Abstract
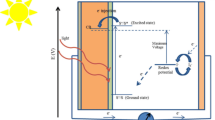
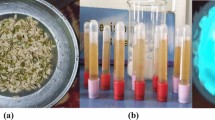
A fast and facile electrochemical method called electrooxidation was used to prepare SnO2 nanoparticles. In this route, a sacrificial tin anode is dissolved in an electrolyte by applying a voltage to an electrochemical cell. We used different electrolyte environments, namely tetramethylammonium chloride and different counterions of tetrabutylammonium cation, viz. Br−, Cl−, and ClO −4 . Characterization results showed that the size distribution was more uniform for the nanoparticles created with Br− and Cl− counterions. Furthermore, the particles in these samples were smaller than in the others. The amount of OH groups on the surface of the Br− and Cl− samples was higher than for the other samples, enhancing dye adsorption. Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) were fabricated from the produced SnO2 nanoparticles, and the influence of the different counterions on their performance was investigated. By varying the counterion in the electrolyte, samples with different hydrophilic nature and dye-loading ability were obtained. The dye adsorption and consequently the current density of the cell made from the Br− solution were higher than for the other samples, and the power conversion efficiency in this case reached 1.5%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Asemi, S. Maleki, and M. Ghanaatshoar, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 81, 645–651 (2017).
M. Ameri, M. Raoufi, M.R. Zamani-Meymian, F. Samavat, M.R. Fathollahi, and E. Mohajerani, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 1993–1999 (2018).
T.T. Pham, N. Mathews, Y.M. Lam, and S. Mhaisalkar, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 3801–3807 (2017).
L. Zhang, K. Jin, S. Li, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, and X. Li, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 244–251 (2015).
S. Mohammadnejad, A. Khalafi, and S.M. Ahmadi, Sol. Energy 133, 501–511 (2016).
X. Xiao, L. Liu, J. Ma, Y. Ren, X. Cheng, Y. Zhu, D. Zhao, A.A. Elzatahry, A. Alghamdi, and Y. Deng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 1871–1880 (2018).
A. Birkel, Y.G. Lee, D. Koll, X. Van Meerbeek, S. Frank, M.J. Choi, Y.S. Kang, K. Char, and W. Tremel, Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 5392–5400 (2012).
M. Dadkhah and M. Salavati-Niasari, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 20, 41–48 (2014).
M.M. Rashad, I.A. Ibrahim, I. Osama, and A.E. Shalan, Bull. Mater. Sci. 37, 903–909 (2014).
M.S. Pereira, F.A.S. Lima, C.B. Silva, P.T.C. Freire, and I.F. Vasconcelos, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 84, 206–213 (2017).
M.A. Hossain, G. Yang, M. Parameswaran, J.R. Jennings, and Q. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 21878–21884 (2010).
M. Abrari, M. Ghanaatshoar, S.S.H. Davarani, H.R. Moazami, and I. Kazeminezhad, Appl. Phys. A 123, 326 (2017).
M. Asemi, A. Suddar, and M. Ghanaatshoar, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 15233–15238 (2017).
H.R. Moazami, S.S.H. Davarani, T. Yousefi, and A.R. Keshtkar, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 30, 682–687 (2015).
B.E.A. Saleh and M.C. Teich, Fundamentals of Photonics, 2nd ed. (New York: Wiley, 1991).
H. Cheng, J. Ma, and Z. Zhao, Chem. Mater. 6, 1033–1040 (1994).
M. Asemi and M. Ghanaatshoar, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 5584–5592 (2017).
C. Suryanarayana and M.G. Norton, X-ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach, Vol. 207 (London: Plenum, 1998).
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, and B.N. Dole, J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6, 6 (2012).
S. Chakraborty and P. Kumbhakar, Indian J. Phys. 88, 251–257 (2014).
Y.C. Goswami, V. Kumar, P. Rajaram, V. Ganesan, M.A. Malik, and P. O’Brien, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 69, 617–624 (2014).
U. Aschauer, R. Pfenninger, S.M. Selbach, T. Grande, and N.A. Spaldin, Phys. Rev. B 88, 054111 (2013).
P. Chetri and A. Choudhury, Physica E 47, 257–263 (2013).
H. Zhang, Y. Liu, K. Zhu, G. Siu, Y. Xiong, and C. Xiong, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10, 11121 (1998).
H. Seema, K.C. Kemp, V. Chandra, and K.S. Kim, Nanotechnology 23, 355705 (2012).
H.R. Moazami, S.S.H. Davarani, T. Yousefi, and H. Darjazi, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 38, 240–248 (2015).
S. Zhan, D. Li, S. Liang, X. Chen, and X. Li, Sensors 13, 4378–4389 (2013).
K. Arora, M. Tomar, and V. Gupta, Analyst 139, 837–849 (2014).
M. Asemi and M. Ghanaatshoar, Ceram. Int. 42, 6664–6672 (2016).
M. Asemi, M. Ahmadi, and M. Ghanaatshoar, Ceram. Int. 44, 12862–12868 (2018).
A. Kathalingam, M.R. Kim, Y.S. Chae, J.K. Rhee, and T. Mahalingam, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 55, 2476–2481 (2009).
K. Anandan and V. Rajendran, J. Non-Oxide Glasses 2, 83–89 (2010).
D.F. Cox, T.B. Fryberger, and S. Semancik, Phys. Rev. B 38, 2072 (1988).
Q. Wali, Z.H. Bakr, N.A. Manshor, A. Fakharuddin, and R. Jose, Sol. Energy 132, 395–404 (2016).
M. Asemi and M. Ghanaatshoar, Appl. Phys. A 122, 853 (2016).
M. Asemi and M. Ghanaatshoar, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 52, 489–503 (2017).
A. Zaban, M. Greenshtein, and J. Bisquert, ChemPhysChem 4, 859–864 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abrari, M., Ghanaatshoar, M., Moazami, H.R. et al. Synthesis of SnO2 Nanoparticles by Electrooxidation Method and Their Application in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: The Influence of the Counterion. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 445–453 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6724-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6724-5