Abstract
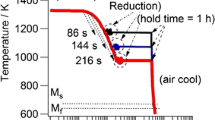
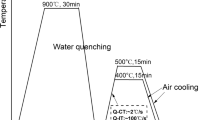
The effects of normalizing and tempering temperatures on the microstructures and mechanical properties of China Low Activation Martensitic (CLAM) steel with and without yttrium were studied. Based on the optimized traditional heat treatment, two special intermediate heat treatments were studied to improve the mechanical properties of the steels. The AC3 temperature of the CLAM steel was increased by adding yttrium. The optimized traditional heat treatments were 1000 °C × 30 min + 755 °C × 90 min and 1050 °C × 30 min + 755 °C × 90 min for the C1 and C2 alloys, respectively. The intermediate heat treatment results indicated that the precipitation behavior of carbides was effectively controlled. The size of the M23C6 carbides was refined during the two intermediate heat treatments due to the priority precipitation of MX particles. However, coarsening of grains and martensite laths occurred during heat treatment with furnace cooling. The twice-quenched tempering samples had a smaller grain size and martensite lath width than the other samples. The ductile–brittle transition temperature was − 69 and − 103 °C for the C1 and C2 alloys with twice quenching, and the yield strengths were 745 and 760 MPa, respectively. An excellent balance of strength and impact toughness was obtained with the twice-quenching and once tempering heat treatment process.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Wang, C. Zhang, J.J. Zhao, Z. Yang, and W.B. Liu, Microstructure Evolution and Yield Strength of CLAM Steel in Low Irradiation Condition, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 682, p 563–568
Y. Li, Q. Huang, Y. Wu, T. Nagasaka, T. Nagasaka, and T. Muroga, Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of China Low Activation Martensitic Steel Compared with JLF–1, J. Nucl. Mater., 2007, 367–370, p 117–121
Y. Li, T. Nagasaka, and T. Muroga, Long-Term Thermal Stability of Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steels as Structural Materials of Fusion Blanket, Plasma Fusion Res., 2010, 5, p S1036–S1039
S. Gao, Q. Huang, Z. Zhu, Z. Guo, X. Ling, and Y. Chen, Corrosion Behavior of CLAM Steel in Static and Flowing LiPb at 480 °C and 550 °C, Fusion Eng. Des., 2011, 86, p 2627–2631
Z.Y. Zhong, H. Saka, T.H. Kim, E.A. Holm, Y.F. Han, and X.S. Xie, The Structure and Properties of Low Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steels, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, 475–479, p 1383–1386
S. Noh, B. Kim, R. Kasada, and A. Kimura, Diffusion Bonding Between ODS Ferritic Steel and F82H Steel for Fusion Applications, J. Nucl. Mater., 2012, 426, p 208–213
Y.F. Li, Q.Y. Huang, Y.C. Wu, Y.N. Zheng, Y. Zuo, and S. Zhu, Effects of Addition of Yttrium on Properties and Microstructure for China Low Activation Martensitic (CLAM) Steel, Fusion Eng. Des., 2007, 82, p 2683–2688
W. Yan, P. Hu, W. Wang, L.J. Zhao, Y.Y. Shan, and K. Yang, Effect of Yttrium on Mechanical Properties of 9Cr-2WVTa Low Active Martensite Steel, Chin. J. Nucl. Sci. Eng., 2009, 29, p 50–55
S. Liu, Q.Y. Huang, C. Li, and B. Huang, Influence of Non-metal Inclusions on Mechanical Properties of CLAM Steel, Fusion Eng. Des., 2009, 84, p 1214–1218
H. Sakasegawa, H. Tanigawa, S. Kano, and H. Abe, Material Properties of the F82H Melted in an Electric Arc Furnace, Fusion Eng. Des., 2015, 98–99, p 2068–2071
A. Sawahata, H. Tanigawa, and M. Enomoto, Effects of Electro Slag Remelting on Inclusion Formation and Impact Property of Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steels, J. Jpn. I. Met., 2008, 72, p 176–180
D. Kim and K. Park, Effect of Electro-Slag Remelting Process on Low Cycle Fatigue Property of Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steels, New Renew. Energy, 2015, 11, p 62–70
G.X. Qiu, D.P. Zhan, C.S. Li, M. Qi, Z.H. Jiang, and H.S. Zhang, Effects of Yttrium on Microstructure and Properties of Reduced Activation Ferritic Martensitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2018, 34, p 2018–2029
G.X. Qiu, D.P. Zhan, C.S. Li, M. Qi, Z.H. Jiang, and H.S. Zhang, Effect of Y/Zr Ratio on Inclusions and Mechanical Properties of 9Cr-RAFM Steel Fabricated by Vacuum Melting, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28, p 1067–1076
G.X. Qiu, D.P. Zhan, C.S. Li, M. Qi, Z.H. Jiang, and H.S. Zhang, Effects of Y and Ti Addition on Microstructure Stability and Tensile Properties of Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steel, Nucl. Eng. Technol., 2019, 51, p 1365–1372
H. Tanigawa, A. Sawahata, M.A. Sokolov, M. Enomoto, R.L. Klueh, and A. Kohyama, Effects of Inclusions on Fracture Toughness of Reduced-Activation Ferritic/Martensitic F82H–IEA Steels, Mater. Trans., 2007, 48, p 570–573
F. Pan, J. Zhang, H.L. Chen, Y.H. Su, C.L. Kuo, Y.H. Su, S.H. Chen, K.J. Lin, P.H. Hsieh, and W.S. Hwang, Effects of Rare Earth Metals on Steel Microstructures, Materials, 2017, 9, p 1
W. Mu, P. Hedström, H. Shibata, P.G. Jönsson, and K. Nakajima, High-Temperature Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Studies of Ferrite Formation in Inclusion-Engineered Steels, p A Review, JOM, 2018, 70, p 2283–2295
P. Bate, The Effect of Deformation on Grain Growth in Zener Pinned Systems, Acta Mater., 2001, 49, p 1453–1461
G. Dimmler, P. Weinert, E. Kozeschnik, and H. Cerjaka, Quantification of the Laves Phase in Advanced 9–12% Cr Steels Using a Standard SEM, Mater. Charact., 2003, 51, p 341–352
S.K. Dhua, A. Ray, S.K. Sen, M.S. Prasad, K.B. Mishra, and S. Jha, Influence of Nonmetallic Inclusion Characteristics on the Mechanical Properties of Rail Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1999, 9, p 700–709
W. Rees and B. Hopkins, Intergranular Brittleness in Iron-Oxygen Alloys, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1952, 172, p 403–409
T. Furuhara, B. Poorganji, H. Abe, and T. Maki, Dynamic Recovery and Recrystallization in Titanium Alloys by Hot Deformation, JOM, 2007, 59, p 64–67
E.R. Parker and V.F. Zackay, Microstructural Features Affecting Fracture Toughness of High Strength Steels, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1975, 7, p 371–375
M.C. Zhao, K. Yang, and Y.Y. Shan, Comparison on Strength and Toughness Behaviors of Micro Alloyed Pipeline Steels with Acicular Ferrite and Ultrafine Ferrite, Mater. Lett., 2003, 57, p 1496–1500
A. Moitra, A. Dasgupta, S. Sathyanarayanan, G. Sasikala, S.K. Albert, S. Saroja, A.K. Bhaduri, E.R. Kumar, and T. Jayakumar, A Study of Fracture Mechanisms in RAFM Steel in the Ductile to Brittle Transition Temperature Regime, Proc. Eng., 2014, 86, p 258–263
N.J. Petch, The Cleavage Strength of Polycrystalline, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, 173, p 25–28
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51874081, 51574063), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N150204012), and Liaoning Province Doctoral Research Initiation Fund Guidance Project (No. 20170520079). We thank Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, G., Zhan, D., Li, C. et al. Effects of Yttrium and Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CLAM Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 42–52 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04574-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04574-7