Abstract
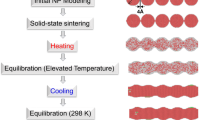
Understanding coalescing or sintering between particles at atomic scale is of significance for accurately controlling additive manufacturing processes. In this research, thermodynamics quantities and rotation behaviors are monitored to reveal multi-stages scenario of structural changes during sintering two equally sized Ti particles, where bulk Ti can undergo the transformation between a low-temperature HCP and a high-temperature BCC. The coalescing or sintering process and finally packing structure is significantly affected by temperature and contacting facets with various crystallographic orientations. Coalescing and sintering temperature regimes are identified from the calculations of the melting point for single particle. Energy and visually packing images characterize structural transitions including HCP-BCC, rearrangements of surface atoms, and BCC-melt. The temporal evolution of shrinkage factor and atomic level stresses show different stages for the inelastic encounter between the particles. Nanoparticles undergo reorientation, deformation, atomic diffusion, and rearrangements in surface and interfacial regions, which affect the formation and growth of connecting region. Our simulation results reveal that some orientation contacts and temperatures are effective in terms of coalescing or sintering.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.Y. Zhang, D. Qiu, M.A. Glbson, Y.F. Zheng, H. Fraser, D.H. StJohn and M.A. Easton, Additive Manufacturing of Ultrafine-Grained High-Strength Titanium Alloys, Nature, 2019, 576, p 91–96.
H.S. Yoon, H.T. Lee, K.H. Jang, C.S. Kim, H.S. Park, D.W. Kim, K.W. Lee, S.K. Min and S.H. Ahn, CAD/CAM for Scalable Nanomanufacturing: a Network-Based System for Hybrid 3D Printing, Microsyst. Nanoeng., 2017, 3, p 7072.
T. Debroy, T. Mukherjee, J.O. Milewski, J.W. Elmer, B. Ribic, J.J. Blecher and W. Zhang, Scientific, Technological and Economic Issues in Metal Printing and Their Solutions, Nature Mate., 2019, 18, p 1026–1032.
A.J. Clarke, Fine-Grained Metals from 3D Printing, Nature, 2019, 576, p 41–42.
M. Qian and D.L. Bourell, Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys, JOM, 2017, 69, p 2677–2678.
Y. Lu, G.F. Sun, X.F. Xiao and J. Mazumder, Online Stress Measurement During Laser-Aided Metallic Additive Manufacturing, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, p 7630.
A.A. Martin, N.P. Calta, S.A. Khairallah, J. Wang, P.J. Depond, A.Y. Fong, V. Thampy, G.M. Guss, A.M. Kiss, K.H. Stong, C.J. Tassone, J.N. Weker, M.F. Toney, T. Buuren and M.J. Matthews, Dynamics of Pore Formation During Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing, Nature Comm., 2019, 10, p 1987.
A. Basalah, S. Esmaeili and E. Toyserkani, On the influence of sintering protocols and layer thickness on the physical and mechanical properties of additive manufactured titanium porous bio-structures, J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2016, 238, p 341–351.
X.Y. Xu, P. Nash and D. Mangabhai, Characterization and Sintering of Armstrong Process Titanium Powder, JOM, 2017, 69, p 770–775.
I.M. Pohrelyuk, A.G. Lukyanenko, O.V. Tkachum and K.S. Shlyahetka, Corrosion Resistance of Sintered Commercially Pure Titanium in Inorganic Acids After Oxidation and Nitriding, JOM, 2019, 71, p 4910–4916.
J. Stoltz, Influence of Mechanical Forces on Cells and Tissues, Regener. Med. Cell. Ther., 2012, 77, p 111–120.
A.R. Amini, C.P. Laurencin and S.P. Nukavarapu, Bone Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Challenges, Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 2012, 40, p 363–408.
L. Zhang, Atomic Simulations of Packing Patterns and Thermal Behavior in Ti Clusters, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2019, 29, p 237–243.
F.H. Froes, Titanium Powder Metallurgy: A Review, Adv. Mater. Process., 2012, 170, p 16–22.
T. Mukherjee, J.S. Zuback, A. Debroy and T. De, Printability of Alloys for Additive Manufacturing, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, p 19717.
B.L. Decost, H. Jain, A.D. Rollett and E.A. Holm, Computer Vision and Machine Learning for Autonomous Characterization of AM Powder Feedstocks, JOM, 2017, 69, p 456–465.
M. Borish, B.K. Post, A. Roschli, P.C. Chesser, L.J. Love and K.T. Gaul, Defect Identification and Migration via Visual Inspection in Large-Scale Additive Manufacturing, JOM, 2019, 71, p 893–899.
L. Yan, X.Y. Chen, Y.L. Zhang, J.W. Newkirk and F. Liou, Fabrication of Functionally Graded Ti and γ-TiAl by Laser Metal Deposition, JOM, 2017, 69, p 2756–2761.
P.A. Pires, O. Desmaison and M. Megahed, ICME Manufacturability Assessment in Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing, JOM, 2018, 70, p 1677–1685.
J. Bishop, A. Clarke and G. Wagner, Integrated Computational and Experimental Methods for Additive Manufacturing, JOM, 2018, 70, p 1587–1588.
T. Gatsos, K.A. Elsayed, Y.W. Zhai and D.A. Lados, Review on Computational Modeling of Process-Microstructure-Property Relationships in Metal Additive Manufacturing, JOM, 2020, 72, p 403–419.
L. Zhang and Q.N. Fan, Effect of Quenching Temperature and Size on Atom Movement and Local Structural Change for Small Copper Clusters Containing 51-54 Atoms During Quenching Processes, Indian J. Phys., 2016, 90, p 9–20.
L. Zhang and Q.N. Fan, Modeling the Freezing of Molten Copper Nanoclusters: The Effect of Quenching Temperature and Cluster Size, J. Phys. Soc. Jap., 2013, 82, p 054601.
A.L. Gould, A.J. Logsdail and C.R. Catlow, Influence of Composition and Chemical Arrangement on the Kinetic Stability of 147-Atom Au-Ag Bimetallic Nanoclusters, J. Phys. Chem., 2015, 119, p 23685–23697.
C. Mottet, G. Rossi, F. Baletto and R. Ferrando, Single Impurity Effect on the Melting of Nanoclusters, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 95, p 035501.
L. Zhang, Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Atom Packing Characteristics of Three Deformed Silver Nanoparticles at Room Temperature, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18, p 7310–7317.
X.W. Zhou, R.A. Johnson and H.N.G. Wadley, Misfit-Energy-Increasing Dislocations in Vapor-Deposited CoFe/NiFe Multilayers, Phys. Rev. B, 2004, 69, p 144113.
L. Zhang, Study for the Effect of Continuous Applied Load on a Compressed Ag Nanoparticle at Room Temperature by Atomic Scale Simulations, J. Phys. Soc. Japan, 2016, 85, p 054602.
G. Agareal and A.M. Dongare, Modeling the Thermodynamic Behavior and Shock Response of Ti Systems at the Atomic Scales and Mesoscales, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52, p 10853–10870.
J.Q. Wang, S.H. Shin and A.M. Hu, Geometrical Effects on Sintering Dynamics of Cu-Ag Core-Shell Nanoparticles, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, p 17791–17800.
J.L. Cui, J.W. Zhang, X.W. Wang, B. Theogene, W.J. Wang, H. Tohmyoh, X.Q. He and X.S. Mei, Atomic-Scale Simulation of the Contact Behavior and Mechanism of the SWNT-AgNW Heterostructure, J. Phys. Chem., 2019, 123, p 19693–19703.
J.L. Cui, H.H. Mei, J.W. Zhang, Z.J. Fan, J. Yang, W.J. Wang, H. Tohmyoh and X.S. Mei, Interfacial Contact Behavior Between CNTs and AgNW with Molecular Dynamics Simulation, Mater., 2020, 13, p 1290.
J.L. Cui, X.Y. Ren, H.H. Mei, X.W. Wang, J.W. Zhang, Z.J. Fan, W.J. Wang, H. Tohmyoh and X.S. Mei, Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study on the Interfacial Contact Behavior Between Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Nanowires, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 512, p 145696.
L. Zhang and Y.M. Wang, Packing Changes in Melting, Freezing, and Coalescence of Titanium Nanoparticles from Atomic Simulations, JOM, 2019, 71, p 4917–4924.
L. Zhang, Studying Stability of Atom Packing for Ti Nanoparticles on Heating by Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2019, 21, p 1800531.
D. Nelli, G. Rossi, Z.W. Wang, R.E. Palmer and R. Ferrando, Structure and Orientation Effects in the Coalescence of Au Clusters, Nanoscale, 2020, 12, p 7688.
R. Theissmann, M. Fendrich, R. Zinetullin, G. Guenther, G. Schierning and D.E. Wolf, Crystallographic Reorientation and Nanoparticle Coalescence, Phys. Rev. B, 2008, 78, p 205413.
R. Pasianot and E. Savino, Embedded-Atom-Method Interatomic Potentials for HCP Metals, Phys. Rev. B, 1992, 12, p 12704–12710.
K. Laasonen, E. Panizon, D. Bochicchio and R. Ferrando, Computational Between Icosahedral Motifs in AgCu, AgNi, and AgCo Nanoalloys: a Combined Atimistic-DFT Study, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117, p 26405–26413.
V. Vitek and T. Egami, Atomic Level Stresses in Solid and Liquids, Phys. Stat. Sol. (b), 1987, 144, p 145–156.
P. Piseri, T. Mazza, G. Bongiorno, C. Lenardi, L. Ravagnan, F.D. Foglia, F. DiFonzo, M. Coreno, M. DeSimone, K.C. Prince and P. Milani, Core Level Spectroscopy of Free Titanium Clusters in Supersonic Beams, New J. Phys., 2006, 8, p 1.
L.M. Farigliano, M.A. Villarreal, E.P.M. Leiva and S.A. Paz, Thermodynamics of Nanoparticle Coalescence at Different Temperatures via Well-Tempered Metadynamics, J. Phys. Chem., 2020, 124, p 24009.
J.E. Bonevich and L.D. Marks, The Sintering Behavior of Ultrafine Alumina Particles, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7, p 1489.
Funding
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51671051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, data analysis, and writing, LZ. The author has read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L. Modeling the Effect of Crystallographic Orientations on Coalescing and Sintering for Two Ti Nanoparticles with Equal Size at Atomic Scale. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 8336–8348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06018-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06018-2