Abstract
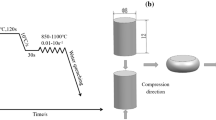
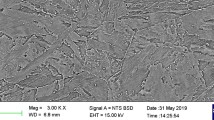
Hot deformation behavior of 35CrMo steel was investigated by compression tests in the temperature range of 850 to 1150 °C and strain rate range of 0.01 to 20 s−1 on a Gleeble-3810 thermal simulator. According to processing maps constructed based on the experimental data and using the principle of dynamic materials modeling (DMM), when the strain is 0.8, three safe regions with comparatively high efficiency of power dissipation were identified: (850 to 920) °C/(0.01 to 0.02) s−1, (850 to 900) °C/(10 to 20) s−1, and (1050 to 1150) °C/(0.01 to 1) s−1. And the domain of (920 to 1150) °C/(2.7 to 20) s−1 is within the instability range, whose efficiency of power dissipation is around 0.05. The deformed optical microstructure indicated that the combination of low deformation temperature (850 °C) and a relatively high strain rate (20 s−1) resulted in the smallest dynamic recrystallized grains, but coarser grains were obtained when a much higher strain rate was employed (50 s−1). A lower strain rate or a higher temperature will accelerate the growth of grains, and both high temperature and high strain rate can cause microcracks in the deformed steel. Integration of the processing map into the optical microstructure identified the region of (850 to 900) °C/(10 to 20) s−1 as the ideal condition for the hot deformation of 35CrMo steel.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Park, A. Shibata, D. Terada, and N. Tsuji, Flow Stress Analysis for Determining the Critical Condition of Dynamic Ferrite Transformation in 6Ni-0.1C Steel, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, p 163–173
I. Mejía, A. Bedolla Jacuinde, C. Maldonado, and J.M. Cabrera, Determination of the Critical Conditions for the Initiation of Dynamic Recrystallization in Boron Microalloyed Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 4133–4140
G.Z. Quan, G.C. Luo, J.T. Liang, D.S. Wu, A. Mao, and Q. Liu, Modelling for the Dynamic Recrystallization Evolution of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy in Two-Phase Temperature Range and a Wide Strain Rate Range, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2015, 97, p 136–147
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lark, and D.R. Barker, Modeling of Dynamic Material Behavior in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242, MTA, 1984, 15, p 1883–1892
T.D. Kil, J.M. Lee, and Y.H. Moon, Formability Estimation of Ring Rolling Process by using Deformation Processing Map, Proc. Eng., 2014, 81, p 298–303
S.S. Zhou, K.K. Deng, J.C. Li, K.B. Nie, F.J. Xu, H.F. Zhou, and J.F. Fan, Hot Deformation Behavior and Workability Characteristics of Bimodal Size SiCp/AZ91 Magnesium Matrix Composite with Processing Map, Mater. Des., 2014, 64, p 177–184
M. El Mehtedi, F. Gabrielli, and S. Spigarelli, Hot Workability in Process Modeling of a Bearing Steel by Using Combined Constitutive Equations and Dynamic Material Model, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 398–404
P. Zhang, C. Hu, C.G. Ding, Q. Zhu, and H.Y. Qin, Plastic Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of a Ni-Based Superalloy, Mater. Des., 2015, 65, p 575–584
A. Łukaszek Sołek and J. Krawczyk, The Analysis of the Hot Deformation Behaviour of the Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Zr-4Mo Alloy, Using Processing Maps, a Map of Microstructure and of Hardness, Mater. Des., 2015, 65, p 165–173
Y. Liu, Y. Ning, Y. Nan, H. Liang, Y. Li, and Z. Zhao, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of FGH4096-GH4133B Dual Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 633, p 505–515
A. Amiri, M.H. Sadeghi, and G.R. Ebrahimi, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behavior of AMS 5708 Nickel-Based Superalloy Using Processing Map, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 3940–3945
D.X. Wen, Y.C. Lin, H.B. Li, X.M. Chen, J. Deng, and L.T. Li, Hot Deformation Behavior and Processing Map of a Typical Ni-Based Superalloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 591, p 183–192
X. Shang, J. Zhou, X. Wang, and Y. Luo, Optimizing and Identifying the Process Parameters of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy in Hot Compression on the Base of Processing Maps, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 629, p 155–161
J. Yan, Q.L. Pan, B. Li, Z.Q. Huang, Z.M. Liu, and Z.M. Yin, Research on the Hot Deformation Behavior of Al-6.2Zn-0.70Mg-0.3Mn-0.17Zr Alloy Using Processing Map, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 632, p 549–557
H. Rastegari, A. Kermanpur, A. Najafizadeh, D. Porter, and M. Somani, Warm Deformation Processing Maps for the Plain Eutectoid Steels, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 626, p 136–144
L. Wang, F. Liu, J.J. Cheng, Q. Zuo, and C.F. Chen, Hot Deformation Characteristics and Processing Map Analysis for Nickel-Based Corrosion Resistant Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 623, p 69–78
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Microstructural Evolution in 42CrMo Steel During Compression at Elevated Temperatures, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, p 2132–2135
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Constitutive Modeling for Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of 42CrMo Steel, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2008, 42, p 470–477
Y. Li, S. Zhao, S. Fan, and G. Yan, Study on the Material Characteristic and Process Parameters of the Open-Die Warm Extrusion Process of Spline Shaft with 42CrMo Steel, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 571, p 12–20
Y.C. Lin, M.-S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Prediction of 42CrMo steel flow stress at high temperature and strain rate, Mech. Res. Commun., 2008, 35, p 142–150
Y.C. Lin, M.-S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Effect of Temperature and Strain Rate on the Compressive Deformation Behavior of 42CrMo Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 205, p 308–315
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhang, Modeling of Flow Stress of 42CrMo Steel Under Hot Compression, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 499, p 88–92
G. Kang, Y. Liu, J. Ding, and Q. Gao, Uniaxial Ratcheting and Fatigue Failure of Tempered 42CrMo Steel: Damage Evolution and Damage-Coupled Visco-Plastic Constitutive Model, Int. J. Plast., 2009, 25, p 838–860
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhong, Numerical Simulation for Stress/Strain Distribution and Microstructural Evolution in 42CrMo Steel During Hot Upsetting Process, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2008, 43, p 1117–1122
Y.C. Huang, Y.C. Lin, J. Deng, G. Liu, and M.-S. Chen, Hot Tensile Deformation Behaviors and Constitutive Model of 42CrMo Steel, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 349–356
J.W. Zhang, L.T. Lu, K. Shiozawa, W.N. Zhou, and W.H. Zhang, Effect of Nitrocarburizing and Post-Oxidation on Fatigue Behavior of 35CrMo Alloy Steel in Very High Cycle Fatigue Regime, Int. J. Fatigue, 2011, 33, p 880–886
J. Zhang, L. Lu, G. Cui, X. Shen, H. Yi, and W. Zhang, Effect of Process Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Gas Oxynitrocarburized 35CrMo Alloy Steel, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 2654–2658
J.W. Zhang, L.T. Lu, P.B. Wu, J.J. Ma, G.G. Wang, and W.H. Zhang, Inclusion Size Evaluation and Fatigue Strength Analysis of 35CrMo Alloy Railway Axle Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 562, p 211–217
Elevated-Temperature Properties of Ferritic Steels: Metals Handbook, 10th ed., ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 1990, Vol. 1, p 617–652, Int. J. Fatigue. doi:10.1016/0142-1123(91)90190-A
Z.Q. Sheng and R. Shivpuri, Modeling Flow Stress of Magnesium Alloys at Elevated Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 419, p 202–208
R.E. Smallman and R.J. BiShop, Chapter 7—Mechanical Behaviour of Materials, Modern Physical Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, 6th ed., R.E. Smallman and R.J. BiShop, Ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 1999, p 197–258
M.J. Luton and C.M. Sellars, Dynamic Recrystallization in Nickel and Nickel-Iron Alloys During High Temperature Deformation, Acta Metall., 1969, 17, p 1033–1043
A. Najafizadeh and J.J. Jonas, Predicting the Critical Stress for Initiation of Dynamic Recrystallization, ISIJ Int., 2006, 46, p 1679–1684
S. Solhjoo, Determination of Critical Strain for Initiation of Dynamic Recrystallization, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 1360–1364
H. Sun, Y. Sun, R. Zhang, M. Wang, R. Tang, and Z. Zhou, Study on Hot Workability and Optimization of Process Parameters of a Modified 310 Austenitic Stainless Steel Using Processing Maps, Mater. Des., 2015, 67, p 165–172
Y.V.R.K. Prasad and T. Seshacharyulu, Modelling of Hot Deformation for Microstructural Control, Int. Mater. Rev., 1998, 43, p 243–258
Y.V.R.K. Prasad and T. Seshacharyulu, Processing Maps for Hot Working of Titanium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 243, p 82–88
S.V.S.N. Murty and B.N. Rao, On the Development of Instability Criteria During Hotworking with Reference to IN 718, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 254, p 76–82
Z. Yang, F. Zhang, C. Zheng, M. Zhang, B. Lv, and L. Qu, Study on Hot Deformation Behaviour and Processing Maps of Low Carbon Bainitic Steel, Mater. Des. A, 2015, 66, p 258–266
Y. Wang, Q. Pan, Y. Song, C. Li, and Z. Li, Hot Deformation and Processing Maps of X-750 Nickel-Based Superalloy, Mater. Des., 2013, 51, p 154–160
J. Luo, L. Li, and M.Q. Li, The Flow Behavior and Processing Maps During the Isothermal Compression of Ti17 Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 606, p 165–174
F. Chen, Z. Cui, and S. Chen, Recrystallization of 30Cr2Ni4MoV Ultra-Super-Critical Rotor Steel During Hot Deformation. Part I: Dynamic Recrystallization, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 5073–5080
R. Ebrahimi and E. Shafiei, Mathematical Modeling of Single Peak Dynamic Recrystallization Flow Stress Curves in Metallic Alloys, Recrystallization, P.K. Sztwiertnia, Ed., Rijeka, InTech, 2012,
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (No. 2014CB046702) and to Wang Zi in the School of Powder Metallurgy Research Institute of Central South University, Changsha, for providing the testing facilities for carrying out of the present investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Zb., Huang, Yc. & Liu, Y. Plastic Deformation Behavior and Processing Maps of 35CrMo Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1219–1227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1933-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1933-7