Abstract
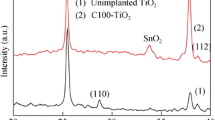
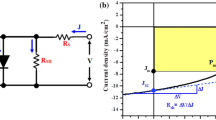
The current work investigates ion implantation of a transition metal (Ag) into MXene/TiO2 films utilizing low energy at different fluence rates of 5 × 1012, 5 × 1013, 5 × 1014, and 5 × 1015 ions-cm−2 respectively. The morphology and crystal structure of the transition metal-implanted MXene/TiO2 samples were characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. In addition, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed the presence of Ag(I) oxidation state at 5 × 1014 ions-cm−2 fluence, whereas at a higher fluence of 5 × 1015 ions-cm−2, both Ag(I) and Ag(0) states were found. The optical properties of the transition metal-implanted MXene/TiO2 samples were also investigated via UV-visible and photoluminescence studies. The transition metal implantation significantly enhanced the light absorption and reduced the charge recombination owing to the formation of defect states. Finally, the quantum dot-sensitized solar cell (QDSSC) device fabricated with 5 × 1014 ions-cm−2 (Ag_3) exhibited the highest power conversion efficiency of 3.94% versus the unimplanted MXene/TiO2-based QDSSC (2.48%), which is attributed to enhanced absorption and minimization of charge recombinations, as confirmed by photovoltaic characteristics and Nyquist plots.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
I. Singh, V. Bhullar, and A. Mahajan, Interfacial engineering of a TiO2 photoanode via graphene nanoribbons for efficient quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Energy Fuels 37, 15054 (2023).
N. Singh, V. Murugadoss, S. Nemala, S. Mallick, and S. Angaiah, Cu2ZnSnSe4 QDs sensitized electrospun porous TiO2 nanofibers as photoanode for high performance QDSC. Sol. Energy 171, 571 (2018).
N.T. Chung, P.T. Nguyen, H.T. Tung, and D.H. Phuc, Quantum Dot sensitized solar cell: photoanodes, counter electrodes, and electrolytes. Mol. 26(9), 2638 (2021).
S.S. Rayalu, D. Jose, M.V. Joshi, P.A. Mangrulkar, K. Shrestha, and K. Klabunde, Photocatalytic water splitting on Au/TiO2 nanocomposites synthesized through various routes: enhancement in photocatalytic activity due to SPR effect. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 142–143, 684 (2013).
M.A.K.L. Dissanayake, H.K.D.W.M.N. Divarathna, C.B. Dissanayake, G.K.R. Senadeera, P.M.P.C. Ekanayake, and C.A. Thotawattage, An innovative TiO2 nanoparticle/nanofibre/nanoparticle, three layer composite photoanode for efficiency enhancement in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 322–323, 110 (2016).
I. Singh, V. Bhullar, D. Devi, F. Singh, S. Chopra, A. Krishna Debnath, D. Kumar Aswal, and A. Mahajan, Au ion beam engineered MXene incorporated TiO2 photoanodes for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Mat. Sci. Eng. B. 290, 116342 (2023).
V. Bhullar, S. Sardana, and A. Mahajan, Size modeling of TiO2 nanofibers for efficient TiO2 sensitized mesoscopic solar cells. Sol. Energy 230, 177 (2021).
R. Zhou, Q. Zhang, E. Uchaker, L. Yang, N. Yin, Y. Chen, M. Yin, and G. Cao, Photoanodes with mesoporous TiO2 beads and nanoparticles for enhanced performance of CdS/CdSe quantum dot co-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 135, 284 (2014).
M. Marandi, P. Talebi, and L. Moradi, Co-application of TiO2 nanoparticles and randomly directed TiO2 nanorods in the photoelectrode of the CdS: Mn quantum dots sensitized solar cells and optimization of the doping for the efficiency improvement. Opt. Mater. 94, 224 (2019).
T. Toyoda and Q. Shen, Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells: effect of nanostructured TiO2 morphologies on photovoltaic properties. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 1885 (2012).
A. Tanvi, R.K. Mahajan, S. Bedi, V. Kumar, A. Saxena, D.K. Singh, and Aswal, Broadband enhancement in absorption cross-section of N719 dye using different anisotropic shaped single crystalline silver nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 6, 48064 (2016).
N. Kaur, V. Bhullar, D.P. Singh, and A. Mahajan, Bimetallic implanted plasmonic photoanodes for TiO2 sensitized third generation solar cells. Sci. Rep. 10, 7657 (2020).
V. Bhullar, D. Devi, F. Singh, S. Chopra, A.K. Debnath, D.K. Aswal, and A. Mahajan, Ion implanted substitutionally dispersed Au in TiO2 nanostructures for efficient and stable dye sensitized solar cells. Opt. Mater. 132, 112800 (2022).
T. Raguram and K.S. Rajni, Synthesis and characterisation of Cu - doped TiO2 nanoparticles for DSSC and photocatalytic applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 47, 4674 (2022).
Y.X. Dong, X.L. Wang, E.M. Jin, S.M. Jeong, B. Jin, and S.H. Lee, One-step hydrothermal synthesis of Ag decorated TiO2 nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cell application. Renew. Energy 135, 1207 (2019).
Z. Yu, W. Feng, W. Lu, B. Li, H. Yao, K. Zeng, and J. Ouyang, MXenes with tunable work functions and their application as electron- and hole-transport materials in non-fullerene organic solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A. 7, 11160 (2019).
H.-C. Fu, V. Ramalingam, H. Kim, C.-H. Lin, X. Fang, H.N. Alshareef, and J.-H. He, MXene-contacted silicon solar cells with 11.5% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1900180 (2019).
C. Dall’Agnese, Y. Dall’Agnese, B. Anasori, W. Sugimoto, and S. Mori, Oxidized Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets for dye-sensitized solar cells. New J. Chem. 42, 16446 (2018).
A. Agresti, A. Pazniak, S. Pescetelli, A. Di Vito, D. Rossi, A. Pecchia, M. Auf der Maur, A. Liedl, R. Larciprete, D.V. Kuznetsov, D. Saranin, and A. Di Carlo, Titanium-carbide MXenes for work function and interface engineering in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. 18, 1228 (2019).
H.G. Lemos, R.M. Ronchi, G.R. Portugal, J.H.H. Rossato, G.S. Selopal, D. Barba, E.C. Venancio, F. Rosei, J.T. Arantes, and S.F. Santos, Efficient Ti3C2Tx MXene/TiO2 hybrid photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 5, 15928 (2022).
Y. Chen, D. Wang, Y. Lin, X. Zou, and T. Xie, In suit growth of CuSe nanoparticles on MXene (Ti3C2) nanosheets as an efficient counter electrode for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 316, 248 (2019).
I. Zada, W. Zhang, W. Zheng, Y. Zhu, Z. Zhang, J. Zhang, M. Imtiaz, W. Abbas, and D. Zhang, The highly efficient photocatalytic and light harvesting property of Ag-TiO2 with negative nano-holes structure inspired from cicada wings. Sci. Rep. 7, 17277 (2017).
Z. Du, F. Yin, D. Han, S. Mao, J. Wang, A.R. Aleem, Z. Pan, and J. Tang, Plasmonic effect with tailored Au@TiO2 nanorods in photoanode for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 5917 (2019).
H. Zhao, F. Huang, J. Hou, Z. Liu, Q. Wu, H. Cao, Q. Jing, S. Peng, and G. Cao, Efficiency enhancement of quantum dot sensitized TiO2/ZnO nanorod arrays solar cells by plasmonic Ag nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 26675 (2016).
Z.S. Seddigi, S.A. Ahmed, S. Sardar, and S.K. Pal, Carbonate doping in TiO2 microsphere: The key parameter influencing others for efficient dye sensitized solar cell. Sci. Rep. 6, 23209 (2016).
V. Bhullar and A. Mahajan, Cu implanted TiO2 based dye sensitized solar cells: Unraveling the effect of doping mechanism and type of metal ion on the photovoltaic properties. Sol. Energy 254, 8 (2023).
A.K. Navjyoti, V. Sharma, A.K. Sharma, V. Debnath, and A. Saxena, Mahajan, MXene supported nickel-cobalt layered double hydroxide as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. ACS J. Alloy. Compd. 939, 168779 (2023).
M. Pogorielov, K. Smyrnova, S. Kyrylenko, O. Gogotsi, V. Zahorodna, and A. Pogrebnjak, MXenes—A new class of two-dimensional materials: structure, properties and potential applications. Nanomaterials 11(12), 3412 (2021).
L. Zhang, W. Su, Y. Huang, H. Li, L. Fu, K. Song, X. Huang, J. Yu, and C.-T. Lin, In situ high-pressure X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy study of Ti3C2Tx MXene. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 343 (2018).
H. Wang, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, G. Li, H. Huang, X. Zhang, and Q. Jiang, Enhancement of the electrical properties of MXene Ti3C2 nanosheets by post-treatments of alkalization and calcination. Mat. Lett. 160, 537 (2015).
Y. Li, M. Ma, W. Chen, L. Li, and M. Zen, Preparation of Ag-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by a miniemulsion method and their photoactivity in visible light illuminations. Mat. Chem. Phys. 129, 501 (2011).
S. Demirci, T. Dikici, M. Yurddaskal, S. Gultekin, M. Toparli, and E. Celik, Synthesis and characterization of Ag doped TiO2 heterojunction films and their photocatalytic performances. Appl. Surf. Sci. 390, 591 (2016).
W.-C. Peng, Y.-C. Chen, J.-L. He, S.-L. Ou, R.-H. Horng, and D.-S. Wuu, Tunability of p- and n-channel TiOx thin film transistors. Sci. Rep. 8, 9255 (2018).
V. Bhullar, D. Devi, F. Singh, S. Chopra, A.K. Debnath, D.K. Aswal, and A. Mahajan, Ag implanted TiO2 nanoparticle/nanofibers composites for dye sensitized solar cells applications. Sol. Energy 241, 109 (2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to IUAC, New Delhi, India, for providing the beam time facility and financial assistance under project No. UFR-69304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, I., Devi, D., Singh, F. et al. Modification of the Properties of Titanium Carbide MXene by Ag Doping via Ion Implantation for Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cell Applications. J. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11063-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11063-3