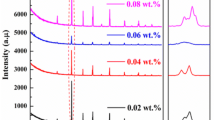
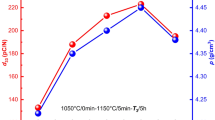
Abstract
Fabrication of 0.74(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-0.26SrTiO3 (abbreviated as BNST26) ceramics via both conventional furnace sintering (CFS) and microwave sintering (MWS) was investigated in this work. MWS at 1100°C for 5 min resulted in ceramic with density comparable to that of ceramic fabricated via CFS at 1175°C for 2 h. Average grain sizes of 3.2 μm and 2.4 μm were calculated for the ceramics prepared by CFS and MWS, respectively, which was attributed to the lower temperature and shorter sintering time for MWS compared with CFS. In order to investigate the effect of sintering method on the electrical properties of the prepared ceramics, the polarization hysteresis, bipolar and unipolar strain curves, and temperature dependence of permittivity were explored. The results revealed that the remanent polarization (Pr) and coercive field (Ec) of the ceramic prepared by MWS at 1100°C for 5 min were comparable to those of the ceramic under CFS at 1175°C for 2 h. However, the maximum polarization (Pmax) of the CFS ceramic was higher than that of the MWS ceramic. In the case of electric field-induced strain, there was no considerable difference between the MWS and CFS ceramics, and normalized strain d33* = 501 pm/V was obtained for the MWS ceramic at 1100°C, indicating the effectiveness of MWS for fabrication of BNT-based piezoceramics at lower temperature and shorter time versus CFS.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, M.R. Bafandeh, upon reasonable request.
References
T. Yamamoto, Ferroelectric Properties of the PbZrO3-PbTiO3 System. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 5104 (1996).
B. Malic, M. Otonicar, K. Radan, J. Koruza, Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. Encyclopedia of Materials Technical Ceramics and Glasses (2021) 358
T. Takenaka, H. Nagata, and Y. Hiruma, Current Developments and Prospective of Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 3787 (2008).
J. Rodel, W. Jo, K.T.P. Seifert, E. Anton, and T. Granzow, Perspective on the Development of Lead-Free Piezoceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1153 (2009).
E. Aksel and J.L. Jones, Advances in Lead-Free Piezoelectric Materials for Sensors and Actuators. Sensors 10, 1935 (2010).
P.K. Panda and B. Sahoo, PZT to Lead Free Piezo Ceramics: A Review. Ferroelectrics 474, 128 (2015).
H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Advanced Piezoelectric Materials, Chap. 4, Bi-Based Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics, Tokyo University of Science, Chiba, Japan, 2017
H. Nagata, T. Shinya, Y. Hiruma, T. Takenaka, I. Sakaguchi, and H. Haneda, Piezoelectric Properties of Bismuth Sodium Titanate Ceramics. Ceram. Trans. 167, 213 (2005).
K. Sakata and Y. Masuda, Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric Properties of (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-SrTiO3 Solid Solution Ceramics. Ferroelectrics 7, 347 (1974).
T. Takenaka and K. Sakata, Dielectric, Piezoelectric and Pyroelectric Properties of (BiNa)1/2TiO3-Based Ceramics. Ferroelectrics 95, 153 (1989).
T. Takenaka, K. Maruyama, and K. Sakata, (Bi, Na)TiO3-BaTiO3 System for Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 2236 (1991).
H. Yilmaz, G.G. Messing, and S.T. Mckinstry, (Reactive) Templated Grain Growth of Textured Sodium Bismuth Titanate (Na1/2Bi1/2TiO3-BaTiO3) Ceramics-II Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties. J. Electroceram. 11, 217 (2003).
A. Herabut and A. Safari, Processing and Electrochemical Properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)(1–1.5x)LaxTiO3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2954 (1997).
J.Y. Yi, J.K. Lee, and K.S. Hong, Dependence of the Microstructure and the Electrical Properties of Lanthanum-Substituted (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3 on Cation Vacancies. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 3004 (2003).
Y. Watanabe, Y. Hiruma, H. Nagata, and T. Takenaka, Phase Transition Temperatures and Electrical Properties of Divalent Ions (Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+) Substituted (Bi1/2Na1/2) TiO3 Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 34, 761 (2008).
H. Nagata, Electrical Properties and Tracer Diffusion of Oxygen in some Bi-Based Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 116, 271 (2008).
A. Watcharapasorn, S. Jiansirisomboon, and T. Tunkasiri, Sintering of Fe-Doped Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 at <1000°C. Matter. Lett. 61, 2986 (2007).
Y. Zhang, R. Chu, Z. Xu, J. Hao, G. Li, and Q. Yin, Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of low Temperature Sintering Lead Free (Bi0.5Na0.7+xK0.2Li0.1)0.5TiO3 Piezoelectric Ceramics. Physica B Condens. Matter. 405, 1228 (2010).
X. Wu, T.H. Chung, H. Sun, and K.W. Kwok, Tunable Photoluminescence Properties of Pr3+/Er3+-Doped 0.93Bi05Na0.5TiO3–0.07BaTiO3 Low-Temperature Sintered Multifunctional Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 42, 9899 (2016).
T.H. Chung and K.W. Kwok, Low-Temperature-Sintered Pr-Doped 0.93(Bi05Na0.5)TiO3–0.07BaTiO3multifunctional Ceramics with Li2CO3 Sintering Aid. J. Alloys Compd. 737, 317 (2018).
Y.H. Hong, H.S. Han, G.H. Jeong, Y.S. Park, T.H. Dinh, C.W. Ahn, and J.S. Lee, High Electromechanical Strain Properties by the Existence of Nonergodicity in LiNbO3-Modified Bi1/2Na1/2TiO3-SrTiO3relaxor Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 44, 21138 (2018).
W. Jo, J.B. Ollagnier, J.L. Park, E.M. Anton, O.J. Kwon, C. Park, H.H. Seo, J.S. Lee, E. Erdem, R.A. Eichel, and J. Rodel, CuO as a Sintering Additive for (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3–BaTiO3–(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 Lead-Free Piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2107 (2011).
N.B. Do, H.D. Jang, I. Hong, H.S. Han, D.T. Le, W.P. Tai, and J.S. Lee, Low Temperature Sintering of Lead-Free Bi0.5(Na0.82K0.18)0.5TiO3 Piezoelectric Ceramics by co-Doping with CuO and Nb2O5. Ceram. Int. 38, S359 (2012).
C.H. Lee, H.S. Han, T.A. Duong, T.H. Dinh, C.W. Ahn, and J.S. Lee, Stabilization of the Relaxor Phase by Adding CuO in Lead-Free (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-SrTiO3-BiFeO3 Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43, 11071 (2017).
P. Fan, Y. Zhang, S.T. Zhang, B. Xie, Y. Zhu, M.A. Marwat, W. Ma, K. Liu, L. Shu, and H. Zhang, Low-Temperature Sintered (Na1/2Bi1/2)TiO3-Based Incipient Piezoceramics for co-Fired Multilayer Actuator Application. J. Materiom. 5, 480 (2019).
F. Zhang, X. Qiao, Q. Shi, X. Chao, Z. Yang, and D. Wu, High Energy Storage Density Realized in Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-Based Relaxor Ferroelectric Ceramics at Ultralow Sintering Temperature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 368 (2021).
M.R. Bafandeh, R. Gharahkhani, and J.S. Lee, Sintering Behavior, Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Sodium Potassium Niobate-Based Ceramics Prepared by Single Step and Two-Step Sintering. Ceram. Int. 41, 163 (2015).
Z.Y. Shen, W.Q. Luo, Y. Tang, S. Zhang, and Y. Li, Microstructure and Electrical Properties of Nb and Mn co-Doped CaBi4Ti4O15 High Temperature Piezoceramics Obtained by Two-Step Sintering. Ceram. Int. 42, 7868 (2016).
J.H. Kim, D.S. Kim, S.H. Han, H.W. Kang, H.G. Lee, J.S. Kim, and C.I. Cheon, Preparation of CuO-Doped (K, Na, Li)(Nb, Ta)O3 Ceramics with a Homogeneous Microstructure by Two-Step Sintering for Multilayered Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters. Matter. Lett. 241, 202 (2019).
Y. Zhang, M. Li, S. Yang, and J. Zhai, Low-Temperature Sintering of KNN-Based Lead Free Ceramics. Solid State Commun. 324, 114133 (2021).
Y. Zhang, J. Zhai, and S. Xue, Effect of Three Step Sintering on Piezoelectric Properties of KNN-Based Lead Free Ceramics. Chem. Phys. Lett. 758, 137906 (2020).
F. Benabdallah, C. Elissalde, U.C. Seu, D. Michau, A.P. Quintin, M. Gayot, P. Garreta, H. Khemakhem, and M. Maglione, Structure-microstructure-property relationships in lead-free BCTZ piezoceramics processed by conventional sintering and spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 4153 (2015).
D. Kuscer, A. Kocjan, M. Majcen, A. Meden, K. Radan, J. Kovac, and B. Malic, Evolution of Phase Composition and Microstructure of Sodium Potassium Niobate-Based ceramic During Pressure-Less Spark Plasma Sintering and Post-Annealing. Ceram. Int. 45, 10429 (2019).
V. Bijalwan, V. Prajzler, J. Erhart, H. Tan, P. Roupcova, D. Sobola, P. Tofel, and K. Maca, Rapid Pressure-Less and Spark Plasma Sintering of (Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1T0.9)O3 Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 2514 (2021).
F. Delorme, C. Chen, F. Schoenstein, N. Jaber, F. Jean, M. Bah, Q. Simon, T. Chartier, P. Laffez, I.M. Laffez, and F. Giovannelli, Low Intrinsic Thermal Conductivity of Spark Plasma Sintered Dense KNbO3 and NaNbO3 Perovskite Ceramics. Thermochim Acta 695, 178807 (2021).
S. Sharma, R.K. Patel, C. Prakash, and P. Kumar, Structural, Dielectric and Ferroelectric Study of microwave Sintered Lanthanum Substituted BaTiO3 Ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 191 (2011).
R.K. Sonia, P. Patel, C. Prakash, C. Prakash, and D.K. Agrawal, Low Temperature Synthesis and Dielectric, Ferroelectric and Piezoelectric Study of Microwave Sintered BaTiO3 Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 38, 1585 (2012).
Z. Sun, Y. Pu, Z. Dong, Y. Hu, P. Wang, X. Liu, and Z. Wang, Impact of Fast Microwave Sintering on the Grain Growth, Dielectric Relaxation and Piezoelectric Properties on Ba0.18Ca0.02Ti0.09Zr0.10O3 Lead-Free Ceramics Prepared by Different Methods. Ceram. Int. 41, 163 (2015).
M.R. Bafandeh, R. Gharahkhani, and J.S. Lee, Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of sodium Potassium Niobate-Based Ceramics Sintered in Microwave Furnace. Mater. Chem. Phys. 156, 254 (2015).
K. Orlik, Y. Lorgouilloux, P. Marchet, A. Thuault, F. Jean, M. Rguiti, and C. Courtois, Influence of Microwave Sintering on Electrical Properties of BCTZ Lead Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40, 1212 (2020).
S.W. Zhang, H. Zhang, B.P. Zhang, and G. Zhao, Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of (Ba0.95Ca0.05)(Ti0.88Zr0.12)O3 Ceramics Sintered in a Protective Atmosphere. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 3235 (2009).
X. Vendrell, J.E. Garcia, F.R. Marcos, D.A. Ochoa, L. Mestres, and J.F. Fernandez, Exploring Different Sintering Atmospheres to Reduce Nonlinear Response of Modified KNN Piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 825 (2013).
C.S. Chen, P.Y. Chen, C.S. Tu, T.L. Chang, and C.K. Chai, The Effects of Sintering Atmosphere on Microstructures and Electrical Properties of Lead-Free (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-Based Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 40, 9591 (2014).
L. Gao, S. Dursun, A.E. Gurdal, E. Hennig, S. Zhang, and C.A. Randall, Atmospheric Controlled Processing Enabling Highly Textured NKN with Enhanced Piezoelectric Performance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 963 (2019).
R. Cong, G. Qiu, C. Yue, M. Guo, F. Cheng, and M. Zhang, Oxygen-Enriched Sintering for Improved Piezoelectric Performance of (K0.5Na0.5)(Ta0.3Nb0.7)O3 Lead-Free Ceramics: The Impact of Defects. Ceram. Int. 44, 19764 (2018).
D.U. Seifert, L. Li, K.Y. Lee, M.J. Hoffmann, D.C. Sinclair, and M. Hinterstein, Processing and Properties of translucent Bismuth Sodium Titanate Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 1221 (2021).
T. Reimann, S. Frohlich, A. Bochmann, A. Kynast, M. Topfer, E. Hennig, and J. Topfer, Low pO2 Sintering and Reoxidation of Lead-Free KNNLT Piezoceramic Laminates. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 344 (2021).
K.I. Rybakov, E.A. Olevsky, and E.V. Krikun, Microwave Sintering: Fundamentals and Modeling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1003 (2013).
T.A. Duong, H.S. Han, Y.H. Hong, Y.S. Park, H.T.K. Nguyen, T.H. Dinh, and J.S. Lee, Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Bi1/2Na1/2TiO3-SrTiO3 Lead-Free Ceramics. J. Electroceram. 41, 73 (2018).
C.C. Wang, Z. Meini, and X. Wei, High temperature Dielectric Relaxation in Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 Single Crystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1521 (2013).
X. Li, X. Fan, Z. Xi, P. Liu, W. Long, P. Fang, F. Guo, and R. Nan, Dielectric Relaxor and Conductivity Mechanism in Fe-Substituted PMN-32PT Ferroelectric Crystal. Crystal 9, 241 (2019).
V.V. Westphal, W. Kleemann, and M.D. Glinchuk, Diffuse Phase Transitions and Random-Field-Induced Domain States of the Relaxor Ferroelectric PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 847 (1992).
K. Wang, A. Hussain, W. Jo, and J. Rodel, Temperature-Dependent Properties of (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3-(Bi1/2K1/2)TiO3-SrTiO3 Lead-Free Piezoceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 2241 (2012).
T. Wang, J. Ma, B. Wu, F. Wang, S. Wang, M. Chen, and W. Wu, Structure and Electrical Properties of Microwave Sintered BTS-BCT-xBF Lead-Free Piezoelectric. Mater 15, 1789 (2022).
M. Feizpour, H.B. Bafrooei, R. Hayati, and T. Ebadzadeh, Microwave-Assisted Synthesis and Sintering of Potassium Sodium Niobate Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. Ceram. Inter 40, 871 (2014).
M.R. Bafandeh, R. Gharahkhani, M.H. Abbasi, A. Saidi, J.S. Lee, and H.S. Han, Improvement of Piezoelectric and Ferroelectric Properties in (K, Na)NbO3-Based Ceramics via Microwave Sintering. J. Electro. Ceram. 33, 128 (2014).
O.P. Thakur, C. Prakash, and D.K. Agrawal, Microwave Synthesis and Sintering of Ba0.95Sr0.05TiO3. Mater. Lett. 56, 970 (2002).
H. Takahashi, Y. Numamoto, J. Tani, and S. Tsurekawa, Piezoelectric Properties of BaTiO3 Ceramics with High Performance Fabricated by Microwave Sintering. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 7405 (2006).
P. Kumar, S. Singh, J.K. Juneja, C. Prakash, and K.K. Raina, Improved Properties of BPT Ceramics Using Microwave Sintering. Mater. Lett. 142, 84 (2015).
P.S. Abraira, E. Morán, M.E.V. Castrejón, R.V. Ocampo, and L. Pardo, Ba0.9Ca0.1TiO3: Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis and Piezoelectric Properties. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 117, 72 (2017).
Acknowledgments
JS Lee acknowledges financial support from a National Research Foundation (NRF) of the Republic of Korea Grant (2016R1D1A3B01008169), and HS Han acknowledges financial support from a National Research Foundation (NRF) of the Republic of Korea Grant (2020R1C1C1007375).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhlishah, A.D., Lee, SH., Duong, T.A. et al. Characterization of 0.74(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-0.26SrTiO3 Lead-Free Piezoceramic Fabricated via Conventional and Microwave Sintering. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 7064–7072 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09940-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09940-w