Abstract
Hot press forming (HPF) steels with a full martensite structure and 2.0 GPa strength (HPF2.0) were friction stir welded as bead-on-plate using a WC–Co12% tool. The stir zone was composed of recrystallized grains of various sizes and had comparable to or higher hardness than the base material. However, the intercritical heat-affected zone (ICHAZ) and subcritical HAZ experience softening. During the tensile test, fractures consistently occurred at the softened HAZ. The minimum hardness of the ICHAZ in the friction stir welds was 300 HV, which was similar to that in the arc welds with polygonal ferrite (328 HV) and lower than that in the laser welds with needle-like ferrite (400 HV). Remarkably, the softened width of the friction stir welds was narrower than half that of the arc welds. These results confirm the possibility of expanding the application of friction stir welding to next-generation HPF steels.











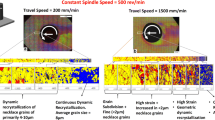
Reproduced from Reference 21 under the CC BY license

Copyright 2022, Laser Institute of America
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Taub, E. De Moor, A. Luo, D.K. Matlock, J.G. Speer, and U. Vaidya, Materials for Automotive Lightweighting, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2019, 49(1), p 327–359.
P.K. Mallick, Joining for lightweight vehicles, Materials, design and manufacturing for lightweight vehicles. Elsevier, New Jersey, 2021, p 321–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818712-8.00008-2
F. Hochhauser, W. Ernst, R. Rauch, R. Vallant, and N. Enzinger, Influence of the Soft Zone on The Strength of Welded Modern Hsla Steels, Weld. World, 2013, 56(5–6), p 77–85.
C. Kim, J.-K. Choi, M. Kang, and Y.-D. Park, A Study on the CO2 Laser Welding Characteristics of High Strength Steel up to 1500 MPa for Automotive Application, J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng., 2010, 39(1), p 79–86.
K. Kim, N. Kang, M. Kang, and C. Kim, Assessment of Heat-Affected Zone Softening of Hot-Press-Formed Steel over 2.0 GPa Tensile Strength with Bead-On-Plate Laser Welding, Appl. Sci., 2021, 11(13), p 5774.
K. Kim, H. Park, N. Kang, S. Kang, M. Kang, and C. Kim, Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Autogenous Arc Welds of 2 GPa-Strength Hot-Pressforming Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022, 210, p 2103.
T. Majeed, M.A. Wahid, M.N. Alam, Y. Mehta, and A.N. Siddiquee, Friction Stir Welding: A Sustainable Manufacturing Process, Mater. Today Proc., 2021, 46, p 6558–6563.
M. Kimura, Y. Kusumoto, M. Kusaka, and K. Kaizu, Improving the Tensile Strength Between Pure Al and Low Carbon Steel Joint Fabricated by Friction Welding, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022, 32(10), p 4655–4667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07396-x
Y. Li, J. Zhao, J. Zhou, Y. Yang, X. Huang, and Z. Liu, Evaluation of Residual Stress Fields in Friction Stir Welded Zone Based on the Plastic Strain Increment and Mises Yield Criterion, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07477-x
H. Fujii, L. Cui, N. Tsuji, M. Maeda, K. Nakata, and K. Nogi, Friction Stir Welding of Carbon Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 429(1–2), p 50–57.
C. Ling, F. Hidetoshi, T. Nobuhiro, N. Kazuhiro, N. Kiyoshi, I. Rinsei, and M. Muneo, Transformation in Stir Zone of Friction Stir Welded Carbon Steels with Different Carbon Contents, ISIJ Int., 2007, 47(2), p 299–309.
Y.D. Chung, H. Fujii, R. Ueji, and N. Tsuji, Friction Stir Welding of High Carbon Steel with Excellent Toughness and Ductility, Scripta Mater., 2010, 63(2), p 223–226.
R. Rai, A. De, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, and T. DebRoy, Review: Friction Stir Welding Tools, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2013, 16(4), p 325–342.
B.T. Gibson, D.H. Lammlein, T.J. Prater, W.R. Longhurst, C.D. Cox, M.C. Ballun, K.J. Dharmaraj, G.E. Cook, and A.M. Strauss, Friction Stir Welding: Process, Automation, and Control, J. Manuf. Process., 2014, 16(1), p 56–73.
D. Micallef, D. Camilleri, A. Toumpis, A. Galloway, and L. Arbaoui, Local Heat Generation and Material Flow in Friction Stir Welding of Mild Steel Assemblies, Proc. Instit. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl., 2015, 230(2), p 586–602.
Y. Hovanski, M.L. Santella, and G.J. Grant, Friction Stir Spot Welding of Hot-Stamped Boron Steel, Scripta Mater., 2007, 57(9), p 873–876.
S.H. Hong, S.-J. Sung, and J. Pan, Failure Mode and Fatigue Behavior of Dissimilar Friction Stir Spot Welds in Lap-Shear Specimens of Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel and Hot-Stamped Boron Steel Sheets, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2015, 137(5), p 051023.
A.A.M. da Silva, E. Aldanondo, P. Alvarez, E. Arruti, and A. Echeverría, Friction Stir Spot Welding of AA 1050 Al Alloy and Hot Stamped Boron Steel (22MnB5), Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2013, 15(8), p 682–687.
S. Li, Y. Chen, J. Kang, B.S. Amirkhiz, and F. Nadeau, Friction Stir Lap Welding of Aluminum Alloy to Advanced High Strength Steel Using a Cold-Spray Deposition as an Interlayer, Mater. Lett., 2019, 239, p 212–215.
M. Kang, J. Yoon, and C. Kim, Hook Formation and Joint Strength in Friction Stir Spot Welding of Al Alloy and Al-Si-Coated Hot-Press Forming Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, 106(5–6), p 1671–1681.
H. You, M. Kang, S. Yi, S. Hyun, and C. Kim, Comprehensive Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded Low-Carbon High-Strength Steels with Tensile Strengths Ranging from 590 MPa to 1.5 GPa, Appl. Sci., 2021, 11(12), p 5728.
S. Kaizu, Y. Shinbo, and M. Ono, Relationship Between Vickers Hardness of Laser Weld and Chemical Composition of Steel Sheets, Prepr. Natl. Meet. JWS, 1994, 55, p 118–119.
I.-H. Jeon, C. Kim, and J.-D. Kim, Hardness Estimation of Laser Welded Boron Steel Welds with the Carbon Equivalent, J. Weld. Join., 2016, 34(5), p 1–5.
B.-H. Yoon, Characteristics of Sulfide Stress Cracking of High Strength Pipeline Steel Weld by Heat Input, J. Weld. Join., 2018, 36(3), p 38–44.
M. Kang, J. Yoon, and C. Kim, Hook Formation and Joint Strength in Friction Stir Spot Welding of Al Alloy and Al–Si-Coated Hot-Press Forming Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 106(5–6), p 1671–1681.
P. Biswas, N.R. Mandal, O.P. Sha, and M.M. Mahapatra, Thermo-Mechanical and Experimental Analysis of double Pass Line Heating, J. Mar. Sci. Appl., 2011, 10(2), p 190–198.
S. Mironov, Y.S. Sato, and H. Kokawa, Microstructural Evolution during Friction Stir-Processing of Pure Iron, Acta Mater., 2008, 56(11), p 2602–2614.
S. Takaki, K. Fukunaga, J. Syarif, and T. Tsuchiyama, Effect of Grain Refinement on Thermal Stability of Metastable Austenitic Steel, Mater. Trans., 2004, 45(7), p 2245–2251.
G.R. Purdy and Y.J.M. Brechet, A Solute Drag Treatment of the Effects of Alloying Elements on the Rate of the Proeutectoid Ferrite Transformation in Steels, Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, 43(10), p 3763–3774.
S.-J. Lee and Y.-K. Lee, Prediction of Austenite Grain Growth During Austenitization of Low Alloy Steels, Mater. Des., 2008, 29(9), p 1840–1844.
W. Zexi, N. Tomoya, U. Kohsaku, M. Goro, and F. Hidetoshi, Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Friction Stir Welded 0.2%C-Si-Mn Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 799, p 140068.
A. Toumpis, A. Galloway, S. Cater, and N. McPherson, Development of a Process Envelope for Friction Stir Welding of DH36 Steel–A Step Change, Mater. Des., 2014, 1980–2015(62), p 64–75.
D.G. Mohan and C. Wu, A Review on Friction Stir Welding of Steels, Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2021, 34(1), p 655.
M. Al-Moussawi and A.J. Smith, Defects in Friction Stir Welding of Steel, Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis, 2018, 7(2), p 194–202.
A.K. Lakshminarayanan and V. Balasubramanian, Understanding the Parameters Controlling Friction stir Welding of AISI 409M Ferritic Stainless Steel, Met. Mater. Int., 2011, 17(6), p 969–981.
K. Elangovan and V. Balasubramanian, Influences of Pin Profile and Rotational Speed of the Tool on the Formation of Friction Stir Processing zone in AA2219 Aluminium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2007, 459(1–2), p 7–18.
Y.G. Kim, H. Fujii, T. Tsumura, T. Komazaki and K. Nakata, Three Defect Types in Friction Stir Welding of Aluminum Die Casting Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 415(1–2), p 250–254.
J. Yoon, C. Kim and S. Rhee, Compensation of Vertical Position Error Using a Force–Deflection Model in Friction Stir Spot Welding, Met., 2018, 8(12), p 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121049
S. Nam, H.W. Lee, C. Kim, C.-Y. Jung and Y.-M. Kim, Effects of High-Power Laser Heat Input on the Mechanical Properties of GPa-Grade Advanced High Strength TRIP Steel, J. Weld. Join., 2021, 39(5), p 505–512.
E.J. Pavlina and C.J. Van Tyne, Correlation of Yield Strength and Tensile Strength with Hardness for Steels, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2008, 17(6), p 888–893.
M. Maalekian, The Effects of Alloying Elements on Steels (I), Technische Universität Graz, Graz, Austria, 2007
K. Kim, N. Kang, M. Kang and C. Kim, Effect of Laser Beam Wobbling on the Overlap Joint Strength of Hot-Press-Forming Steel Over 20 GPa Tensile Strength, J. Laser Appl., 2022, 34(1), p 12012.
T. Wu, F. Zhao, H. Luo, H. Wang and Y. Li, Temperature Monitoring and Material Flow Characteristics of Friction Stir Welded 2A14-t6 Aerospace Aluminum Alloy, Mater., 2019, 12(20), p 3387.
O.S. Salih, H. Ou and W. Sun, Heat Generation, Plastic Deformation and Residual Stresses in Friction stir Welding of Aluminium Alloy, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2023, 238, p 107827.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the Industrial Strategic Technology Development Program (20014820) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE, Korea), and in part by the MOTIE (Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy) in Korea, under the Fostering Global Talents for Innovative Growth Program (P0017303) supervised by the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H., Yoon, J., Kang, M. et al. Microstructure and Hardness Behavior of Friction Stir Welds of 2 GPa Strength Hot Press Forming Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08372-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08372-9