Abstract
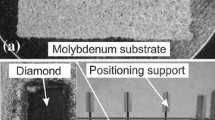
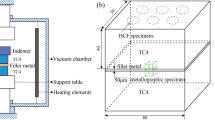
The corrugated sandwich structure, consisting of a CP Ti (commercially pure titanium) core between two Ti-6Al-4V face sheets, was brazed using pasty Ti-37.5Zr-15Cu-10Ni as filler alloy, at the temperature of 870°C for 5, 10, 20, and 30 min. The effect of brazing time on the microstructure and elemental distribution of the brazed joints was examined by means of SEM, EDS, and XRD analyses. It was found that various intermetallic phases were formed in the brazed joints, following a brazing time of 5 min, and their contents were decreased by the increment of brazing time, while prolonged brazing time resulted in a fine, acicular Widmanstätten microstructure throughout the entire joint. In addition, shear testing was performed in the brazed corrugated specimens in order to indirectly assess the quality of the joints. The debonding between CP Ti and Ti-6Al-4V was observed in the specimen brazed for 5 min and the fracture of the CP Ti corrugated core occurred after 30 min of brazing time. Additionally, when brazed for 10 min or 20 min, brittle intermetallic compounds in the joints and the grain growth of the base metal were controllable. Therefore, the sandwich structures failed without debonding in the joints or fracture within the base metal, demonstrating a good combination of strength and ductility.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Liu, H. Wang, and Z. Guan, Experimental and Numerical Study on the Mechanical Response of Nomex Honeycomb Core Under Transverse Loading, Compos. Struct., 2015, 121, p 304–314
V. Crupi, G. Epasto, and E. Guglielmino, Collapse Modes in Aluminium Honeycomb Sandwich Panels Under Bending and Impact Loading, Int. J. Impact Eng, 2012, 43, p 6–15
E. Bormashenko, R. Pogreb, Y. Bormashenko, R. Grynyov, and O. Gendelman, Low Voltage Reversible Electrowetting Exploiting Lubricated Polymer Honeycomb Substrates, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 104(17), p 171601
K. Kang, S.K. Hong, D.S. Noh, and H.S. Ryou, Heat Transfer Characteristics of a Ceramic Honeycomb Regenerator for an Oxy-fuel Combustion Furnace, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2014, 70(1), p 494–500
S. Lee, F. Barthelat, J.W. Hutchinson, and H.D. Espinosa, Dynamic Failure of Metallic Pyramidal Truss Core Materials-Experiments and Modeling, Int. J. Plast., 2006, 22(11), p 2118–2145
D.G. Ahn, G.H. Nam, C.G. Jung, and D.Y. Yang, Experimental Determination of Elastic Properties of the Core in a Thin Sandwich Plate with a Metallic Truss Core, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Man., 2009, 10(5), p 107–113
J. Liu, X. Zhu, Z. Zhou, and L. Ma, Effects of Thermal Exposure on Mechanical Behavior of Carbon Fiber Composite Pyramidal Truss Core Sandwich Panel, Compos. B, 2014, 60, p 82–90
H. Ikeda, and K. Inamori, Thermoplastic Resin Foam, Method of Producing the Same, and Light Reflecting Material Using the Same, U.S. Patent No. 8,853,288
W. Li, G. Huang, Y. Bai, Y. Dong, and S. Feng, Dynamic Response of Spherical Sandwich Shells with Metallic Foam Core Under External Air Blast Loading-Numerical Simulation, Compos. Struct., 2014, 116, p 612–625
M.R.M. Rejab and W.J. Cantwell, The Mechanical Behaviour of Corrugated-Core Sandwich Panels, Compos. B, 2013, 47, p 267–277
K. Wei, R. He, X. Cheng, R. Zhang, Y. Pei, and D. Fang, Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight ZrO2 Ceramic Corrugated Core Sandwich Panels, Mater. Des., 2014, 64, p 91–95
T.A. Barnes and I.R. Pashby, Joining Techniques for Aluminium Spaceframes used in Automobiles: Part II-Adhesive Bonding and Mechanical Fasteners, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 99(1), p 72–79
J. Banhart and H.W. Seeliger, Aluminium Foam Sandwich Panels: Manufacture, Metallurgy and Applications, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2008, 10(9), p 793–802
S.D. Elrod, D.T. Lovell, and R. Davis, Aluminum Brazed Titanium Honeycomb Sandwich Structure—A New System, Weld. J., 1973, 52(10), p 425
L. Wan, Y. Huang, S. Lv, and J. Feng, Fabrication and Interfacial Characterization of Aluminum Foam Sandwich via Fluxless Soldering with Surface Abrasion, Compos. Struct., 2015, 123, p 366–373
C.G. Jung, D.Y. Seung, D.Y. Yang, S.J. Na, and D.G. Ahn, Development of a Continuous Fabrication System for a Metallic Sandwich Plate with a Three-Dimensional Truss Core, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2009, 45(3–4), p 352–361
L. Valdevit, J.W. Hutchinson, and A.G. Evans, Structurally Optimized Sandwich Panels with Prismatic Cores, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2004, 41(18), p 5105–5124
A. Elrefaey and W. Tillmann, Brazing of Titanium to Steel with Different Filler Metals: Analysis and Comparison, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45(16), p 4332–4338
S. Lathabai, B.L. Jarvis, and K.J. Barton, Comparison of Keyhole and Conventional Gas Tungsten Arc Welds in Commercially Pure Titanium, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 299(1), p 81–93
E. Ganjeh and H. Sarkhosh, Microstructural, Mechanical and Fractographical Study of Titanium-CP and Ti-6Al-4V Similar Brazing with Ti-Based Filler, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, p 119–129
X.L. Gao, L.J. Zhang, J. Liu, and J.X. Zhang, A Comparative Study of Pulsed Nd: YAG Laser Welding and TIG Welding of Thin Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Plate, Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, p 14–21
E. Ganjeh, H. Sarkhosh, M.E. Bajgholi, H. Khorsand, and M. Ghaffari, Increasing Ti-6Al-4V Brazed Joint Strength Equal to the Base Metal by Ti and Zr Amorphous Filler Alloys, Mater. Charact., 2012, 71, p 31–40
K. Aydın, Y. Kaya, and N. Kahraman, Experimental Study of Diffusion Welding/Bonding of Titanium to Copper, Mater. Des., 2012, 37, p 356–368
V.A. Sidyakin, D.K. Pechenkin, V.M. Arbuzov, and V.S. Khaustov, Butt Welding of Steel-Titanium Pipe Transition Pieces, Weld. Int., 2004, 18(12), p 977–981
B. Qin, G.M. Sheng, J.W. Huang, B. Zhou, S.Y. Qiu, and C. Li, Phase Transformation Diffusion Bonding of Titanium Alloy with Stainless Steel, Mater. Charact., 2006, 56(1), p 32–38
B. Kurt, N. Orhan, E. Evin, and A. Çalik, Diffusion Bonding Between Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and Ferritic Stainless Steel, Mater. Lett., 2007, 61(8), p 1747–1750
A. Shapiro and A. Rabinkin, State of the Art of Titanium-Based Brazing Filler Metals, Weld. J., 2003, 82(10), p 36–43
Sandin T, What’s Happening with Aerospace Brazing, Weld. J., 2013, 92(10), p 56–58
R. Beeranur, K.K. Waghmare, and R.K. Singh, Characterization of Vacuum Brazing of SS 304 and Alumina Ceramic with Active Brazing Alloy, Procedia Mater. Sci., 2014, 5, p 969–977
T. Onzawa, A. Suzumura, and M.W. Ko, Brazing of Titanium Using Low-Melting-Point Ti-Based Filler Metals, Weld. Res. Suppl., 1990, 69(12), p 462–467
K.J. Doherty, J.R. Tice, S.T. Szewczyk, and G.A. Gilde, Brazing Titanium for Structural and Vehicle Applications, Weld. J., 2007, 86(9), p 41
C.T. Chang, Z.Y. Wu, R.K. Shiue, and C.S. Chang, Infrared Brazing Ti-6Al-4V and SP-700 Alloys Using the Ti-20Zr-20Cu-20Ni Braze Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2007, 61(3), p 842–845
D.H. Kang, J.H. Sun, D.M. Lee, S.Y. Shin, and H.S. Kim, Partially Alloyed Filler Sheet for Brazing of Ti and Its Alloys Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering Method, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 527(1), p 239–244
M. Iijima, W.A. Brantley, I. Kawashima, N. Baba, S.B. Alapati, T. Yuasa, H. Ohno, and I. Mizoguchi, Microstructures of Beta-Titanium Orthodontic Wires Joined by Infrared Brazing, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2006, 79(1), p 137–141
G. Lütjering and J.C. Williams, Titanium, 2nd ed., B. Derby, Ed., Springer, Berlin, 2003, p 29–32
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Funding of Jiangsu Innovation Program for Graduate Education (No. KYLX_0263) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Fan, M., Li, J. et al. Interfacial Microstructure Evolution and Shear Strength of Titanium Sandwich Structures Fabricated by Brazing. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 774–780 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1905-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1905-y