Abstract
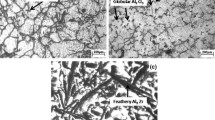
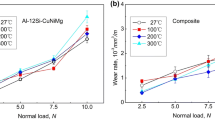
A direct-melt reaction was used to successfully synthesize A356/3 wt.% Al3Zr composites at 750 °C, 770 °C and 790 °C from the Al-K2ZrF6 system. The friction and wear characteristics of composites synthesized at 750℃ were determined by carrying out dry sliding tests of varying loads and sliding speeds. Polarized light microscopy, metallurgical microscopy, x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy were applied to identify the phase compositions and observe the microstructure and morphology of the worn surfaces. Finally, the wear mechanism of composites and matrix was analyzed by observing the SEM pictures of the wear surfaces. The results indicate that Al3Zr particles are successfully formed in the matrix. At 750℃, the particles were the smallest and dispersed well in the matrix. The size of the reinforced particles increases with increasing reaction temperature. The hardness of the composites is greatly improved compared to that of the matrix, and the highest hardness reaches 245.6 HV. The experiments show that the friction coefficient of the composites is lower than that of the matrix, and the smallest average friction coefficient is 0.367. The volume wear loss of the composites is less than that of the matrix. The wear mechanism of composites is mainly adhesive wear and is accompanied by abrasive wear and fatigue wear because of the change in experimental parameters. Eventually, delamination wear occurs, and the wear resistance is better than that of the matrix.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Emamy, S.V. Yeganeh, A. Razaghian and K. Tavighi, Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Hot-extruded Al Matrix Composites Containing Different Amounts of Mg2Si, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct., 2013, 586, p 190–196.
S.L. Zhang, X.X. Shi, Y.T. Zhao, B.R. Zhang, Z.P. Liang, H.S. Yin, B.Y. Dou, Q. Zhang and C.X. Wang, Preparation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of in situ (TiB2+ZrB2)/AlSi9Cu3 Composites, J. Alloy Compd., 2016, 673, p 349–357.
S. Khoramkhorshid, M. Alizadeh, A.H. Taghvaei and S. Scudino, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-based Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced with Al84Gd6Ni7Co3 Glassy Particles Produced by Accumulative Roll Bonding, Mater. Des., 2016, 90, p 137–144.
X. Kai, K. Tian, C. Wang, L. Jiao, G. Chen and Y. Zhao, Effects of Ultrasonic Vibration on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of the Nano ZrB2/2024Al Composites Synthesized by Direct Melt Reaction, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 668, p 121–127.
H.-J. Yang, Y.-T. Zhao, G. Chen, S.-L. Zhang and D.-B. Chen, Preparation and Microstructure of in-situ (ZrB2 +Al2O3 +Al3Zr)p/A356 Composite Synthesized by Melt Direct Reaction, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China., 2012, 22(3), p 571–576.
A. Omyma El-Kady, Fathy, Effect of SiC Particle Size on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Extruded Al Matrix Nanocomposites, Mater. Des., 2014, 54, p 348–353.
M. Sharitabar, A. Sarani, S. Khorshahian and M.S. Afarani, Fabrication of 5052Al/Al2O3 Nano Ceramic Particle Reinforced Composites via Friction Stir Processing Route, Mater. Des., 2011, 32(8), p 4164–4172.
A. Canakci, Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Behaviour of B4C Particle Reinforced 2014 Al Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Sci., 2011, 46(8), p 2805–2813.
Z. Zhihao, Z. Yutao, K. Xizhou, T. Ran, D. Renfa and L. Liang, Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of in-situ nano ZrB2 Reinforced AA6111 Matrix Composites, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(2), p 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaed02
S.H. Seyed Ebrahimi, M. Emamy, N. Pourkia and H.R. Lashgari, The Microstructure, Hardness and Tensile Properties of a New Super High Strength Aluminum Alloy with Zr Addition, Mater. Des., 2010, 31(9), p 4450–4456.
G. Manchang, J. Jun, L. Peijie, C. Yuyong 合金元素对铸造Al-Si-Cu-Mg合金机械性能的影响 (The Influences of Alloying Elements on the Mechanical Properties of Cast Al-Si-Cu-Mg Alloy), 材料科学与工艺(Mater. Sci. Technol.), 1(4), 73–79 (in Chinese) (1993)
B. Ravi, B. Balu Naik and J. Udaya Prakash, Characterization of Aluminium Matrix Composites (AA6061/B4C) Fabricated by Stir Casting Technique, Mater. Today-Proc., 2015, 2(4–5), p 2984–2990.
M. Esmaily, N. Mortazavi, J.E. Svensson, M. Halvarsson, M. Wessén, L.G. Johansson and A.E.W. Jarfors, A New Semi-solid Casting Technique for Fabricating SiC-Reinforced Mg Alloys Matrix Composites, Compos. Pt. B-Eng., 2016, 94, p 176–189.
M. Zabihi, M.R. Toroghinejad and A. Shafyei, Shear Punch Test in Al/Alumina Composite Strips Produced by Powder Metallurgy and Accumulative Roll Bonding, Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct., 2016, 667, p 383–390.
M. Meng, G. Chen, Z. Zhang and Y. Zhao, Analysis of Properties for in situ Al2O3p/A356 Composites Synthesised from the Al-SiO2 System, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 18(33), p 2290–2297.
K.L. Tian, Y.T. Zhao, L. Jiao, S.L. Zhang, Z.Y. Zhang and X. Wu, Effects of in situ Generated ZrB2 Nano-particles on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of 2024Al Matrix Composite, J. Alloy. Compd., 2014, 594, p 1–6.
S.L. Zhang, J. Yang, B.R. Zhang, Y.T. Zhao, G. Chen, X.X. Shi and Z.P. Liang, A Novel Fabrication Technology of in situ TiB2/6063Al Composites: High Energy Ball Milling and Melt in situ Reaction, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 639, p 215–223.
Q. Gao, S. Wu, S. Lü, X. Xiong, R. Du and P. An, Improvement of Particles Distribution of in-situ 5 vol% TiB2 Particulates Reinforced Al-4.5 Cu Alloy Matrix Composites with Ultrasonic Vibration Treatment, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 639, p 215–223.
S. Li, Y. Su, X. Zhu, H. Jin, Q. Ouyang and D. Zhang, Enhanced Mechanical Behavior and Fabrication of Silicon Carbide Particles Covered by in-situ Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced 6061 Aluminum Matrix Composites, Mater. Des., 2016, 107, p 130–138.
Z.L. Liu, Chap 3, 摩擦学原理 (Principles of Tribology), First edition, Beijing, Higher Education Press, 2009, p 57–79
D.-B.Chen, X.-Y. Huo, S.-L. Zhang, Y.-T. Zhao (2008) (Al2O3+Al3Zr)p/Al-22Si 铝基复合材料的制备及摩擦学性能(Fabrication and Tribological Properties of in situ (Al2O3+Al3Zr)p/Al-22Si Composites), 机械工程材料(Mater. Mech. Eng.), 32(12), 47–50+58 (in Chinese)
A. Kumar, R.K. Gautam and R. Tyagi, Dry Sliding Wear Characteristics of in situ Synthesized Al-TiC Composites, Compos. Interfaces, 2016, 23(6), p 469–480.
F. Chang, Gu. Dongdong, D. Dai and P. Yuan, Selective Laser Melting of in-situ Al4SiC4+SiC Hybrid Reinforced Al Matrix Composites: Influence of Starting SiC Particle Size, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 272, p 15–24.
J. Teng, H.-P. Li and G. Chen, Wear Mechanism for Spray Deposited Al-Si/SiCp Composites Under Dry Sliding Condition, J. Cent. South Univ., 2015, 22(08), p 2875–2882.
J. Lei, Z. Yutao, Y. Houshang, Z. Yang and Z. Jiayu, 锻压对原位Al3Ti/6063Al 复合材料微结构及摩擦磨损性能的影响(Effects of Forging on Microstructure and Friction and Wear Properties of Al3Ti/6063Al in-situ Composites), Rare Metal Mat. Eng., 2016, 45(09), p 2391–2396. (in Chinese)
I. Barin and O. Knacke, Thermochemical Properities of Inorganic Substance, Springer, New York, 1973, p 792
H. Zhu, C. Jar, J. Song, J. Zhao, J. Li and Z. Xie, High Temperature Dry Sliding Friction and Wear Behavior of Aluminum Matrix Composites (Al3Zr+α-Al2O3)/Al, Tribol. Int., 2012, 48, p 78–86.
K. Huang, R.-P. Jiang, X.-Q. Li, R.-Q. Li, L.-H. Zhang (2019) 超声外场对原位TiB2/2A14铝基复合材料的摩擦磨损性能的影响 (Effects of Ultrasonic Field on Friction and Wear Properties of in-situ TiB2/2A14 Composite Materials), 材料工程 (J. Mater. Eng.), 47(12), 78–84 (in Chinese)
Xu. Li Hui, J.L. Pinyi and Lu. Shengbo, Preparation and Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Al3Zr+6082Al Composites Fabricated by Magnetic Stirring in situ, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6, p 1–8.
Y.Z. Zhang, Chap 6, 材料的干摩擦 (Dry Friction of Materials), 2nd ed. Science Press, Beijing, 2012, p 172
C. Zou, Z. Chen, H. Kang, W. Wang, R. Li, T. Li and T. Wang, Study of Enhanced Dry Sliding Wear Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Cu-TiB2 Composites Fabricated by in situ Casting Process, Wear, 2017, 392, p 118–125.
Xu. Li Hui, J.L. Pinyi and Lu. Shengbo, Surface Wear Behavior and Strengthening Mechanism of Al3Zr Particle Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites Prepared in situ, Surf. Topogr.-Metrol. Prop., 2019, 7, p 1–13.
Acknowledgment
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51605206; Jiangsu Province key Laboratory of High-end structural Materials, No. hsm1806.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Jiao, L., Xu, R. et al. Surface Wear Behavior and Friction and Wear Mechanism Studies of A356/3 wt.% Al3Zr Composites. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 3892–3902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05707-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05707-2