Abstract
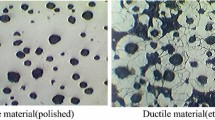
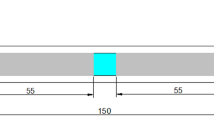
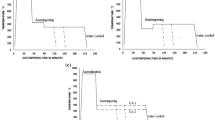
The influence of casting section thickness on fatigue strength of austempered ductile iron was investigated in this study. ASTM A536 65-45-12 grade of ductile iron was produced, machined into round samples of 10, 15, 20 and 25 mm diameter, austenitized at a temperature of 820 °C, quenched into an austempering temperature (\(T_{\text{A}}\)) of 300 and 375 °C and allowed to be isothermally transformed at these temperatures for a fixed period of 2 h. From the samples, fatigue test specimens were machined to conform to ASTM E-466. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and x-ray diffraction (XRD) methods were used to characterize microstructural morphology and phase distribution of heat-treated samples. The fatigue strength decreases as the section thickness increases. The SEM image and XRD patterns show a matrix of acicular ferrite and carbon-stabilized austenite with ferrite coarsening and volume fraction of austenite reducing as the section thickness increases. The study concluded that the higher the value of carbon-stabilized austenite the higher the fatigue strength while it decreases as the ausferrite structure becomes coarse.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.L. Hayrynen and K.R. Brandenberg, Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron (CADI)—The New Wear Material, AFS Trans., 2003, 111, p 845–850
M. Bahmani and R. Elliot, Effects of Pearlite Formation on Mechanical Properties of Austempered Ductile Iron, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1994, 10, p 1068–1072
M. Bahmani, R. Elliot, and N. Varahram, The Austempering Kinetics and Mechanical Properties of an Austempered Cu-Ni-Mo-Mn Alloyed Ductile Cast Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 1997, 32, p 4783–4791
K.L. Hayrynen and J.R. Keough, Wear Properties of Austempered Ductile Irons, AFS Trans., 2005, 113, p 803–812
J.R. Keough and K.L. Hayrynen, Developments in the Technology and Engineering Application of Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI), in Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Science and Processing of Cast Iron, Beijing, China, October 16–19, 2006, p 474–479.
C. Brunetti, M.V. Leite, and G. Pintaude, Effect of Specimen Preparation on Contact Fatigue Wear Resistance of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron, Wear, 2007, 263(1–6), p 663–668
A.N. Damir, A. Elkhatib, and G. Nassef, Prediction of Fatigue Life Using Modal Analysis for Grey and Ductile Cast Iron, Int. J. Fatigue, 2007, 29(3), p 499–507. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.05.004
T. Tun and K.T. Lwin, Optimizing the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austempered Ductile Iron for Automobile Differential Gear, J. Met. Mater. Miner., 2008, 18(2), p 199–205
B. Atzori, M. Zappalorto, and F. Berto, A Theoretical Treatise for Notch and Defect Sensitivity Under Torsion, Mech. Res. Commun., 2010, 37(2), p 173–176
S.L. Guang, Property and Application of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron, Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, 328–330, p 1297–1300
G. Meneghetti, M. Cagol, and F. Bonollo, Notch and Defect Sensitivity of Austempered Ductile Irons, in Proceedings 33rd AIAS National Congress, September 2004.
B. Atzori, F. Bonollo, and G. Meneghetti, Notch Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics of Austempered Ductile Irons, Key Eng. Mater., 2011, 457, p 181–186
G. Meneghetti and S. Masaggia, Estimation of the Fatigue Limit of Components Made of Austempered Ductile Iron Weakened by V-Shaped Notches, in World Foundry Congress 2012.
J.R. Keough, Austempered Ductile Iron, Ductile Iron Society, 1998, http://www.ductile.org/didata/section4/4intro.hmt, (14 October, 2012).
L. Magalhães, J. Seabra, and C. Sá, Experimental Observations of Contact Fatigue Crack Mechanisms for Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) Discs, Wear, 2000, 246, p 134–148
J. Yang and S.K. Putatunda, Near Threshold Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron (ADI) Processed by a Novel Two-Step Austempering Process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 393, p 254–268
S.B. Amir, Y. Sasan, and A. Behzad, Effect of Shot Peening Process on Fatigue Behavior of an Alloyed Austempered Ductile Iron, China Foundry, 2011, 8(3), p 325–330
L. Bartosiewicz, B.V. Kovacs, A.R. Krause, and S.K. Putatunda, Fatigue Crack Growth Behaviour of Austempered Ductile Cast Iron, Am. Foundry Soc. Trans., 1992, 92, p 135–142
H.A. Mohamed, Fatigue Properties of an Alloyed Austempered Ductile Iron of Initially Ferritic Matrix Structure Using Thermography as NDT, in 2nd International Conference on Technical Inspection and NDT (TINDT2008), Tehran, Iran, October 2008.
T.J. Marrow and H. Centinel, Short Fatigue Cracks in Austempered Ductile Cast Iron (ADI), Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2000, 23, p 425–434
T.J. Marrow, H. Centinel, M. Al-Zalmah, S. Mardonald, P.J. Withers, and J. Walton, Fatigue Crack Nuclei in Austempered Ductile Cast Iron, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2001, 25, p 635–648
B. Stokes, N. Gao, K.K. Lee, and P.A.S. Reed, Effects of Carbides on Fatigue Characteristics of Austempered Ductile Iron, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36, p 977–988
L. Chin-Kuang and C. Chin-Wei, Influence of Heat Treatment on Fatigue Crack Growth of Austempered Ductile Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 2002, 37, p 709–716
O. Erić, D. Rajnovic, S. Zec, L. Sidjanin, and M.T. Jova-Novic, Microstructure and Fracture of Alloyed Austempered Ductile Iron, Mater. Charact., 2006, 57(4–5), p 211–217
R.L. Miller, Trans. ASM, 1964, 57, p 892–899
ASTM A 536, Ductile Iron Casting Specific: Tensile–Yield–Elongation, in Annual Book of ASTM Standard, American Society for Testing and Materials International, West Conshohocken, PA, 1998, vol. 1, no. 2, p 321–325
P. Shanmugam, P.P. Rao, K.R. Udupa, and N. Venkataraman, Effect of Microstructure on the Fatigue Strength of an Austempered Ductile Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 1994, 29, p 4930–4933
M. Bahmani, R. Elliot, and N. Varahram, Austempered Ductile Iron: A Competitive Alternative for Forged Induction-Hardened Steel Crankshafts, Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 1997, 9, p 249–257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olawale, J.O., Ibitoye, S.A. Influence of Casting Section Thickness on Fatigue Strength of Austempered Ductile Iron. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 4997–5008 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2964-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2964-4