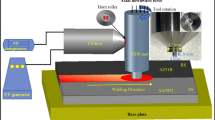
Abstract
Single-point incremental forming (SPIF) process comprises a set of process variables, such as forming tool diameter, vertical pitch, spindle rotation speed, and tool velocity, which may affect the forming behavior of the sheet to be deformed. The objective of this work is to study the effect of SPIF process parameters on forming characteristics and microstructure development for the AA-6061 (T6) aluminum alloy sheet. The SPIF experiments and finite element (FE) simulations were performed at different process parameters to achieve conical shapes from the AA-6061 blanks. The effect of process parameters on forming forces, thickness uniformity in wall region of the cone and surface roughness of the blank was analyzed. A detailed microstructure study was performed to analyze the effect of process variables on microstructure and texture evolution during the SPIF process. This study reveals that the process parameters are likely to influence the texture development especially at high tool diameter and vertical pitch values. Therefore, suitability and consequences of using different combinations of tool diameter and vertical pitch values are discussed for AA-6061 alloy.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Venukumar, S. Muthukumaran, S.G. Yalagi, and S.V. Kailas, Failure Modes and Fatigue Behavior of Conventional and Refilled Friction Stir Spot Welds in AA 6061-T6 Sheets, Int. J. Fatigue, 2014, 61, p 93–100
M.W. Fu, Y.W. Tham, H.H. Hng, and K.B. Lim, The Grain Refinement of Al-6061 via ECAE Processing: Deformation Behavior, Microstructure and Property, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 526(1–2), p 84–92
V.K. Barnwal, A. Tewari, K. Narasimhan, and S.K. Mishra, Effect of Plastic Anisotropy on Forming Behavior of AA-6061 Aluminum Alloy Sheet, J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des., 2016, 51(7), p 507–517
C.R. Brooks, ASM Handbook Heat Treating, 4, 2001.
V.K. Barnwal, Forming Behavior and Microstructure Evolution during Conventional and Incremental Sheet Forming of AA-6061 Aluminum Alloy Sheet, Dissertation Indian Institute of Technology Bombay India, 2016.
J. Jeswiet, F. Micari, G. Hirt, A. Bramley, J. Duflou, and J. Allwood, Asymmetric Single Point Incremental Forming of Sheet Metal, CIRP Ann., 2005, 54(2), p 88–114
A.K. Behera, R.A. De Sousa, G. Ingarao, and V. Oleksik, Single Point Incremental Forming: An Assessment of the Progress and Technology Trends from 2005 to 2015, J. Manuf. Process., 2017, 27, p 37–62
V.C. Do, Q.T. Pham, and Y.S. Kim, Identification of Forming Limit Curve at Fracture in Incremental Sheet Forming, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, 92(9), p 4445–4455
A. Mohammadi, L. Qin, H. Vanhove, M. Seefeldt, A. Van Bael, and J.R. Duflou, Single Point Incremental Forming of an Aged AL-Cu-Mg Alloy: influence of Pre-heat Treatment and Warm Forming, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25(6), p 2478–2488
G. Hussain, G. Lin, N. Hayat, N.U. Dar, and A. Iqbal, New Methodologies for the Determination of Precise Forming Limit Curve in Single Point Incremental Forming Process, Adv. Mater. Res., 2010, 97–101, p 126–129
C. Raju, N Halo, and C. Sathiya Narayanan, Strain Distribution and Failure Mode in Single Point Incremental Forming (SPIF) of Multiple Commercially Pure Aluminum sheets, J. Manuf. Process., 2017, 30, p 328–335.
W.C. Emmens and A.H. van den Boogaard, An Overview of Stabilizing Deformation Mechanisms in Incremental Sheet Forming, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(8), p 3688–3695
K. Jackson and J. Allwood, The Mechanics of Incremental Sheet Forming, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(3), p 1158–1174
K. Essa and P. Hartley, An Assessment of Various Process Strategies for Improving Precision in Single Point Incremental Forming, Int. J. Mater. Form., 2010, 4(4), p 401–412
J.J. Park and Y.H. Kim, Fundamental Studies on the Incremental Sheet Metal Forming Technique, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 140(1–3), p 447–453
M. Durante, A. Formisano, and A. Langella, Observations on the Influence of Tool-Sheet Contact Conditions on an Incremental Forming Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, 20(6), p 941–946
M. Durante, A. Formisano, A. Langella, and F.M.C. Minutolo, The Influence of Tool Rotation on an Incremental Forming Process, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(9), p 4621–4626
C. Bouffioux, P. Eyckens, C. Henrard, R. Aerens, A.V. Bael, H. Sol, and A.M. Habraken, Identification of Material Parameters to Predict Single Point Incremental Forming Forces, Int. J. Mater. Form., 2008, 1(S1), p 1147–1150
G. Ambrogio, L. Filice, and F. Gagliardi, Enhancing Incremental Sheet Forming Performance Using High Speed, Key Eng. Mater., 2011, 473, p 847–852
M. Durante, A. Formisano, and A. Langella, Comparison Between Analytical and Experimental Roughness Values of Components Created by Incremental Forming, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2010, 210(14), p 1934–1941
G. Hussain, L. Gao, N. Hayat, Z. Cui, Y.C. Pang, and N.U. Dar, Tool and Lubrication for Negative Incremental Forming of a Commercially Pure Titanium Sheet, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 203(1–3), p 193–201
C. Henrard, C. Bouffioux, P. Eyckens, J. Sol, J.R. Duflou, P.V. Houtte, A.V. Bael, L. Duchêne, and A.M. Habraken, Forming Forces in Single Point Incremental Forming: Prediction by Finite Element Simulations, Validation and Sensitivity, Comput. Mech., 2010, 47(5), p 573–590
J. Jeswiet, J.R. Duflou, and A. Szekeres, Forces in Single Point and Two Point Incremental Forming, Adv. Mater. Res., 2005, 6–8, p 449–456
A. Bansal, R. Lingam, S.K. Yadav, and N.V. Reddy, Prediction of Forming Forces in Single Point Incremental Forming, J. Manuf. Process., 2017, 28, p 486–493
R. Aerens, P. Eyckens, A.V. Bael, and J.R. Duflou, Force Prediction for Single Point Incremental Forming Deduced from Experimental and FEM Observations, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2009, 46(9–12), p 969–982
V.K. Barnwal, R. Raghavan, A. Tewari, K. Narasimhan, and S.K. Mishra, Effect of Microstructure and Texture on Forming Behaviour of AA-6061 Aluminium Alloy Sheet, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 679, p 56–65
V.K. Barnwal, S. Chakrabarty, A. Tewari, K. Narasimhan, and S.K. Mishra, Forming Behavior and Microstructural Evolution During Single Point Incremental Forming Process of AA-6061 Aluminum Alloy Sheet, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, 95(1–4), p 921–935
P. Shrivastava and P. Tandon, Effect of Preheated Microstructure Vis-à-vis Process Parameters and Characterization of Orange Peel in Incremental Forming of AA1050 Sheets, J. Mater. Eng. and Perform., 2019, 28(5), p 2530–2542
D. Banabic, Formability of Metallic Materials: Plastic Anisotropy, Formability Testing, Forming Limits, Springer, 2000
V.K. Barnwal, S.Y. Lee, J.H. Kim, and F. Barlat, Failure Characteristics of Advanced High Strength Steels at Macro and Micro Scales, Mat. Sci. and Eng. A, 2019, 754, p 411–427
S.K. Mishra, S.S.V. Tatiparti, S.M. Tiwari, R.S. Raghavan, J.E. Carsley, and J. Li, Annealing Response of AA5182 Deformed in Plane Strain and Equibiaxial Strain Paths, Philos. Mag., 2013, 93(20), p 2613–2629
R. Aerens, J.R. Duflou, P. Eyckens, and A.V. Bael, Advances in Force Modelling for SPIF, Int. J. Mater. Form., 2009, 2(S1), p 25–28
G. Ambrogio, I. Costantino, L.D. Napoli, L. Filice, L. Fratini, and M. Muzzupappa, Influence of Some Relevant Process Parameters on the Dimensional Accuracy in Incremental Forming: A Numerical and Experimental Investigation, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, 153–154(1–3), p 501–507
E.R. Davies, Introduction to Texture Analysis. Handbook of Texture Analysis Imperial College Press, 2008.
R. Narayanasamy, R. Ravindran, K. Manonmani, and J. Satheesh, A Crystallographic Texture Perspective Formability Investigation of Aluminium 5052 Alloy Sheets at Various Annealing Temperatures, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(5), p 1804–1817
Y.P. Chen, W.B. Lee, and S. To, Influence of Initial Texture on Formability of Aluminum Sheet Metal by Crystal Plasticity FE Simulation, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 192–193, p 397–403
J. Hu, K. Ikeda, and T. Murakami, Effect of Texture Components on Plastic Anisotropy and Formability of Aluminium alloy Sheets, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1998, 73, p 49–56
X.Y. Wen, Z.D. Long, W.M. Yin, T. Zhai, Z. Li, and S.K. Das, Texture Evolution in Continuous Casting Aluminum alloy AA5052 Hot Band During Biaxial Stretching, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 454, p 245–251
W.C. Liu, T. Zhai, and J.G. Morris, Texture Evolution of Continuous Cast and Direct Chill Cast AA 3003 Aluminum Alloys During Cold Rolling, Scr. Mater., 2004, 51(2), p 83–88
P.V. Houtte, S. Li, M. Seefeldt, and L. Delannay, Deformation Texture Prediction: From the Taylor Model to the Advanced Lamel Model, Int. J. Plast., 2005, 21, p 589–624
O. Engler and J. Hirsch, Texture Control by Thermomechanical Processing of AA6xxx Al-Mg-Si Sheet Alloys for Automotive Applications—A Review, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 336, p 249–262
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided for this work by the National Centre for Aerospace Innovation and Research, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnwal, V.K., Chakrabarty, S., Tewari, A. et al. Influence of Single-Point Incremental Force Process Parameters on Forming Characteristics and Microstructure Evolution of AA-6061 Alloy Sheet. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 7141–7154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04446-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04446-9