Abstract
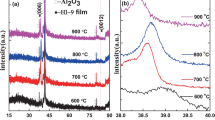
Amorphous Fe-Ti-Sb (FTS) thin film was prepared on a 0.3-µm SiO2/Si wafer by a DC magnetron sputtering method to investigate the spintronic thermoelectric (STE) properties based on the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE) and spin Seebeck effect (SSE). A platinum (Pt) ultra-thin layer was coated on top FTS (Pt/FTS) thin film surface to be used for the spin Hall detector. The crystal structure, morphology, composition and magnetic characteristics of as-deposited FTS and Pt/FTS thin films were carried out by x-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), respectively. As a result, the crystal structure and morphology displayed a metallic-glass type within the amorphous phase and a smooth surface. The magnetic characterization showed that an ANE and SSE of FTS thin film to yield a spin Seebeck coefficient (Ss) of around 0.35 µV K− 1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Dehkordi, M. Zebarjadi, J. He, and T.M. Tritt, Thermoelectric power factor: enhancement mechanisms and strategies for higher performance thermoelectric materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 97, 1–22 (2015).
J.R. Sootsman, D.Y. Chung, and M.G. Kanatzidis, New and old concepts in thermoelectric materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 8616–8639 (2009).
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, M.Y. Tang, R. Yang, H. Lee, D. Wang, Z. Ren, J.-P. Fleurial, and P. Gogna, New directions for low-dimensional thermoelectric materials. Adv. Mater. 19, 1043–1053 (2007).
X. Hu, P. Jood, M. Ohta, M. Kunii, K. Nagase, H. Nishiate, M.G. Kanatzidis, and A. Yamamoto, Power generation from nanostructured PbTe-based thermoelectrics: comprehensive development from materials to modules. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 517–529 (2016).
Q. Zhang, J. Liao, Y. Tang, M. Gu, C. Ming, P. Qiu, S. Bai, X. Shi, C. Uher, and L. Chen, Realizing a thermoelectric conversion efficiency of 12% in bismuth telluride/skutterudite segmented modules through full-parameter optimization and energy-loss minimized integration. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 956–963 (2017).
X.L. Shi, J. Zou, and Z.G. Chen, Advanced thermoelectric design: from materials and structures to devices. Chem. Rev. 120, 7399–7515 (2020).
N. Prainetr, A. Vora-ud, M. Horprathum, P. Muthitamongkol, S. Thaowonkaew, T. Santhaveesuk, T.B. Phan, and T. Seetawan, Transfer of p-type to n-type thermoelectric properties of Ag-Sb-Te thin film through temperature annealing and its electrical power generation. J. Elect. Mater. 49, 572–576 (2020).
S. Thaowonkaew, M. Kumar, and A. Vora-ud, Thermoelectric properties of Ag-doped Sb2Te3 thin films on SiO2 and polyimide substrates with rapid thermal annealing. J. Elect. Mater. 50, 2669–2673 (2021).
Y. Zou, Z.G. Chen, Y. Huang, L. Yang, J. Drennan, and J. Zou, Anisotropic electrical properties from vapor–solid–solid grown Bi2Se3 nanoribbons and nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 20620–20626 (2014).
G.E.W. Bauer, E. Saitoh, and B.J. van Wees, Spin caloritronics. Nat. Mater. 11, 391–399 (2012).
S.R. Boona, R.C. Myers, and J.P. Heremans, Spin caloritronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 885–910 (2014).
C.H. Back, G.E.W. Bauer, and B.L. Zink, Special issue on spin caloritronics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 52, 230301 (2019).
S.J. Mason, A. Hojem, D.J. Wesenberg, A.D. Avery, and B.L. Zink, Determining absolute Seebeck coefficients from relative thermopower measurements of thin films and nanostructures. J. Appl. Phys. 127, 085101 (2020).
K. Uchida, S. Takahashi, K. Harii, J. Ieda, W. Koshibae, K. Ando, S. Maekawa, and E. Saitoh, Observation of the spin Seebeck effect. Nature 455, 778 (2008).
K. Uchida, H. Adachi, T. Kikkawa, A. Kirihara, M. Ishida, S. Yorozu, S. Maekawa, and E. Saitoh, Thermoelectric generation based on spin Seebeck effects. Proc. IEEE 104, 1946–1973 (2016).
P. Wongjom, and S. Pinitsoontorn, Investigation of the spin Seebeck effect and anomalous Nernst effect in a bulk carbon material. Results Phys. 8, 1245–1249 (2018).
T. Kikkawa, K. Uchida, S. Daimon, Y. Shiomi, H. Adachi, Z. Qiu, D. Hou, X.-F. Jin, S. Maekawa, and E. Saitoh, Separation of longitudinal spin Seebeck effect from anomalous Nernst effect: determination of origin of transverse thermoelectric voltage in metal/insulator junctions. Phys. Rev. B 88, 214403 (2013).
K. Tolborg and B.B. Iversen, Chemical bonding origin of the thermoelectric power factor in half-Heusler semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 33, 5308–5316 (2021).
S. Jiang and K. Yang, Review of high-throughput computational design of Heusler alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 867, 158854 (2021).
J. Kübler, A. William, and C. Sommers, Formation and coupling of magnetic moments in Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B 28, 1745 (1983).
T. Graf and C. Felser, in Spintronics: From Materials to Devices, ed by C. Felser and G.H. Fecher (Springer, Dordrecht, 2013)
C. Felser, G.H. Fecher, and B. Balke, Spintronics: a challenge for materials science and solid-state chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 668–699 (2007).
B. Balke, S. Wurmehl, G.H. Fecher, C. Felser, and J. Kübler, Rational design of new materials for spintronics: Co2FeZ(Z=Al, Ga, Si, Ge). Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9, 014102 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/9/1/014102.
D. Serrate, J.M. De Teresa, and M.R. Ibarra, Double perovskites with ferromagnetism above room temperature. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 023201 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/2/023201.
H. Kandpal, V. Ksenofontov, M. Wojcik, R. Seshadri, and C. Felser, Electronic structure, magnetism and disorder in the Heusler compound Co2TiSn. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 1587 (2007).
R. Ohshima, A. Sakai, Y. Ando, T. Shinjo, K. Kawahara, H. Ago, and M. Shiraishi, Observation of spin-charge conversion in CVD-grown single-layer graphene. Appl. Phys. Let. 105, 162410 (2014).
M. Kim, S.J. Park, and H. Jin, Enhancing the spin Seebeck effect by controlling interface condition in Pt/polycrystalline nickel ferrite slabs. J. Appl. Phys. 127, 085105 (2020).
A. Miura, T. Kikkawa, R. Iguchi, K.I. Uchida, E. Saitoh, and J. Shiomi, Probing length-scale separation of thermal and spin currents by nanostructuring YIG. Phys. Rev. Mater. 1, 014601 (2017).
K.I. Uchida, T. Nonaka, T. Ota, and E. Saitoh, Longitudinal spin-Seebeck effect in sintered polycrystalline (Mn, Zn)F2O4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 262504 (2010).
J.D. Arboleda, O. Arnache, M.H. Aguirre, R. Ramos, A. Anadon, and M.R. Ibarra, Evidence of the spin Seebeck effect in Ni-Zn ferrites polycrystalline slabs. Solid State Commun. 270, 140–146 (2018).
J.D. Arboleda, O. Arnache Olmos, M.H. Aguirre, R. Ramos, A. Anadon, and M.R. Ibarra, Spin Seebeck effect in a weak ferromagnet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 232401 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) as part of SICORP (Grant Number: JPMJSC21E3), the Council of Thailand (NRCT) through the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development Research and Innovation (PMU-B) (B16F650001) and the Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation through a Research Grant for New Scholars (Grant No. RGNS 65-174).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author, on behalf of all authors, declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vora-ud, A., Wongjom, P., Thaowonkaew, S. et al. Spintronic Thermoelectric Properties of Amorphous Fe-Ti-Sb Thin Films. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 989–993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10107-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10107-w