N. Azzerri, Ageing of Passive Surfaces of Stainless Steels in an Urban-Industrial Atmosphere, Corros. Sci., 1982, 22, p 867–876.
C.A. Somreck, L. Gobboon, M. Noriko, and T. Misako, Investigation of the Passive Film Formed on SUS SS304 Exposed in an Urban-Industrial Atmosphere, J. Metals Mater. Miner., 2002, 11, p 8–18.
S. Syed, Degradation of AISI304 Stainless Steel by Atmospheric Exposure in Saudi Arabia, Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol., 2009, 44, p 297–303.
M.P. Ryan, D.E. Williams, R.J. Chater, B.M. Hutton, and D.S. McPhail, Why Stainless Steel Corrodes, Nature, 2002, 415, p 770–774.
Q. Meng, G.S. Frankel, H.O. Colijn, and S.H. Goss, Stainless-Steel Corrosion and MnS Inclusions, Nature, 2003, 424, p 389–390.
G.D. Bao, J.E. Zuo, Y.J. Wang, and L.L. Gan, Corrosion of Stainless Steel 201, 304 and 316L in the Simulated Sewage Pipes Reactor, Environ. Sci., 2014, 35, p 3002–3006.
H. Vashishtha, R. V. Taiwade, and S. Sharma, Effect of Acetic Acid on Corrosion Behavior of AISI 201, 304 and 430 Stainless Steels, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2017, 108, p 406–415.
ASTM G50-20, Standard Practice for Conducting Atmospheric Corrosion Tests on Metals, West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 2020.
S. Tokuda, I. Muto, Y. Sugawara, and N. Hara, Pit Initiation on Sensitized Type 304 Stainless Steel Under Applied Stress: Correlation of Stress, Cr-Depletion, and Inclusion Dissolution, Corros. Sci, 2020, 167, 108506.
S. Amatsuka, M. Nishimoto, I. Muto, M. Kawamori, Y. Takara, and Y. Sugawara, Micro-Electrochemical Insights into Pit Initiation Site on Aged UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel, Npj Mat Degrad., 2023, 7, 1–10.
ISO, 9223:2012(E) Corrosion of Metals and Alloys-Corrosivity of Atmospheres-Classification, Determination and Estimation, in: ISO, Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
T.E. Graedel, Copper Patinas Formed in the Atmosphere—II, A Qualitative Assessment of Mechanisms, Corros. Sci., 1987, 27, p 721–740.
P.B.P. Phipps and D.W. Rice, The Role of Water in Atmospheric Corrosion, Corros. Chem., 1979, 89, p 235–261.
P. Dhaiveegan, N. Elangovan, T. Nishimura, and N. Rajendran, Corrosion Behavior of 316L and 304 Stainless Steels Exposed to Industrial-Marine-Urban Environment: Field Study, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, p 47314–47324.
X. Wang, H. Su, Y. Xie, J. Wang, C. Feng, D. Li, and T. Wu, Atmospheric Corrosion of T2 Copper and H62 Brass Exposed in an Urban Environment, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2023, 299, p 1–16.
Z.-L. Li, K. Xiao, C.-F. Dong, X.-Q. Cheng, W. Xue, and W. Yu, Atmospheric Corrosion Behavior of Low-Alloy Steels in a Tropical Marine Environment, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2019, 26, p 1315–1328.
Y.-N. Niu, N. Dong, S. Liu, J. Yang, P.-D. Han, and Y.-C. Wu, Effects of Different Alloying Elements M (M = Fe, Ni, Mn, Si, Mo, Cu, Y) on Cr2O3 with Cl-: A First-Principles Study, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2021, 28, p 613–620.
C.F. Dong, H. Luo, K. Xiao, Y. Ding, P.H. Li, and X.G. Li, Electrochemical Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel in Marine Atmosphere and Its Simulated Solution, Anal. Lett., 2013, 46, p 142–155.
D. Kong, C. Dong, X. Ni, L. Zhang, H. Luo, R. Li, L. Wang, C. Man, and X. Li, The Passivity of Selective Laser Melted 316L Stainless Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 504, p 1–12.
Y. Zhao, H. Xiong, X. Li, W. Qi, J. Wang, Y. Hua, T. Zhang, and F. Wang, Improved Corrosion Performance of Selective Laser Melted Stainless Steel 316L in the Deep-Sea Environment, Corros. Commun., 2021, 2, p 55–62.
D. Kong, X. Ni, C. Dong, L. Zhang, C. Man, J. Yao, K. Xiao, and X. Li, Heat Treatment Effect on the Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of 316L Stainless Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2018, 276, p 293–303.
J. Castle and J. Qiu, The Application of ICP-MS and XPS to Studies of Ion Selectivity during Passivation of Stainless Steels, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1990, 137, p 2031–2038.
J. Torkkeli, T. Saukkonen, and H. Hänninen, Effect of MnS Inclusion Dissolution on Carbon Steel Stress Corrosion Cracking in Fuel-Grade Ethanol, Corros. Sci., 2015, 96, p 14–22.
A. Chiba, I. Muto, Y. Sugawara, and N. Hara, Effect of Atmospheric Aging on Dissolution of MnS Inclusions and Pitting Initiation Process in Type 304 Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2016, 106, p 25–34.
Acknowledgment
We are grateful for financial support of Provincial Key R&D Program of Hunan (2021GK2008), Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (CX20220558) and the National Scholarship Foundation (No. 202008430013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, Z., Wang, J., Su, H. et al. Study on Short-Term Corrosion of Stainless Steels 201 and 304 in Urban Atmosphere. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08857-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08857-7