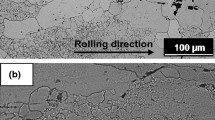
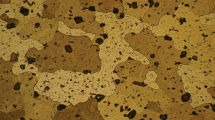
Abstract
A new four-stage aging treatment, which is composed of pre-aging, retrogression, natural aging (NA) and re-aging, is designed to increase the tensile properties and the fatigue life of forged 7050 aluminum alloy in this work. As compared to traditional T74 and RRA treatments, the four-stage aging-treated sample exhibits the highest tensile properties and ductility. The tensile strength and yield strength are 627 and 608 MPa, respectively, and the elongation is 11.3%. The results of TEM and DSC show that an increased G.P zones and fine η′ phase distributed in the matrix of the alloy are subjected by this new aging processing as compared with T74 and RRA treatments. The natural aging in four-stage aging treatment accelerates the diffusion of Mg vacancies, and promotes the precipitation of G.P zones in grain interior during re-aging stage. On the basis of dislocation shearing mechanism, more dense and fine G.P zones of four-stage aging temper result in the superior tensile strength as compared to T74 and RRA temper. In addition, a combination of shearable precipitates, fine GBPs and narrow PFZs is beneficial to the slip reversibility in the plastic zone at the crack tip, thereby reducing fatigue damage accumulation and increasing the fatigue life.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ma, T. Hu, H. Yang et al., Coupling of Dislocations and Precipitates: Impact on the Mechanical Behavior of Ultrafine Grained Al-Zn-Mg Alloys, Acta Mater., 2016, 103(15), p 153–164
L.M. Wu, W.H. Wang, Y.F. Hsu et al., Effects of Homogenization Treatment on Recrystallization Behavior and Dispersoid Distribution in an Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr allOy, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 456(1), p 163–169
A. Heinz, A. Haszler, C. Keidel et al., Recent Development in Aluminium Alloys for Aerospace Applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 280(1), p 102–107
X.Z. Li, V. Hansen, J. Gjønnes et al., HREM Study and Structure Modeling of the η′ Phase, the Hardening Precipitates in Commercial Al-Zn-Mg Alloys, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(9), p 2651–2659
L.F. Mondolfo, N.A. Gjostein, and D.W. Levinson, Structural Changes During the Aging in an Al-Mg-Zn Alloy, JOM, 1956, 8(10), p 1378–1385
A. Deschamps and Y. Brechet, Influence of Quench and Heating Rates on the Aging Response of an Al-Zn-Mg-(Zr) Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 251(1–2), p 200–207
K. Stiller, P.J. Warren, V. Hansen et al., Investigation of Precipitation in an Al-Zn-Mg Alloy After Two-Step Aging Treatment at 100 and 150 °C, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 270(1), p 55–63
F. Viana, A.M.P. Pinto, H.M.C. Santos et al., Retrogression and Re-aging of 7075 Aluminium Alloy: Microstructural Characterization, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1999, 92, p 54–59
Cina B, December 24, 1974, U.S. patent 3,856,584.
A.F. Oliveira, Jr., M.C. De Barros, K.R. Cardoso et al., The Effect of RRA on the Strength and SCC Resistance on AA7050 and AA7150 Aluminium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 379(1–2), p 321–326
J.K. Park and A.J. Ardell, Effect of Retrogression and Reaging Treatments on the Microstructure of Ai-7075-T651, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1984, 15(8), p 1531–1543
X. Chen, Z. Liu, M. Lin et al., Enhanced Fatigue Crack Propagation Resistance in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy by Retrogression and Reaging Treatment, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, 21(11), p 2345–2353
M.N. Desmukh, R.K. Pandey, and A.K. Mukhopadhyay, Effect of Aging Treatments on the Kinetics of Fatigue Crack Growth in 7010 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 435, p 318–326
G. Sha and A. Cerezo, Early-Stage Precipitation in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy (7050), Acta Mater., 2004, 52(15), p 4503–4516
L. Lu, Y. Shen, X. Chen et al., Ultrahigh Strength and High Electrical Conductivity in Copper, Science, 2004, 304(5669), p 422–426
Q. Zhao, Z. Qian, X. Cui et al., Influences of Fe, Si and Homogenization on Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Dilute Al-Mg-Si Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 666, p 50–57
R. Ferragut, A. Somoza, and A. Tolley, Microstructural Evolution of 7012 Alloy During the Early Stages of Artificial Aging, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(17), p 4355–4364
R. Ferragut, A. Somoza, and A. Dupasquier, On the Two-Step Aging of a Commercial Al-Zn-Mg Alloy; A Study by Positron Lifetime Spectroscopy, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 1996, 8(45), p 8945
J.F. Li, Z. Peng, C.X. Li et al., Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behaviors and Microstructures of 7075 Aluminium Alloy With Various Aging Treatments, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2008, 18(4), p 755–762
J.M. Fragomeni and B.M. Hillberry, A Micromechanical Method for Predicting the Precipitation Hardening Response of Particle Strengthened Alloys Hardened by Ordered Precipitates, Acta Mech., 1999, 138(3–4), p 185–210
J. Chen, L. Zhen, S. Yang et al., Investigation of Precipitation Behavior and Related Hardening in AA 7055 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 500(1–2), p 34–42
Y. Liu, D. Jiang, B. Li et al., Effect of Cooling Aging on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 57, p 79–86
D. Dumont, A. Deschamps, and Y. Brechet, On the Relationship Between Microstructure, Strength and Toughness in AA7050 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 356(1–2), p 326–336
T. Marlaud, A. Deschamps, F. Bley et al., Evolution of Precipitate Microstructures During the Retrogression and Re-aging Heat Treatment of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Acta Mater., 2010, 58(14), p 4814–4826
F. Chun, Z.Y. Liu, A.L. Ning et al., Retrogression and Re-aging Treatment of Al-9.99% Zn-1.72% Cu-2.5% Mg-0.13% Zr Aluminum Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2006, 16(5), p 1163–1170
R.K.W. Marceau, G. Sha, R. Ferragut et al., Solute Clustering in Al-Cu-Mg Alloys During the Early Stages of Elevated Temperature Aging, Acta Mater., 2010, 58(15), p 4923–4939
S. Suresh, Fatigue of Materials, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998
K.S. Chan, Roles of Microstructure in Fatigue Crack Initiation, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, 32(9), p 1428–1447
K.S. Al-Rubaie, M.A. Del Grande, D.N. Travessa et al., Effect of Pre-strain on the Fatigue Life of 7050-T7451 Aluminium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 464(1–2), p 141–150
S. Bai, Z. Liu, Y. Li et al., Microstructures and Fatigue Fracture Behavior of an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag Alloy with Addition of Rare Earth Er, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(7–8), p 1806–1814
Y.L. Wang, Q.L. Pan, L.L. Wei et al., Effect of Retrogression and Reaging Treatment on the Microstructure and Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior of 7050 Aluminum Alloy Thick Plate, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 857–863
E. Hornbogen, Martensitic Transformation at a Propagating Crack, Acta Metall., 1978, 26(1), p 147–152
Handbook A S M, Fatigue and Fracture, vol. 19 (ASM International, 1996).
B. Cai, B.L. Adams, and T.W. Nelson, Relation Between Precipitate-Free Zone Width and Grain Boundary Type in 7075-T7 Al Alloy, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(5), p 1543–1553
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0300900), the National Key Fundamental Research Project of China (2012CB619506-3), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51171209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Bai, S. et al. The Effect of Multistage Aging on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Forged 7050 Aluminum Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 3590–3599 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04115-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04115-x