Abstract
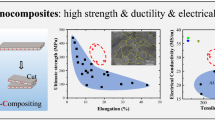
In this paper, we present alumina (Al2O3) nanocomposites reinforced with various graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) concentrations (0.75 and 1.25 wt.%) and fabricated by rapid high frequency-induction heat (HF-IH) sintering route. The influence of the GNP on the microstructures, mechanical properties, and interfacial connections of the resulting nanocomposites were thoroughly investigated. GNPs were synthesized using combined chemical oxidation and thermal exfoliation processes and dispersed homogenously into base Al2O3 ceramic matrix using colloidal chemistry technique. Pressure-assisted HF-IH sintering rapidly consolidated nanocomposites close to theoretical densities (~99%) without damaging the GNP intrinsic nanostructures and electron microscopy revealed firmly bonding of the nanocomposite constituents at interfaces. Nanocomposite samples containing 0.75 wt.% GNP demonstrated 60% finer microstructure with 45% higher fracture toughness (K IC) and 9% improvement in hardness against benchmarked monolithic Al2O3. However, nanocomposites loaded with higher GNP contents (1.25 wt.%) showed deprived properties due to GNP accumulations. Homogenous dispersions and two-dimensional features allowed GNP to interact wide area of the matrix grains thus refined the microstructure and gave rise the grain anchoring mechanism thereby led nanocomposite to superior mechanical properties following GNP crack-bridging and pull-out toughening mechanisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, and A.A. Firsov, Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films, Science, 2004, 306, p 666–669
S. Bai and X. Shen, Graphene-Inorganic Nanocomposites, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, p 64–98
H. Shifeng and C. Xin, Effect of Carbon Black on Properties of 0-3 Piezoelectric Ceramics/Cement Composites, Curr. Appl. Phys., 2009, 9, p 1191–1194
K. Niihara, New Design Concept of Structural Ceramics-Ceramics Nanocomposites, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 1999, 99, p 974–982
A. Centeno, V.G. Rocha, B. Alonso, A. Fernández, C.F. Gutierrez-Gonzalez, R. Torrecillas, and A. Zurutuza, Graphene for Tough and Electroconductive Alumina Ceramics, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2013, 33, p 3201–3210
Y. Wu, X. Zhang, and J. Guo, Microstructural Development and Mechanical Properties of Self-Reinforced Alumina with CAS Addition, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2001, 2, p 581–587
G. Evans, Perspective on the Development of High-Toughness Ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1990, 73, p 187–206
J.R. Martinlli and F.F. Sene, Electrical Resistivity of Ceramic-Metal Composite Materials: Application in Crucibles for Induction Furnaces, Ceram. Int., 2000, 26, p 325–335
L. Osayande and I. Okoli, Fracture Toughness Enhancement for Alumina System: A Review, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2008, 5, p 313–323
J. Llorca, M. Elices, and J.A. Celemin, Toughness and Microstructural Degradation at High Temperature in SiC Fiber-Reinforced Ceramics, Acta Mater., 1998, 46, p 2441–2453
F. Yongqing, Y.W. Gu, and D. Hejun, SiC Whisker Toughened Al2O3-(Ti, W)C Ceramic Matrix Composites, Scr. Mater., 2001, 44, p 111–116
D.E. Garcıa, S. Schicker, J. Bruhn, R. Janssen, and N. Claussen, Processing and Mechanical Properties of Pressureless-Sintered Niobium-Alumina-Matrix Composites, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1998, 81, p 429–432
N. Padture, Multifunctional Composites of Ceramics and Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, p 1767–1770
Tougher. Peigney, Ceramics with Nanotubes, Nat. Mater., 2003, 2, p 15–16
J. Fan, D. Zhao, and J. Song, Preparation and Microstructure of Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes Toughened Al2O3 Composite, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89, p 750–753
C. Laurent, A. Peigney, and A. Rousset, Carbon Nanotubes-Fe-Alumina Nanocomposites: Part II: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Hot-Pressed Composites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 1998, 18, p 2005–2013
G. Zhan, J. Kuntz, J. Wan, and K. Mukherjee, Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes as Attractive Toughing Agent in Alumina Based Nanocomposites, Nat. Mater., 2003, 2, p 38–42
S. Sarkar and P.K. Das, Microstructure and Physicomechanical Properties of Pressure-Less Sintered Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube/Alumina Nanocomposites, Ceram. Int., 2012, 38, p 423–432
I. Ahmad, A. Kennedy, and Y.Q. Zhu, Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Alumina Nanocomposites: Mechanical Properties and Interfacial Investigations, J. Compos. Sci. Technol., 2010, 70, p 1199–1206
F. Inam, T. Pijis, and M.J. Reece, The Production of Advanced Fine-Grained Alumina by Carbon Nanotubes Addition, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 31, p 2853–2859
I. Ahmad, H. Cao, H. Chen, H. Zhao, A. Kennedy, and Y.Q. Zhu, Carbon Nanotube Toughened Aluminium Oxide Nanocomposites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 30, p 865–873
I. Ahmad, A. Kennedy, and Y.Q. Zhu, Wear Resistance Properties of Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Al2O3 Nanocomposite, Wear, 2010, 26, p 971–978
Y.C. Fan, L.J. Wang, J.L. Li, J.Q. Li, S.K. Sun, F. Chen, L.D. Chen, and W. Jiang, Preparation and Electrical Properties of Graphene Nanosheet/ Al2O3 Composites, Carbon, 2010, 48, p 1743–1749
T. He, J.L. Li, L.J. Wang, J.J. Zhu, and W. Jiang, Preparation and Consolidation of Alumina/Graphene Composite Powders, Mater. Trans., 2009, 50, p 749–751
C.W. Lam, J.T. James, R. McCluskey, S. Arepalli, and R.L. Hunter, A Review of Carbon Nanotube Toxicity and Assessment of Potential Occupational and Environmental Health Risks, Crit. Rev. Toxicol., 2006, 36, p 189–217
L.S. Walker and E.L. Corral, Toughness in Grapheme Ceramic Composites, ACS Nano, 2011, 4, p 3182–3190
J. Dusza and C. Balaszi, Microstructure and Farcture Toughness of Si3N4 + GNP Platelet Composites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 32, p 3389–3397
K. Wang and T. Wei, Preperation of Graphene Nanosheets/Alumina Composites by Spark Plasma Sintering, Mater. Res. Bull., 2011, 46, p 315–318
L. Jain and H.K. Jiang, Mechanical Properties of Graphene Platelets-Reinforced Alumina Ceramics Composites, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39, p 6215–6221
H. Porwal, P. Tatarko, S. Grasso, J. Khaliq, I. Dlouhy, and M.J. Reece, Graphene Reinforced Alumina Nano-Composites, Carbon, 2013, 64, p 359–369
H. Porwal, S. Grasso, and M.J. Reece, Review of Graphene-Ceramic Matrix Composites, Adv. Appl. Ceram., 2013, 112, p 443–454
W.S. Hummers and R.E. Offeman, Preparation of Graphitic Oxide, J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1958, 80, p 1339
S. Pei and H. Cheng, The Reduction of Graphene Oxide, Carbon, 2012, 50, p 3210–3228
I. Ahmad, M. Islam, A.A. Almajid, B. Yazdani, and Y.Q. Zhu, Investigation of Yttria-Doped Al2O3 Nanocomposites Reinforced by Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40, p 9327–9335
A. Chorfa, M.A. Madjoubi, M. Amidouche, N. Bouras, J. Rubio, and F. Rubiom, Glass Hardness and Elastic Modulus Determination by Nanoindentation Using Displacement and Energy Methods, Ceram. Silik., 2010, 54, p 225–234
G.R. Anstis, P. Chantikul, and D.B. Marshal, A Critical Evaluation of Indentation Technique for Measuring Fracture Toughness: I. Direct Crack Method, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1981, 64, p 533–538
H.C. Schniepp, J.L. Li, M.J. McAllister, H. Sai, M. Herrera-Alonso, D.H. Adamson, R.K. Prudhomme, R. Car, D.A. Saville, and I.A. Aksay, Functionalized Single Graphene Sheets Derived from Splitting Graphite Oxide, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 11, p 8535–8539
H.C. Kim, D.Y. Oh, and I.J. Shon, Sintering of Nanophase WC-15 vol.% Co Hard Metals by Rapid Sintering Process, Int. J. Refract. Hard Mater., 2004, 22, p 197–203
S.W. Kim and K.A. Khalil, High-Frequency Induction Heat Sintering of Mechanically Alloyed Alumina–Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Nano-bioceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89, p 1280–1285
B. Yazdani, Y. Xi, I. Ahmad, and Y.Q. Zhu, Graphene and Carbon Nanotube (GNT)-Reinforced Alumina Nanocomposites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 35, p 179–186
I. Ahmad, M. Islam, F. Xu, S.I. Shah, and Y.Q. Zhu, Magnesia Tuned Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes-Reinforced Alumina Nanocomposites, Mater. Character., 2015, 99, p 210–219
Y. Fan, M. Estili, G. Igarashi, and A. Kawasakia, The Effect of Homogeneously Dispersed Few-Layer Graphene on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al2O3 Nanocomposites, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2014, 34(2), p 443–451
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding of this research through the Research Group Project No. RGP-VPP-283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, I., Islam, M., Subhani, T. et al. Characterization of GNP-Containing Al2O3 Nanocomposites Fabricated via High Frequency-Induction Heat Sintering Route. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 4236–4243 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1738-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1738-0