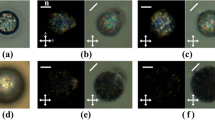
Abstract
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of a co-doped zinc oxide (ZnO) semiconductor nanostructure (Al and Cu) on the dielectric and electro-optical properties of nematic liquid crystal structures. Firstly, Al:ZnO, Cu:ZnO, and (Al-Cu):ZnO (co-doped ZnO) semiconductor nanomaterials were synthesized by a microwave-assisted gel ignition method. Then, new composite structures were formed by doping the synthesized nanomaterial to the nematic liquid crystal. Significant physical parameters including the real and imaginary components of complex dielectric permittivity (\(\varepsilon^{\prime }\) and \(\varepsilon^{\prime \prime }\)), relaxation frequency (\(f_{R}\)), relaxation time (\(\tau\)), dielectric strength (\(\delta \varepsilon^{^{\prime}}\)), and threshold voltage (\(V_{{{\text{th}}}}\)) values were determined using the experimental results. The results showed that Al:ZnO and Cu:ZnO doping into liquid crystal (LC) enhanced the properties of E7 nematic LC. Furthermore, it was observed that the co-doped ZnO contribution to the LC significantly improved the dielectric properties and was found to yield the best results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.K. Tripathi, A.K. Misra, S. Manohar, S.K. Gupta, and R. Manohar, Improved dielectric and electro-optical parameters of ZnO nano-particle (8% Cu2+) doped nematic liquid crystal. J. Mol. Struct. 1035, 371 (2013).
H. Eskalen, S. Uruş, and Ş Özgan, Microwave-assisted synthesis of mushrooms like MWCNT/SiO2@ ZnO nanocomposite: influence on nematic liquid crystal E7 and highly effective photocatalytic activity in degradation of methyl blue. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 763 (2021).
G. Pathak, S. Pandey, R. Katiyar, A. Srivastava, R. Dabrowski, K. Garbat, and R. Manohar, Analysis of photoluminescence, UV absorbance, optical band gap and threshold voltage of TiO2 nanoparticles dispersed in high birefringence nematic liquid crystal towards its application in display and photovoltaic devices. J. Lumin. 192, 33 (2017).
R. Dubey, A. Mishra, K.N. Singh, P.R. Alapati, and R. Dhar, Electric behaviour of a Schiff’s base liquid crystal compound doped with a low concentration of BaTiO3 nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 225, 496 (2017).
C.-J. Hsu, L.-J. Lin, M.-K. Huang, and C.-Y. Huang, Electro-optical effect of gold nanoparticle dispersed in nematic liquid crystals. Crystals 7, 287 (2017).
G. Akgül and F.A. Akgül, Kobalt Katkılı çinko oksit nanoparçacıkların yapısal özelliklerinin incelenmesi. Selçuk Üniv. Mühendis. Bilim Ve Teknol. Derg. 7, 105 (2019).
D. Jayoti, P. Malik, and S.K. Prasad, Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the morphology, dielectric, electro-optic and photo luminescence properties of a confined ferroelectric liquid crystal material. J. Mol. Liq. 250, 381 (2018).
P.K. Labhane, V.R. Huse, L.B. Patle, A.L. Chaudhari, and G.H. Sonawane, Synthesis of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles: crystallographic, optical, FTIR, morphological and photocatalytic study. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 3, 39 (2015).
B.-Y. Oh, M.-C. Jeong, T.-H. Moon, W. Lee, J.-M. Myoung, J.-Y. Hwang, and D.-S. Seo, Transparent conductive Al-doped ZnO films for liquid crystal displays. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 124505 (2006).
D. Dimitrov, C.-L. Tsai, S. Petrov, V. Marinova, D. Petrova, B. Napoleonov, B. Blagoev, V. Strijkova, K.Y. Hsu, and S.H. Lin, Atomic layer-deposited Al-doped ZnO thin films for display applications. Coatings 10, 539 (2020).
A.K. Misra, P.K. Tripathi, K.K. Pandey, B.P. Singh, and R. Manohar, Dielectric properties and activation energies of Cu: ZnO dispersed nematic mesogen N-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-4-butylaniline liquid crystal. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 41, 1283 (2020).
R. Manohar, S.P. Yadav, A.K. Srivastava, A.K. Misra, K.K. Pandey, P.K. Sharma, and A.C. Pandey, Zinc oxide (1% Cu) nanoparticle in nematic liquid crystal: dielectric and electro-optical study. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 101501 (2009).
Y.C. Su, C.C. Chiou, V. Marinova, S.-H. Lin, N. Bozhinov, B. Blagoev, T. Babeva, K.-Y. Hsu, and D.Z. Dimitrov, Atomic layer deposition prepared Al-doped ZnO for liquid crystal displays applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 50, 1 (2018).
T. Minami, T. Miyata, and Y. Ohtani, Optimization of aluminum-doped ZnO thin-film deposition by magnetron sputtering for liquid crystal display applications. Phys. Status Solidi (A) Appl. Mater. Sci. 204, 3145 (2007).
E. Bhawani, G.S. Harish, and P.S. Reddy, Effect of Cu doping on electrical, photoluminescene and band gap engineering of Mg doped ZnO nanoparticles. Am. J. Eng. Res. 6, 30 (2017).
S.D. Kirby and R.B. Van Dover, Improved conductivity of ZnO through codoping with In and Al. Thin Solid Films 517, 1958 (2009).
A. Sharma, P. Malik, R. Dhar, and P. Kumar, Improvement in electro-optical and dielectric characteristics of ZnO nanoparticles dispersed in a nematic liquid crystal mixture. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42, 1 (2019).
H. Eskalen, Ş Özğan, Ü. Alver, and S. Kerli, Electro-optical properties of liquid crystals composite with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Acta Phys. Pol. A 127, 756–760 (2015).
A. Malik, A. Choudhary, P. Silotia, and A.M. Biradar, Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the SmC*-SmA* phase transition temperature in electroclinic liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 064111 (2011).
D.P. Singh, S.K. Gupta, K.K. Pandey, S.P. Yadav, M.C. Varia, and R. Manohar, Ferroelectric liquid crystal matrix dispersed with Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 363, 178 (2013).
Ü.H. Kaynar, M. Ayvacıklı, S.C. Kaynar, and Ü. Hiçsönmez, Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions using nanoporous ZnO prepared with microwave-assisted combustion synthesis. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 299, 1469 (2014).
Ü.H. Kaynar, M. Ayvacıklı, Ü. Hiçsönmez, and S.Ç. Kaynar, Removal of thorium(IV) ions from aqueous solution by a novel nanoporous ZnO: isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Radioact. 150, 145 (2015).
Ü.H. Kaynar, S. Çınar, S. Çam Kaynar, M. Ayvacıklı, and T. Aydemir, Modelling and optimization of uranium(VI) ions adsorption onto nano-ZnO/Chitosan bio-composite beads with response surface methodology (RSM). J. Polym. Environ. 26, 2300 (2018).
U.H. Kaynar, S.Ç. Kaynar, E.E. Karali, M. Ayvacıkli, and N. Can, Adsorption of thorium(IV) ions by metal ion doped ZnO nanomaterial prepared with combustion synthesis: empirical modelling and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 178, 109955 (2021).
S.K. Sharma, G.S. Ghodake, D.Y. Kim, D.Y. Kim, and O.P. Thakur, Synthesis and characterization of hybrid Ag-ZnO nanocomposite for the application of sensor selectivity. Curr. Appl. Phys. 18, 377 (2018).
V. Luthra, A. Singh, D.C. Pugh, and I.P. Parkin, Ethanol sensing characteristics of Zn0.99M0.01O (M = Al/Ni) nanopowders. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 213, 203 (2016).
F. Mouzaia, D. Djouadi, A. Chellouche, L. Hammiche, and T. Touam, Particularities of pure amd Al-doped ZnO nanostructures aerogels elaborated in supercritical isopropanol. Arab J. Basic Appl. Sci. 27, 423 (2020).
S.B. Khan, A. Asiri, and K. Akhtar (eds.), Gas Sensors, 1st edn. (BoD–Books on Demand, London, 2020).
Y. Karakuş, M. Okutan, A. Kösemen, S.E. San, Z. Alpaslan, and A. Demir, Electrical properties of Zn-phthalocyanine and poly(3-hexylthiophene) doped nematic liquid crystal. J. Nanomater. 2011, 1 (2011).
G. Kocakülah, M. Yıldırım, and O. Köysal, Effect of intermolecular charge transfer between Ni(II)Pc and CdSeS/ZnS QD on dielectric relaxation mechanism of nematic liquid crystals in the presence of UV Illumination. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 2583 (2020).
M.S. Peterson, G. Georgiev, T.J. Atherton, and P. Cebe, Dielectric analysis of the interaction of nematic liquid crystals with carbon nanotubes. Liq. Cryst. 45, 450 (2018).
S. Doke, P. Ganguly, and S. Mahamuni, Improvement in molecular alignment of ferroelectric liquid crystal by Co-ZnO/ZnO core/shell quantum dots. Liq. Cryst. 47, 309 (2020).
S.K. Prasad, M.V. Kumar, T. Shilpa, and C.V. Yelamaggad, Enhancement of electrical conductivity, dielectric anisotropy and director relaxation frequency in composites of gold nanoparticle and a weakly polar nematic liquid crystal. RSC Adv. 4, 4453 (2014).
Ö.T. Özmen, K. Goksen, A. Demir, M. Durmuş, and O. Köysal, Investigation of photoinduced change of dielectric and electrical properties of indium(III) phthalocyanine and fullerene doped nematic liquid crystal. Synth. Met. 162, 2188 (2012).
G. Kocakülah and O. Köysal, Electro-optical and dielectric response of quantum dot-doped cholesteric liquid crystal composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 5489 (2022).
H.H. Elkhalgi, S. Khandka, U.B. Singh, K.L. Pandey, R. Dabrowski, and R. Dhar, Dielectric and electro-optical properties of a nematic liquid crystalline material with gold nanoparticles. Liq. Cryst. 45, 1795 (2018).
A. Sharma, P. Malik, and P. Kumar, Electro-optical and dielectric responses of ZnO nanoparticles doped nematic liquid crystal in in-plane switching (IPS) mode. Integr. Ferroelectr. 202, 52 (2019).
U.B. Singh, R. Dhar, R. Dabrowski, and M.B. Pandey, Enhanced electro-optical properties of a nematic liquid crystals in presence of BaTiO3 nanoparticles. Liq. Cryst. 41, 953 (2014).
G. Kocakülah, M. Yıldırım, O. Köysal, and I. Ercan, Influence of UV light ıntensity on dielectric behaviours of pure and dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystals. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 22385 (2020).
A. Katariya Jain and R.R. Deshmukh, Electro-optical and dielectric study of multi-walled carbon nanotube doped polymer dispersed liquid crystal films. Liq. Cryst. 46, 1191 (2019).
G. Kocakülah and O. Köysal, Enhancement of electro-optical and dielectric properties of CdSeS/ZnS semiconductor quantum-dot-doped nematic liquid crystals in the presence of UV-illumination effect. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 125, 1 (2019).
P. Nayek and G. Li, Superior electro-optic response in multiferroic bismuth ferrite nanoparticle doped nematic liquid crystal device. Sci. Rep. 5, 1 (2015).
B.P. Singh, S. Sikarwar, K.K. Pandey, R. Manohar, M. Depriester, and D.P. Singh, Carbon nanotubes blended nematic liquid crystal for display and electro-optical applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2, 466 (2021).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) (Project No:121M185).
Funding
This work was supported financially by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) (Project No:121M185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ÜHK: Synthesis of the NPs, analysis of SEM and XRD data, writing. GO: Doping NPs into the LC, collection and analysis of the dielectric data of the samples, and writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Önsal, G., Kaynar, Ü.H. Synthesis of Doped ZnO Nanoparticles and their Effect on the Dielectric and Electro-Optical Characterization of Nematic Liquid Crystals. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2569–2579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10219-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10219-x