Abstract
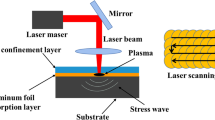
In this study, GCr15 bearing steel with an ultrahigh strength was subjected to surface laser shock processing (LSP). The effects of the laser pulse energy (LPE) on the microstructure, microhardness, residual stress and tribological properties were studied systematically. The results indicated that the martensitic laths and carbide particles underwent severe plastic deformation and were refined into nanostructures. The grain refinement was aggravated with the increase of the LPE. A grain size of 50 nm was obtained on the sample’s surface by LSP at 7 J. Many dislocation tangles and deformation twins were formed, which led to an increase in the microhardness. Furthermore, LSP induced compressive residual stress (CRS) with a high amplitude on the sample’s surface. As the pulse energy of LSP rose, the impact layer of GCr15 steel deepened. The wear rate and the friction coefficient reduced, and the wear resistance increased as the LPE increased. The tribological properties of GCr15 steel were enhanced by the grain refinement and working hardening, and by the formation of a high CRS layer.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Wollmann, S. Nitschke, T. Klauke, T. Behnisch, C. Ebert, R. Füßel, N. Modler, and M. Gude, Investigating the Friction, Wear and Damage Behaviour of Plain Bearing Bushes of the Variable Stator Vane System, Tribol. Int., 2022, 165, p 107280.
M.Y. Sherif, V. Brizmer, R. Meeuwenoord, C. Matta, E. Broitman, and T. Nuijten, The Influence of Steel Microstructure in High-Speed High-Load Bearing Applications, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 37(17), p 1370–1385.
A.S. Barcelos, F.M. Mazzoni, and A.J.M. Cardoso, Bearing Damage Analysis with Artificial Intelligence Algorithms, J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst., 2022, 33, p 282–292.
C.S. Montross, T. Wei, L. Ye, G. Clark, and Y.W. Mai, Laser Shock Processing and its Effects on Microstructure and Properties of Metal Alloys: A Review, Int. J. Fatigue, 2002, 24(10), p 1021–1036.
B.S. Yilbas, A. Arif, S.Z. Shuja, M.A. Gondal, and J. Shirokof, Investigation into Laser Shock Processing, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2004, 13(1), p 47–54.
A. Belyakov, K. Tsuzaki, H. Miura, and T. Sakai, Effect of Initial Microstructures on Grain Refinement in a Stainless Steel by Large Strain Deformation, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(3), p 847–861.
R.Y. Xin, L. Lan, C.Y. Bai, S.A. Gao, B. He, and J. Wang, Fatigue Properties of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Subjected to Laser Shock Processing, J. Mater. Sci., 2022, 57, p 9619–9630.
Y. Wang, X.B. Wang, Z.B. Liu, S.Y. Liu, H. Chen, X.Y. Pan, and H.T. Chen, Effects of Laser Shock Peening in Different Processes on Fatigue Life of 32CrNi Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 796, p 139933.
S. Zulić, D. Rostohar, J. Kaufman, S. Pathak, J. Kopeček, M. Böhm, J. Brajer, and T. Mocek, Fatigue Life Enhancement of Additive Manufactured 316l Stainless Steel by LSP using a DPSS Laser System, Surf. Eng., 2022, 38(2), p 183–190.
J.Z. Lu, K.Y. Luo, F.Z. Dai, J.W. Zhong, L.Z. Xu, C.J. Yang, L. Zhang, Q.W. Wang, J.S. Zhong, D.K. Yang, and Y.K. Zhang, Effects of Multiple Laser Shock Processing (LSP) Impacts on Mechanical Properties and Wear Behaviors of AISI 8620 Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 536, p 57–63.
H.P. Zhang, Z.Y. Cai, J.X. Chi, G.F. Han, R.J. Sun, Z.G. Che, H.Q. Zhang, and W. Guo, Microstructural Evolution, Mechanical Behaviors and Strengthening Mechanism of 300M Steel Subjected to Multi-Pass Laser Shock Peening, Opt. Laser Technol., 2022, 148, p 107726.
Y.T. Bai, H. Wang, S.H. Wang, Y.H. Huang, Y. Chen, W.W. Zhang, A. Ostendorf, and X.H. Zhou, Life Cycle Strengthening of High-Strength Steels by Nanosecond Laser Shock, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 569, p 151118.
T.T. He, G.A. Song, R.N. Shao, S.M. Du, and Y.Z. Zhang, Sliding Friction and Wear Properties of GCr15 Steel Under Different Lubrication Conditions, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022, 31, p 7653–7661.
T. Zhou, Y. Xiong, Z.G. Chen, X.Q. Zha, Y. Lu, T.T. He, F.Z. Ren, H. Singh, J. Kömi, M. Huttula, and W. Cao, Effect of Surface Nano-Crystallization Induced by Supersonic Fine Particles Bombarding on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 300M Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 421, p 127381.
Y.F. Ma, Y. Xiong, Z.G. Chen, X.Q. Zha, T.T. He, Y. Li, H. Singh, J. Kömi, M. Huttula, and W. Cao, Microstructure Evolution and Properties of Gradient Nanostructures Subjected to Laser Shock Processing in 300M ultrahigh-Strength Steel, Steel Res. Int., 2021, 93, p 2100434.
A.K. Rai, R. Biswal, R.K. Gupta, R. Singh, S.K. Rai, K. Ranganathan, P. Ganesh, R. Kaul, and K.S. Bindra, Study on the Effect of Multiple Laser Shock Peening on Residual Stress and Microstructural Changes in Modified 9Cr-1Mo (P91) Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2019, 358, p 125–135.
I. Altenberger, B. Scholtes, U. Martin, and H. Oettel, Cyclic Deformation and Near Surface Microstructures of Shot Peened or Deep Rolled Austenitic Stainless Steel AISI 304, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 264(1–2), p 1–16.
J. Lindemann, C. Buque, and F. Appel, Effect of Shot Peening on Fatigue Performance of a Lamellar Titanium Aluminide Alloy, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(4), p 1155–1164.
A. Siddaiah, B. Mao, Y.L. Liao, and P.L. Menezes, Surface Characterization and Tribological Performance of Laser Shock Peened Steel Surfaces, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 351, p 188–197.
S. Prabhakaran, A. Kulkarni, G. Vasanth, S. Kalainathan, P. Shukla, and V.K. Vasudevan, Laser Shock Peening without Coating Induced Residual Stress Distribution, Wettability Characteristics and Enhanced Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Austenitic Stainless Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 428, p 17–30.
M. Hashempour, H. Razavizadeh, and H. Rezaie, Investigation on Wear Mechanism of Thermochemically Fabricated W-Cu Composites, Wear, 2010, 269, p 405–415.
Y.J. Cao, J.Q. Sun, F. Ma, Y.Y. Chen, X.Z. Cheng, X. Gao, and K. Xie, Effect of the Microstructure and Residual Stress on Tribological Behavior of Induction Hardened GCr15 Steel, Tribol. Int., 2017, 115, p 108–115.
H. Goto and Y. Amamoto, Effect of Varying Load on Wear Resistance of Carbon Steel under Unlubricated Conditions, Wear, 2003, 254, p 1256–1266.
K. Zhang and Z.B. Wang, Strain-Induced Formation of a Gradient Nanostructured Surface Layer on an Ultrahigh Strength Bearing Steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34, p 1676–1684.
Y.P. Yun, H.Y. Wan, Y. Chen, H. Zhu, H. Lu, and X.D. Ren, Effect of Laser Shock Peening and Carbonitriding on Tribological Properties of 20Cr2Mn2Mo Steel Alloy under Dry Sliding Conditions, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 417, p 127215.
W. Luo, U. Selvadurai, and W. Tillmann, Effect of Residual Stress on the Wear Resistance of Thermal Spray Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2016, 25, p 321–330.
D.J. Kong, T.S. Hua, J.N. Ding, N.Y. Yuan, and J.F. Chen, Effects of Laser Quenching on Residual Stresses and Wear Resistance of Grey Cast Iron, Lubr. Eng., 2009, 34, p 21–54.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51905153 and U1804146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TH: Conception, Writing-Original draft preparation, Methodology, Visualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition. TC: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation and Completion of experiment. YX: Experimental design, Investigation, Funding acquisition. SD and YZ: Manuscript modification, language proofing, Writing- Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, T., Cui, T., Xiong, Y. et al. Impact of Laser Shock Processing on Microstructure and Tribological Performance of GCr15 Bearing Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08454-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08454-8