Abstract
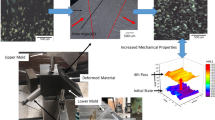
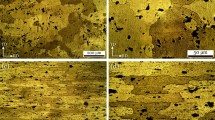
The present paper has focused on improving strength and elongation of AA 1050 alloy via equal channel angular pressing (ECAP), intermediate annealing and post-rolling process. At the first and second ECAP passes, the ideal shear texture component has been developed while by proceeding ECAP passes (n = 3, 4), the intensity of texture component has been weakened. In the following, as a result of intermediate annealing at 150 °C, cube texture component ({001}<110>) was developed in the alloy. Then during post-rolling process, the prior texture component disappeared and the augmentation of copper-type texture component ({110}<112>) has been observed. The first and second ECAP passes lead to increase in ultimate tensile strength at the expense of considerable decrease in elongation and work hardening capacity. However, during third and fourth ECAP passes, the homogenous microstructure with fine equiaxed grain is achieved, also intermediate annealing at 150 and 225 °C and 50-75% rolling reduction attributed to high angle grain boundaries (HAGBs) promotion. Eventually, an appropriate balance of strength, elongation and work hardening capacity of AA 1050 alloy is obtained via ECAP (n = 3, 4), intermediate annealing (T = 150, 225 °C) and post-rolling (r = 50-75%).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ciach, Advanced Light Alloys and Composites, Springer, Warszawa, 2013.
E.G. Totten and D.S. MacKenzie, Handbook of Aluminum: Alloy Production and Materials Manufacturing, CRC Press, Washington, DC, 2003.
L.F. Mondolfo, Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2013.
M.S. Shadabroo, A.R. Eivani, H.R. Jafarian, S.F. Razavi and J. Zhou, Optimization of Interpass Annealing for a Minimum Recrystallized Grain Size and Further Grain Refinement Towards Nanostructured AA6063 During Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Charact., 2016, 112(1–2), p 160.
L. Romero-Reséndiz, A. Flores-Rivera, I.A. Figueroa, C. Braham, C. Reyes-Ruiz, I. Alfonso and G. González, Effect of the Initial ECAP Passes on Crystal Texture and Residual Stresses of 5083 Aluminum Alloy, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater, 2020, 27(6), p 801.
Z.J. Yang, K. Wang and Y. Yang, Optimization of ECAP—RAP Process for Preparing Semisolid Billet of 6061 Aluminum Alloy, Int. J. Min. Met. Mater, 2020, 27, p 792.
M. Howeyze, H. Arabi, A.R. Eivani and H.R. Jarafrian, Strengthening of AA5052 Aluminum Alloy by Equal Channel Angular Pressing Followed by Softening at Room Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 720(21), p 160.
S. Valipour, A.R. Eivani, H.R. Jafarian, S.H. Seyedein and M.R. Aboutalebi, Effect of Pre-Deformation Thermomechanical Processing on the Development of Ultrafine Grain Structure During Equal Channel Angular Extrusion, Mater. Des., 2016, 89(5), p 377.
R. Srinivasan, B. Cherukuri and P.K. Chaudhury, Scaling Up of Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) for the Production of Forging Stock, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2006, 503(4), p 371.
V.M. Segal, Equal Channel Angular Extrusion: From Macro-Mechanics to Structure Formation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 271(4), p 322.
Y.G. Jin, H.M. Baek, S.K. Hwang, Y.T. Im and B.C. Jeon, Continuous High Strength Aluminum Bolt Manufacturing by the Spring-Loaded ECAP System, J. Mater. Process. Technol, 2012, 212(4), p 848.
S. Sivasankaran, Aluminium Alloys: Recent Trends in Processing Characterization Mechanical Behavior and APPLICATIONS, IntechOpen, Croatia, 2017.
K. Nakashima, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto and T.G. Langdon, Influence of Channel Angle on the Development of Ultrafine Grains in Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 1998, 46(5), p 1589.
P. Venkatachalam, S.R. Kumar, B. Ravisankar, V.T. Paul and M. Vijayalakshmi, Effect of Processing Routes on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc., 2010, 20(10), p 1822.
Y. Watanabe, P.D. Sequeira, O. Sitdikov, H. Sato, Z.G. Zhang and L.S. Kim, Effect of Processing Route on Microstructure and Texture Development in ECAP of Al-Ti Alloy, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, 561(11), p 251.
J. Bi, K. Sun, R. Liu, R. Fan and S. Wang, Effect of ECAP Pass Number on Mechanical Properties of 2A12 Al Alloy, J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci, 2008, 23(1), p 71.
A. Nashith, P. Sanjid, M. Shamsudheen, R. Rasheeque, M.K. Ramis and A.R. Shebeer, Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) on Hardness and Microstructure of Pure Aluminum, Int. J. Mater. Eng., 2014, 4(3), p 119.
Z.S. Zahari, D. Awang, M.A. Hassan, and W. Harun, Effect of ECAP die angle to the microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk nanostructured Al-6061, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol 469, No 1, IOP Publishing, 2019, p 12054
M.H. Shaeri, M. Shaeri, M. Ebrahimi, M.T. Salehi and S.H. Seyyedein, Effect of Ecap Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater., 2016, 26(2), p 182.
E.A. El-Danaf, M.S. Soliman, A.A. Almajid and M.M. El-Rayes, Enhancement of Mechanical Properties and Grain Size Refinement of Commercial Purity Aluminum 1050 Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 458(1–2), p 226.
E.A. El-Danaf, Texture Evolution and Fraction of Favorably Oriented Fibers in Commercially Pure Aluminum Processed to 16 ECAP Passes, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 492(1–2), p 141.
M.C.V. Vega, B.H. Piva, R.E. Bolmaro, M. Ferrante, and A.M. Kliauga, The Texture Development of ECAP Processed AA1050 Aluminum, before and After a Final Anneal: Effect of the Initial Texture, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol 63, No 1, IOP Publishing, 2014, p 012152
S.N. Alhajeri, N. Gao and T.G. Langdon, Hardness Homogeneity on Longitudinal and Transverse Sections of an Aluminum Alloy Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(10–11), p 3833.
S. Wronski, J. Tarasiuk, B. Bacroix, K. Wierzbanowski and H. Paul, Microstructure Heterogeneity After the ECAP Process and Its Influence on Recrystallization in Aluminium, Mater. Charact., 2013, 78(15), p 60.
W. Skrotzki, N. Scheerbaum, C.G. Oertel, H.G. Brokmeier, S. Suwas and L.S. Toth, Recrystallization of High-Purity Aluminium During Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(7), p 2211–2218.
W.Q. Cao, A. Godfrey, W. Liu and Q. Liu, Annealing Behavior of Aluminum Deformed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Lett., 2003, 57(24), p 3767.
J.Y. Chang and A. Shan, Intermediate Annealing of Pure Aluminum during Cyclic Equal Channel Angular Pressings, J. Mater. Sci., 2003, 38, p 2613.
A. Zi and lB. StulikovaSmola, Response of Aluminum Processed by Extrusion Preceded ECAP to Isochronal Annealing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(6), p 1469.
M.C.V. Vega, R.E. Bolmaro, M. Ferrante, V.L. Sordi and A.M. Kliauga, The Influence of Deformation Path on Strain Characteristics of AA1050 Aluminium Processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing followed by Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 646(14), p 154.
M. Mhedhbi, M. Khlif and C. Bradai, Investigations of Microstructural and Mechanical Properties Evolution of AA1050 Alloy Sheets Deformed by Cold-Rolling Process and Heat Treatment Annealing, J. Mater. Environ. Sci, 2017, 8(23), p 2967.
A.P. Zhilyaev, K.O. Ishi, G.I. Raab and T.R. McNelley, Influence of ECAP Processing Parameters on Texture and Microstructure of Commercially Pure Aluminum, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 44(1–2), p 245.
J.G. Lenard, Primer on Flat Rolling, Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 2013.
M. Reihanian, R. Ebrahimi, N. Tsuji and M.M. Moshksar, Analysis of the Mechanical Properties and Deformation Behavior of Nanostructured Commercially Pure Al Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 473(1–2), p 189.
A. Goloborodko, O. Sitdikov, R. Kaibyshev, H. Miura and T. Sakai, Effect of Pressing Temperature on Fine-Grained Structure Formation in 7475 Aluminum Alloy During ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 381(1–2), p 121.
R. Lapovok, I. Timokhina, P.W. McKenzie and R. O’Donnell, Processing and Properties of Ultrafine-Grain Aluminium Alloy 6111 Sheet, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 200(1–2), p 441.
M. Kawasaki, Z. Horita and T.G. Langdon, Microstructural Evolution in High Purity Aluminum Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 524(1–2), p 143.
S. Ferrasse, V.M. Segal and F. Alford, Texture Evolution During Equal Channel Angular Extrusion (ECAE): Part II. An Effect of Post-Deformation Annealing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 372(1–2), p 235.
H. Pouraliakbar, S. Firooz, M.R. Jandaghi, G. Khalaj and A. Amirafshar, Combined Effect of Heat Treatment and Rolling on Pre-Strained and SPDed Aluminum Sheet, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 612(14), p 371.
O. Engler and V. Randle, Introduction to Texture Analysis: Macrotexture, Microtexture, and Orientation Mapping, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2009.
W. Wang, A.L. Helbert, T. Baudin, F. Brisset and R. Penelle, Reinforcement of the Cube Texture During Recrystallization of a 1050 Aluminum Alloy Partially Recrystallized and 10% Cold-Rolled, Mater. Charact., 2012, 64(27), p 1.
P. Koprowski, R. Bogucki, M. Bieda, J. Kawałko and K. Sztwiertnia, Thermal Stability of AA1050 Aluminum Alloy After Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Arch. Metal. Matter, 2017, 62(14), p 156.
A. Rosochowski, L. Olejnik and M. Richert, Advanced Methods in Material Forming. D. Banabic Ed., Springer, Berlin, 2007, p 215–232
M. Eizadjou, H. Danesh-Manesh and K. Janghorban, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ultra-Fine Grains (UFGs) Aluminum Strips Produced by ARB Process, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 474(1–2), p 406.
N. Haghdadi, A. Zarei-Hanzaki and D. Abou-Ras, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Commercially Pure Aluminum Processed by Accumulative Back Extrusion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 584(4), p 73.
P.B. Prangnell, J.R. Bowen and P.J. Apps, Ultra-Fine Grain Structures in Aluminum Alloys by Severe Deformation Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 375(1–2), p 178.
J.H. Han, K.H. Oh and J.C. Lee, Effect of Accumulative Strain on Texture Evolution in 1050 Al Alloys Processed by Continuous Confined Strip Shearing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 387(6), p 240.
Q. Liu, X. Huang, D.J. Lloyd and N. Hansen, Microstructure and Strength of Commercial Purity Aluminum (AA 1200) Cold-Rolled to Large Strains, Acta Mater., 2002, 50(4), p 3789.
W. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf, Evolution of FCC Deformation Structures in Polyslip, Acta Metall. Mater., 1992, 40(4), p 205.
J.F. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2012.
F.R. Castro-Fernandez and C.M. Sellars, Static Recrystallisation and Recrystallisation during Hot Deformation of Al-1Mg-1Mn Alloy, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1988, 4(7), p 621.
H.J. McQueen, O. Knustad, N. Ryum and J.K. Solberg, Microstructural Evolution in Al Deformed to Strains of 60 at 400 °C, Scr. Metall., 1985, 19(1), p 73.
W. Blum, Q. Zhu, R. Merkel and H.J. McQueen, Geometric dynamic recrystallization in hot torsion of Al-5Mg-0.6Mn (AA5083), Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 205(1–2), p 23.
M. Bacca, D.R. Hayhurst and R.M. McMeeking, Continuous Dynamic Recrystallization During Severe Plastic Deformation, Mech. Matter, 2015, 90(1), p 148.
A. Mishra, K. Kad, F. Gregori and M.A. Meyers, Microstructural Evolution in Copper Subjected to Severe Plastic Deformation: Experiments and Analysis, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(5), p 13.
T. Sakai, H. Miura, A. Goloborodko and O. Sitdikov, Continuous Dynamic Recrystallization during the Transient Severe Deformation of Aluminum Alloy 7475, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(1), p 153.
S. Ferrasse, V.M. Segal, S.R. Kalidindi and F. Alford, Texture Evolution during Equal Channel Angular Extrusion: Part I. Effect of Route, Number of Passes and Initial Texture, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 368(2), p 28.
A.S. Mohammed-Ahmed, E.A. El-Danaf and A.A. Radwan, A Criterion for Shear Banding Localization in Polycrystalline FCC Metals and Alloys and Critical Working Conditions for Different Microstructural Variables, J. Mater. Process. Technol, 2007, 186(3), p 14.
G.H. Zahid, Y. Huang and P.B. Prangnell, Microstructure and Texture Evolution during Annealing a Cryogenic-SPD Processed Al-Alloy with a Nanoscale Lamellar HAGB Grain Structure, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(12), p 3509.
I.J. Beyerlein and L.S. Tóth, Texture Evolution in Equal-Channel Angular Extrusion, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2009, 54(4), p 427.
S.R. Goodman and H. Hu, Texture Transition in Austenitic Stainless Steels, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1964, 230(4), p 1413.
H. Hu and R.S. Cline, Temperature Dependence of Rolling Textures in High-Purity Silver, J. Appl. Phys., 1961, 32(5), p 760.
S.R. Goodman and H. Hu, Texture Transition in Copper, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1963, 227(4), p 627.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadian, P., Akbarzadeh, A., Asadi, P. et al. Achieving an Optimal Balance of Strength and Elongation in AA 1050 Aluminum Alloy via Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Intermediate Annealing, and Post-Rolling. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 9573–9585 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07009-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07009-7