Abstract
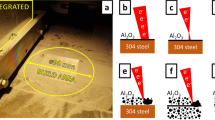
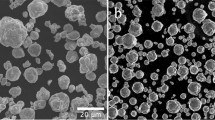
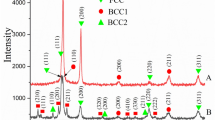
In this study, the Ti2AlC MAX phase was produced by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS) of a mixture of Ti, Al and C powders with a molar ratio of 2:1.1:1. The time of the mechanical alloying process and sintering process temperature were selected as variables, and their effect on the properties of resulted samples was investigated. SPS process was performed on the samples at temperatures of 1000, 1100 and 1200 °C and under the pressure of 30 MPa for 20 min. The cyclic oxidation behavior of the samples was then investigated. The density and hardness of the samples were also examined. The results showed that the best specimen had a density of 4.2 gr cm−3 and a hardness of 995 HV. According to the x-ray diffraction patterns, it was found that the Ti2AlC MAX phase has been formed in all samples. The cyclic oxidation process was performed for 50 h on the selected sample at temperatures 1200 and 1350 °C. The results of oxidation test showed that Al2O3 and TiO2 oxide layers formed with good adhesion on the substrate surface. The weight gain equation of the oxidation test was obtained powerfully at temperatures of 1200 and 1350 °C, where the oxidation constant (ko) increased from 8 × 10–4 to 9 × 10–3 mgn h−1, respectively. In this study, the best results were obtained by MA time of 24 h and then SPS process at the temperature of 1200 °C.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Radovic and M.W. Barsoum, MAX Phases: Bridging the Gap Between Metals and Ceramics, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull., 2013, 92, p 20–27.
M.W. Barsoum, The Mn+1AXn Phases: A New Class of Solids: Thermodynamically Stable Nanolaminates, Prog. Solid State Chem., 2000, 28, p 201–281.
Z.M. Sun, Progress in Research and Development on MAX Phases: A Family of Layered Ternary Compounds, Int. Mater. Rev., 2011, 56, p 143–166.
M. Barsoum and M. Radovic, Elastic and Mechanical Properties of the MAX Phases, Ann. Rev. Mater. Res., 2011, 41, p 195–227.
B. Cui, R. Sa, D.D. Jayaseelan, F. Inam, M.J. Reece, and W.E. Lee, Microstructural Evolution During High-Temperature Oxidation of Spark Plasma Sintered Ti2AlN Ceramics, Acta Mater., 2012, 60, p 1079–1092.
I.R. Shein and A.L. Ivanovskii, Elastic Properties of Superconducting MAX Phases from First-Principles Calculations, Phys. Status Solidi (b), 2011, 248, p 228–232.
I. Low, Advances in Science and Technology of Mn+1AXnPhases, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2012.
B. Anasori, N.C. El’ad, Y. Elraheb, and M.W. Barsoum, On the Oxidation of Ti2GeC in Air, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 580, p 550–557.
Z.M. Sun, H. Hashimoto, Z.F. Zhang, S.L. Yang, and S. Tada, Synthesis and Characterization of a Metallic Ceramic Material–Ti3SiC2, Mater. Trans., 2006, 47, p 170–174.
J.D. Hettinger, S.E. Lofland, P. Finkel, T. Meehan, J. Palma, K. Harrell et al., Electrical Transport, Thermal Transport, and Elastic Properties of M2AlC (M=Ti, Cr, Nb, and V), Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 72(11), p 115120.
J.F. Zhu, G.Q. Qi, F. Wang, and H.B. Yang, High Purity Ti2AlC Powder Prepared by a Novel Method, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, 658, p 340–343.
E. Sadeghi, F. Karimzadeh, and M.H. Abbasi, Thermodynamic Analysis of Ti–Al–C Intermetallics Formation by Mechanical Alloying, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 576, p 317–323.
B. Velasco, E. Gordo, L. Hu, M. Radovic, and S.A. Tsipas, Influence of Porosity on Elastic Properties of Ti2AlC and Ti3SiC2 MAX Phase Foams, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 764, p 24–35.
T. Fey, M. Stumpf, A. Chmielarz, P. Colombo, P. Greil, and M. Potoczek, Microstructure, Thermal Conductivity and Simulation of Elastic Modulus of MAX-Phase (Ti2AlC) Gel-Cast Foams, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 38(10), p 3424–3432.
S. Badie, A. Dash, Y. Sohn, R. Vaßen, O. Guillon, and J. Gonzalez-Julian, Synthesis, Sintering and Effect of Surface Roughness on Oxidation of Submicron Ti2AlC Ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 104(4), p 1669–1688.
R. Benitez, W.H. Kan, H. Gao, M. O’Neal, G. Proust, A. Srivastava et al., Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Evolution of Ti2AlC Under Compression in 25–1100 °C Temperature Range, Acta Mater., 2020, 189, p 154–165.
A. Hendaoui, D. Vrel, A. Amara, P. Langlois, M. Andasmas,and M. Guerioune, Synthesis of High-Purity Polycrystalline MAX Phases in Ti–Al–C SYSTEM THROUGH MECHANICally Activated Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 30(4), p 1049–1057.
M.W. Barsoum, N. Tzenov, A. Procopio, T. El-Raghy, and M. Ali, Oxidation of Tin+1AlXn (n={1 3} and X= C, N): II. Experimental Results, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2001, 148(8), p C551.
W. Yu, V. Mauchamp, T. Cabioc’h, D. Magne, L. Gence, L. Piraux et al., Solid Solution Effects in the Ti2Al(CxNy) MAX Phases: Synthesis, Microstructure, Electronic Structure and Transport Properties, Acta Mater., 2014, 80, p 421–434.
Y. Du, J.-X. Liu, Y. Gu, X.-G. Wang, F. Xu, and G.-J. Zhang, Anisotropic Corrosion of Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 in Supercritical Water at 500 °C, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43(9), p 7166–7171.
F. Wang, Q. Su, M. Nastasi, M.A. Kirk, M. Li, and B. Cui, Evolution of Irradiation Defects in Ti2AlC Ceramics During Heavy Ion Irradiation, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(12), p 14686–14692.
Y. Li, G. Zhao, Y. Qian, J. Xu, and M. Li, Deposition and Characterization of Phase-Pure Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 Coatings by DC Magnetron Sputtering with Cost-Effective Targets, Vacuum, 2018, 153, p 62–69.
W. Wang, M. Sokol, S. Kota, and M. Barsoum, Reaction Paths and Microstructures of Nickel and Ti2AlC Mixtures Reacted in the 1050–1350 °C TEMPERATURE RANGE, J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 828, p 154193.
X. Li, X. Xie, J. Gonzalez-Julian, J. Malzbender, and R. Yang, Mechanical and Oxidation Behavior of Textured Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 MAX Phase Materials, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(15), p 5258–5271.
W. Yu, M. Vallet, B. Levraut, V. Gauthier-Brunet, and S. Dubois, Oxidation Mechanisms in Bulk Ti2AlC: Influence of The Grain Size, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(5), p 1820–1828.
B. Mei, Z. Weibing, J. Zhu, and X. Hong, Synthesis of High-Purity Ti2AlC by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) of the Elemental Powders, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, 39, p 1471–1472.
W.B. Zhou, B.C. Mei, J.Q. Zhu, and X.L. Hong, Rapid Synthesis of Ti2AlC by Spark Plasma Sintering Technique, Mater. Lett., 2005, 59(1), p 131–134.
Y.L. Yue and H.T. Wu, Fabrication of Ti2AlC/TiAl Composites with the Addition of Niobium by Spark Plasma Sintering, Key Eng. Mater., 2008, 368–372, p 1004–1006.
S. Kulkarni and A. Datye, Synthesis of Ti2AlC by Spark Plasma Sintering of TiAl–Carbon Nanotube Powder Mixture, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 490, p 155–159.
Y.L. Chen, X. Zhu, P. Lu, Z. Li, C. Zeng, and M. Yan, Ti2AlC/TiC Functionally Graded Material Fabricated by SPS, Appl. Mech. Mater., 2014, 543–547, p 3869–3873.
G.-H. Jeong, G.-R. Baek, T.F. Zhang, K. Kim, K. Kim, H. Shin et al., MAX-Phase Ti2AlC Ceramics: Syntheses, Properties and Feasibility of Applications in Micro Electrical Discharge Machining, J. Ceram. Process. Res., 2016, 17, p 1116–1122.
K. Kozak, A. Dosi, G. Antou, N. Pradeilles, and T. Chotard, Characterization of Thermomechanical Behavior of Ti3SiC2 and Ti2AlC Ceramics Elaborated by Spark Plasma Sintering Using Ultrasonic Means: Characterization of Thermomechanical Behavior of Ti3SiC2 and Ti2AlC, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2016, 18, p 1952–1957.
R. Benitez, H. Gao, M. O’Neal, P. Lovelace, G. Proust, and M. Radovic, Effects of Microstructure on the Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC in Compression, Acta Mater., 2018, 143, p 130–140.
L. Boatemaa, M. Bosch, A.-S. Farle, G. Bei, S. Zwaag, and W.G. Sloof, Autonomous High Temperature Healing of Surface Cracks in Al2O3 Containing Ti2AlC Particles, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 101, p 5684–5693.
Y. Wada, N. Sekido, T. Ohmura, and K. Yoshimi, Deformation Microstructure Developed by Nanoindentation of a MAX Phase Ti2AlC, Mater. Trans., 2018, 59, p 771–778.
C. Lu, K. Piven, Q. Qi, J. Zhang, G. Hug, and A. Jankowiak, Substitution Behavior of Si Atoms in the Ti2AlC Ceramics, Acta Mater., 2018, 144, p 543–551.
T. Thomas, C. Zhang, A. Sahu, P. Nautiyal, A. Loganathan, T. Laha et al., Effect of Graphene Reinforcement on the Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC Ceramic Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 728, p 45–53.
Z. Zhan, Y. Chen, M. Radovic, and A. Srivastava, Non-classical Crystallographic Slip in a Ternary Carbide – Ti2AlC, Mater. Res. Lett., 2020, 8(7), p 275–281.
A. Koniuszewska and K. Naplocha, Microwave Assisted Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis of Ti2AlC MAX Phase, Compos. Theory Pract., 2016, 16, p 109–112.
W. Chen, J. Tang, X. Shi, N. Ye, Z. Yue, and X. Lin, Synthesis and Formation Mechanism of High-Purity Ti3AlC2 Powders by Microwave Sintering, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2019, 17, p 778–789.
Smialek J. Kinetic aspects of Ti2AlC MAX phase oxidation. Oxidation of Metals. 2015;83.
J.L. Smialek, Environmental Resistance of a Ti2AlC-type MAX Phase in a High Pressure Burner Rig, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 37(1), p 23–34.
J.L. Smialek, B.J. Harder, and A. Garg, Oxidative Durability of TBCs on Ti2AlC MAX Phase Substrates, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, 285, p 77–86.
Z. Zhang, S.H. Lim, D.M.Y. Lai, S.Y. Tan, X.Q. Koh, J. Chai et al., Feature Article, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 37(1), p 43–51.
C. Tang, M. Steinbrück, M. Große, T. Bergfeldt, and H.J. Seifert, Oxidation Behavior of Ti2AlC in the Temperature Range of 1400 °C–1600 °C in Steam, J. Nucl. Mater., 2017, 490, p 130–142.
A. Donchev, M. Schütze, E. Ström, and M. Galetz, Oxidation Behaviour of the MAX-Phases Ti2AlC and (Ti, Nb)2AlC at Elevated Temperatures with and Without Fluorine Treatment, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39(15), p 4595–4601.
L. Smialek, Relative Ti2AlC Scale Volatility Under 1300 °C Combustion Conditions, Coatings, 2020, 10, p 142.
X. Wang and Y. Zhou, High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Ti2AlC in Air, Oxid. Met., 2003, 59(3–4), p 303–320.
J. Byeon, J. Liu, M. Hopkins, W. Fischer, N. Garimella, K. Park, M. Brady, M. Radovic, T. El-Raghy, and Y. Sohn, Microstructure and Residual Stress of Alumina Scale Formed on Ti2AlC at High Temperature in Air, Oxid. Met., 2007, 68, p 97–111.
W. Zhou, K. Li, J. Zhu, S. Tian, and D.-M. Zhu, Low-Temperature Synthesis of High-Purity Ti2AlC Powder by Microwave Sintering, Micro Nano Lett., 2018, 13, p 798–800.
M. Sundberg, G. Malmqvist, A. Magnusson, and T. El-Raghy, Alumina Forming High Temperature Silicides and Carbides, Ceram. Int., 2004, 30, p 1899–1904.
Z.J. Lin, M.J. Zhuo, Y. Zhou, M. Li, and J. Wang, Microstructural Characterization of Layered Ternary Ti2AlC, Acta Mater., 2006, 54, p 1009–1015.
D.J. Tallman, B. Anasori, and M.W. Barsoum, A Critical Review of the Oxidation of Ti2AlC, Ti3AlC2 and Cr2AlC in Air, Mater. Res. Lett., 2013, 1, p 115–125.
M. Munro, Evaluated Material Properties for a Sintered Alpha-Alumina, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1997, 80, p 1919–1928.
A. Li, C. Hu, M. Li, and Y. Zhou, Joining of Ti–Al–C Ceramics by Oxidation at Low Oxygen Partial Pressure, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 29, p 2619–2625.
T. Thomas, Fabrication Techniques to Produce Micro and Macro Porous MAX-Phase Ti2AlC Ceramic (University of Bath, 2015.
J.F. Zhu, G.Q. Qi, F. Wang, and H.B. Yang, High Purity Ti2AlC Powder Prepared by a Novel Method, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publ, Wollerau, 2010, p 340–343
A. Attaei, Mechanical Alloying and Mechanical Activation a Technology for Processing of Nanomaterials (University of Tehran, 2007)
M. Rafiei, M. Salehi, M. Shamanian, and A. Motallebzadeh, Preparation and Oxidation Behavior of B4C–Ni and B4C–TiB2–TiC–Ni Composite Coatings Produced by an HVOF Process, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(8), p 13599–13609.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nejat, B., Ebrahimzadeh, I. & Rafiei, M. Fabrication of Ti2AlC Compound by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering and Investigation of Its Cyclic Oxidation Behavior. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 8846–8857 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08044-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08044-8