Abstract
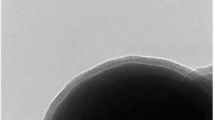
In the present study, spike-like spherical iron manganite (FeMnO3) nanoparticles were synthesized by chemical coprecipitation using chloride precursors subjected to calcination at 600°C for 3 h. The as-synthesized nanostructures were elaborately characterized for structural, morphological, elemental composition, optical, surface area, and availability of functional groups using x-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller theory (BET), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). XRD results showed a pure phase of FeMnO3 with a cubic structure. FESEM images show the spike-like spherical morphology of the synthesized materials indicating higher surface roughness of the particles. PL spectroscopy shows strong absorption in the visible region of the solar spectrum. The photocatalytic response of the spike-like iron manganite nanoparticles was excellent for the degradation of methylene blue and methylene orange dyes under visible light. Owing to higher crystallinity and fewer defects in FeMnO3, the heterostructures display nanoporous/mesoporous structures offering more active sites. A degradation efficiency of approximately 99% was observed within 180 min after light exposure. Iron manganite nanoparticles showed good stability and reusability up to three cycles. The facile preparation, environmentally favorable nature, and superb photocatalytic action of FeMnO3 validate it as a promising candidate for photocatalytic applications in the visible range of the light spectrum.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Sajid, N.A. Shad, A.M. Afzal, Y. Javed, S.B. Khan, N. Amin, A. Shah, I. Yousaf, and H. Zhai, Generation of strong oxidizing radicals from plate-like morphology of BiVO4 for the fast degradation of crystal violet dye under visible light. Appl. Phys. A 126, 314 (2020).
M.M. Sajid, N.A. Shad, Y. Javed, S.B. Khan, Z. Zhang, and N. Amin, Study of the interfacial charge transfer in bismuth vanadate/reduce graphene oxide (BiVO4/rGO) composite and evaluation of its photocatalytic activity. Res. Chem. Intermed 46, 1201 (2020).
M.M. Sajid, N.A. Shad, Y. Javed, S.B. Khan, Z. Zhang, N. Amin, and H. Zhai, Preparation and characterization of Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) for photocatalytic degradation of monoazo and diazo dyes. Surf. Interface 19, 100502 (2020).
F. Wang, and S. Hu, Electrochemical sensors based on metal and semiconductor nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 165, 1 (2009).
A. Afzal, Y. Javed, S. Hussain, A. Ali, M. Yaqoob, and S. Mumtaz, Enhancement in photovoltaic properties of bismuth ferrite/zinc oxide heterostructure solar cell device with graphene/indium tin oxide hybrid electrodes. Ceram. Int. 46, 9161 (2020).
J. Borcherding, J. Baltrusaitis, H. Chen, L. Stebounova, C.-M. Wu, G. Rubasinghege, I.A. Mudunkotuwa, J.C. Caraballo, J. Zabner, and V.H. Grassian, Iron oxide nanoparticles induce Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth, induce biofilm formation, and inhibit antimicrobial peptide function. Environ. Sci. Nano 1, 123 (2014).
K. Cao, H. Liu, X. Xu, Y. Wang, and L. Jiao, FeMnO3: a high-performance Li-ion battery anode material. Chem. Commun. 52, 11414 (2016).
C. Doroftei, P.D. Popa, E. Rezlescu, and N. Rezlescu, Structural and catalytic characterization of nanostructured iron manganite. Compos. B Eng. 67, 179 (2014).
M.H. Habibi, and V. Mosavi, Wet coprecipitation preparation of perovskite-type iron manganite nano powder pure phase using nitrate precursors: structural, opto-electronic, morphological and photocatalytic activity for degradation of Nile blue dye. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 10270 (2017).
M.H. Habibi, and V. Mosavi, Urea combustion synthesis of nano-structure bimetallic perovskite FeMnO3 and mixed monometallic iron manganese oxides: effects of preparation parameters on structural, opto-electronic and photocatalytic activity for photo-degradation of Basic Blue 12. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 8473 (2017).
S. Diodati, L. Nodari, M.M. Natile, A. Caneschi, C. de Julián Fernández, C. Hoffmann, S. Kaskel, A. Lieb, V. Di Noto, and S. Mascotto, Coprecipitation of oxalates: an easy and reproducible wet-chemistry synthesis route for transition-metal ferrites. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 5, 875 (2014).
G.-Y. Zhang, Y.-Q. Sun, D.-Z. Gao, and Y.-Y. Xu, Quasi-cube ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals: hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic activity with TiO2 (Degussa P25) as nanocomposite. Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 755 (2010).
K.G. Pavithra, and V. Jaikumar, Removal of colorants from wastewater: a review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 75, 1 (2019).
M. Ahmaruzzaman, Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals. Adv. Colloid Interface sci. 166, 36 (2011).
F.S. Farahani, B. Mecheri, M.R. Majidi, E. Placidi, and A. D’Epifanio, Carbon-supported Fe/Mn-based perovskite-type oxides boost oxygen reduction in bioelectrochemical systems. Carbon 145, 716 (2019).
K. Maaz, A. Mumtaz, S. Hasanain, and M. Bertino, Temperature dependent coercivity and magnetization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2199 (2010).
M.F. Casula, E. Conca, I. Bakaimi, A. Sathya, M.E. Materia, A. Casu, A. Falqui, E. Sogne, T. Pellegrino, and A.G. Kanaras, Manganese doped-iron oxide nanoparticle clusters and their potential as agents for magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 16848 (2016).
Y. Li, E. Boone, and M.A. El-Sayed, Size effects of PVP−Pd nanoparticles on the catalytic Suzuki reactions in aqueous solution. Langmuir 18, 4921 (2002).
Z.Z. Vasiljevic, M.P. Dojcinovic, J.B. Krstic, V. Ribic, N.B. Tadic, M. Ognjanovic, S. Auger, J. Vidic, and M.V. Nikolic, Synthesis and antibacterial activity of iron manganite (FeMnO3) particles against the environmental bacterium Bacillus subtilis. RSC Adv. 10, 13879 (2020).
M. Li, W. Xu, W. Wang, Y. Liu, B. Cui, and X. Guo, Facile synthesis of specific FeMnO3 hollow sphere/graphene composites and their superior electrochemical energy storage performances for supercapacitor. J. Power Sour. 248, 465 (2014).
B. Saravanakumar, S. Ramachandran, G. Ravi, V. Ganesh, R.K. Guduru, and R. Yuvakkumar, Electrochemical characterization of FeMnO3 microspheres as potential material for energy storage applications. Mater. Res. Exp. 5, 015504 (2018).
L. Leontie, C. Doroftei, and A. Carlescu, Nanocrystalline iron manganite prepared by sol–gel self-combustion method for sensor applications. Appl. Phys. A 124, 750 (2018).
M.V. Nikolic, M.D. Lukovic, and N.J. Labus, Influence of humidity on complex impedance and dielectric properties of iron manganite (FeMnO3). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 12399 (2019).
S. Rayaprol, and S. Kaushik, Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of FeMnO3. Ceram. Int. 41, 9567 (2015).
I. Malaescu, A. Lungu, C. Marin, P. Vlazan, P. Sfirloaga, and G. Turi, Experimental investigations of the structural transformations induced by the heat treatment in manganese ferrite synthesized by ultrasonic assisted co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 42, 16744 (2016).
Y. Niu, M. Yu, A. Meka, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, Y. Yang, and C. Yu, Understanding the contribution of surface roughness and hydrophobic modification of silica nanoparticles to enhanced therapeutic protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 4, 212 (2016).
R. Suresh, R. Udayabhaskar, C. Sandoval, E. Ramírez, R.V. Mangalaraja, H.D. Mansilla, D. Contreras, and J. Yáñez, Effect of reduced graphene oxide on the structural, optical, adsorption and photocatalytic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 42, 8485 (2018).
C. Barglik-Chory, C. Remenyi, C. Dem, M. Schmitt, W. Kiefer, C. Gould, C. Rüster, G. Schmidt, D.M. Hofmann, and D. Pfisterer, Synthesis and characterization of manganese-doped CdS nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5, 1639 (2003).
L.S. Lobo, and A. Rubankumar, Investigation on structural and electrical properties of FeMnO3 synthesized by sol-gel method. Ionics 25, 1341 (2019).
C.H. Nguyen, C.-C. Fu, and R.-S. Juang, Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: efficiency and degradation pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 202, 413 (2018).
K. Xiong, K. Wang, L. Chen, X. Wang, Q. Fan, J. Courtois, Y. Liu, X. Tuo, and M. Yan, Heterostructured ZnFe2O4/Fe2TiO5/TiO2 composite nanotube arrays with an improved photocatalysis degradation efficiency under simulated sunlight irradiation. Nano-Micro Lett. 10, 17 (2018).
D. Zhu, and Q. Zhou, Action and mechanism of semiconductor photocatalysis on degradation of organic pollutants in water treatment: a review. Environ. Nanotech. Monit. Manag. 12, 100255 (2019).
S. Alkaykh, A. Mbarek, and E.E. Ali-Shattle, Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye in aqueous solution by MnTiO3 nanoparticles under sunlight irradiation. Heliyon 6, e03663 (2020).
S. Moosavi, R.Y.M. Li, C.W. Lai, Y. Yusof, S. Gan, O. Akbarzadeh, Z.Z. Chowhury, X.-G. Yue, and M.R. Johan, Methylene blue dye photocatalytic degradation over synthesised Fe3O4/AC/TiO2 nano-catalyst: degradation and reusability studies. Nanomaterials 10, 2360 (2020).
A.A. Ullah, A.F. Kibria, M. Akter, M. Khan, A. Tareq, and S.H. Firoz, Oxidative degradation of methylene blue using Mn3O4 nanoparticles. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 1, 249 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shad, N.A., Jameel, A., Sajid, M.M. et al. Fabrication of Spike-Like Spherical Iron Manganite Nanoparticles for the Augmented Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 900–909 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09371-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09371-z