Abstract
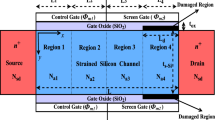
This paper presents explicit analytical modeling of a gate all around (GAA) strained silicon metal-oxide-semicondutor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) with elliptical cross section by incorporating the popular gate work function engineering (WFE) concept of lateral mole fraction variation from source to drain end. Surface potential and threshold voltage formulation of the proposed structure based on a quasi-three-dimensional scaling equation have been introduced. The derived model is further used to investigate the short channel characteristics of the device in terms of hot carrier effect (HCE), drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL), threshold voltage roll off (TVRO), and subthreshold slope. The impact of device parameter variation including gate oxide thickness, effective radius, channel doping concentration, germanium (Ge) mole fraction variation in the strained silicon channel along with applied gate to source and drain biases are evaluated on device performance to justify its efficiency in comparison to its single gate material (SM) MOSFET equivalent. Our analytical analysis is further validated by ATLAS-3D device simulated data to verify the precision of the derived model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The international technology roadmap for semiconductor, emerging research devices. (Published by Semiconductor Industry Association, 2009). https://www.semiconductors.org/wpcontent/uploads/2018/09/ERD.pdf. Accessed 5 Sep 2009.
K.K. Young, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36, 399 (1989).
D. Rechem and S. Latreche, African Phys. Rev. 2, 80 (2008).
A.S. Verhulst, B. Sorée, D. Leonelli, W.G. Vandenberghe, and G. Groeseneken, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 024518 (2010).
M. Kumar, S. Haldar, M. Gupta, and R.S. Gupta, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 31, 1 (2016).
T.K. Chiang and M.L. Chen, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 3283 (2007).
P. Banerjee, T. Kumari, and S.K. Sarkar, Appl. Phys. A (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1567-8.
E. Goel, B. Singh, S. Kumar, K. Singh, and S. Jit, Indian J. Phys. 91, 383 (2017).
C.P. Auth and J.D. Plummer, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 45, 2381 (1998).
R.M.Y. Ng, T. Wang, F. Liu, X. Zuo, J. He, and M. Chan, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 30, 520 (2009).
S. Bangsaruntip, G.M. Cohen, A. Majumdar, and J.W. Sleight, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 903 (2010).
L. Zhang, L. Li, J. He, and M. Chan, IEEE Electron Devices Letters. 32, 1188 (2011).
P. Banerjee and S.K. Sarkar, J Electron Mater 48, 3270 (2019).
B. Manna, S. Sarkhel, N. Islam, S. Sarkar, and S.K. Sarkar, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 3280 (2012).
P. Saha, S. Sarkhel, and S.K. Sarkar, J. Comput. Electron. 16, 648 (2017).
S. Sarkhel and S.K. Sarkar, Superlattices Microstruct. 82, 293 (2015).
M. Kumar, S. Dubey, P.K. Tiwari, and S. Jit, J. Comput. Electron. 12, 20 (2013).
S. Sarkhel, B. Manna, and S.K. Sarkar, J. Low Power Electron. 10, 383 (2014).
T.K. Chiang, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59, 3127 (2012).
C.P. Auth and J.D. Plummer, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 18, 74 (1997).
P. Banerjee and S.K. Sarkar, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 34, 035010 (2019).
P. Saha, P. Banerjee, and S.K. Sarkar, Superlattices Microstruct. 118, 16 (2018).
ATLAS User Manual, 3D Device Simulator (Santa Clara: Silvaco Inc., 2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, P., Sarkar, S.K. Explicit Threshold Voltage Modeling Insight for Short Channel Characterization of a WFE Elliptical GAA Strained-Si MOSFET. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 7486–7494 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08503-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08503-1