Abstract
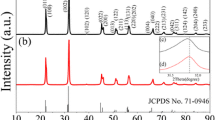
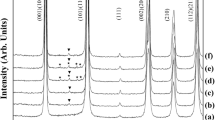
In this work, 0.94(K0.48Na0.52)0.935Li0.065NbO3–0.06BaZrO3 (abbreviated as KNLN–0.06BZ) lead-free ceramics were prepared by conventional sintering (CS) and three-step sintering (TSS). The effects of sintering process on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of ceramics were systematically studied. The result showed that, the ceramic prepared by TSS obtained higher density and better electrical properties compared to the ceramic prepared by CS. As we all know, the formation of defects will have a pinning effect on the domain switching. According to the results of impedance spectroscopy analysis, the ceramics prepared by TSS have fewer oxygen vacancies, which will make domain switching easier at an applied electric field, resulting in more excellent piezoelectric activity. The ceramics prepared by TSS with different sintering conditions showed different properties, but multiple phases may coexist in all ceramic samples according to the analysis of XRD, and the domain can adequately switch at an external electric field due to lower energy barrier at the phase boundary, resulting in high piezoelectric properties of ceramics. Hence, when the sintering condition was 1050 °C/0 min–1150 °C/5 min–1070 °C/20 h, the ceramic samples exhibited an optimal performance of ρ = 4.51 g/cm3, d33 ~ 258 pC/N, kp ~ 0.35, and TC ~ 328 ºC. This superior result manifests that the KNLN–0.06BZ ceramic prepared by TSS is a promising ceramic for industrial application.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Xiao, J. Adv. Dielectr. 01, 33 (2012)
E. Aksel, J.L. Jones, Sensors 10, 1935 (2010)
K. Shibata, F. Oka, A. Ohishi, T. Mishima, I. Kanno, Appl. Phys. Express 1, 011501 (2008)
A. Zhang, Z. Liu, B. Xie et al., Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 279, 119353 (2020)
M. Zheng, Y. Hou, L. Chao, M. Zhu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 9582 (2018)
P.K. Panda, B. Sahoo, Ferroelectrics 474, 128 (2015)
N. Ledermann, P. Muralt, J. Baborowski et al., Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 105, 162 (2003)
W. Shi, J. Du, C. Chen et al., J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 959 (2019)
C. Shi, J. Ma, J. Wu et al., J. Alloys Compd. 846, 156245 (2020)
P. Li, J. Zhai, B. Shen et al., Adv. Mater. 30, 1705171 (2018)
J. Chen, J. Cheng, J. Guo et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 103, 374 (2020)
Y. Wang, J. Wu, D. Xiao et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 2772 (2008)
Y. Wen, G. Fan, M. Hao et al., J. Electron. Mater. 49, 931 (2019)
W. Wu, Z. Wang, D. Xiao et al., Integr. Ferroelectr. 141, 82 (2013)
J. Chen, J. Daniels, J. Jian et al., Acta Mater. 197, 1359 (2020)
H. Tao, H. Wu, J. Wu et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 13987 (2019)
X. Lv, D. Xiao, J. Wu et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 671 (2020)
M. Chandrasekhar, P. Kumar, Ceram. Int. 41, 5574 (2015)
J. Xing, L. Jiang, C. Zhao et al., J. Materiomics 6, 513 (2020)
T. Zheng, Y. Zhang, J. Wu et al., Nano Energy 70, 104559 (2020)
S. Zhang, H.J. Lee, C. Ma, X. Tan, A. Fetiera, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3659 (2011)
Z. Yu, X. Chen, Y. Su et al., J. Mater. Sci. 54, 13457 (2019)
J. Li, K. Wang, B. Zhang, L. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 706 (2006)
M. Feizpour, H. Barzegar-Bafrooei, R. Hayati, T. Ebadzadeh, Ceram. Int. 40, 871 (2014)
M. Chi, W. Ma, J. Guo et al., J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 21435 (2019)
D. Liu, X. Zhang, W. Su et al., J. Alloys Compd. 779, 800 (2019)
Y. Zhang, J. Zhai, S. Xue, Chem. Phys. Lett. 758, 137906 (2020)
T. Chu, C. He, H. Tailor, X. Long, Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 4, 296 (2014)
J. Zhou, J. Li, K. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 5111 (2011)
X. Lv, J. Wu, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, X. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 1191 (2018)
Z. Cen, Y. Huan, W. Feng et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 23904 (2018)
S. Yang, C. Hong, C. Tsai, Y. Liou, S. Chu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 1643 (2012)
L. Liu, H. Fan, L. Fang, X. Chen, H. Dammak, M.P. Thi, Mater. Chem. Phys. 117, 138 (2009)
Z. Zeng, Q. Wu, M. Hao et al., J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 8279 (2018)
F. Zeng, G. Fan, M. Hao et al., J. Alloys Compd. 831, 154853 (2020)
M. Saiful Islam, J. Mater. Chem. 10, 1027 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by International Scientific and Technological Innovation Cooperation Key Projects for National Key R&D Program of China (No: 2016YFE0203900), National Key R&D Program of China (No: 2018YFC0116100), and Nature Science Foundation of HuBei Province of China (2018CFB771). The authors thank the Analytical and Testing Center of the Huazhong University of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wen, Y., Hao, M. et al. Enhanced properties of KNLN–BZ lead-free piezoelectric ceramics via three-step sintering. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 19778–19785 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06502-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06502-4