Abstract
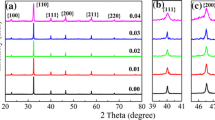
Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics (Bi0.5Na0.5)0.935Ba0.065Ti1−x (Ni0.5Sb0.5) x O3 (BNBT6.5-xNS) have been fabricated using conventional solid sintering technique. The effect of (Ni, Sb) doping on the phase structure and electrical properties of BNBT6.5 ceramics were systematically investigated. Results show that the addition of (Ni, Sb) destroyed the ferroelectric long-range order of BNBT6.5 and shifted the ferroelectric–relaxor transition temperature (T F–R) down to room temperature. Thus, this process induced an ergodic relaxor phase at zero field in samples with x = 0.005. Under the electric field, the ergodic relaxor phase could reversibly transform to ferroelectric phase, which promotes the strain response with peak value of 0.38% (at 80 kV/cm, corresponding to d 33 * = 479 pm/V) at x = 0.005. Temperature-dependent measurements of both polarization and strain confirmed that the large strain originated from a reversible field-induced ergodic relaxor to ferroelectric phase transformation. The proposed material exhibits potential for nonlinear actuators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J. Zhang, R. Xia, and T.R. Shrout, J. Electroceram. 19, 251 (2007).
J.G. Wu, D.Q. Xiao, and J.G. Zhu, Chem. Rev. 115, 2559 (2015).
J.G. Wu, Z. Fan, and D.Q. Xiao, et al., Prog. Mater Sci. 84, 335 (2016).
T.R. Shrout and S.J. Zhang, J. Electroceram. 19, 113 (2007).
J. Rodel, W. Jo, and K.T.P. Seifert, et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1153 (2009).
P. Jarupoom and P. Jaita, Electron. Mater. Lett. 11, 1 (2015).
Y.R. Zhang, J.F. Li, B.P. Zhang, and C.E. Peng, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 074109 (2008).
R. Sumang, N. Vittayakorn, and T. Bongkarn, Ceram. Int. 39, S409 (2013).
W.-S. Kang and J.-H. Koh, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 2057 (2015).
S.T. Zhang, A.B. Kounga, A. Emil, and Y. Deng, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 3950 (2008).
A. Sasaki, T. Chiba, Y. Mamiya, and E. Otsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 5564 (1999).
K. Yoshii, Y. Hiruma, H. Nagata, and T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 4493 (2006).
A.B. Kounga, S.T. Zhang, W. Jo, and T. Granzow, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 222902 (2008).
W. Bai, Y. Bian, J. Hao, B. Shen, J. Zhai, and S. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 246 (2013).
P. Fu, Z. Xu, R. Chu, X. Wu, W. Li, and X. Li, Mater. Des. 46, 322 (2013).
X. Wang, X. Tang, and H. Chan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 91 (2004).
S.T. Zhang, A.B. Kounga, E. Aulbach, and H. Ehrenberg, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 112906 (2007).
T. Takenaka, K.I. Maruyama, and K. Sakata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 2236 (1991).
H.L. Li, C.D. Feng, and P.H. Xiang, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 7387 (2003).
D.W. Kang, T.G. Park, J.W. Kim, S.K. Jin, and H.S. Lee, Electron. Mater. Lett. 6, 145 (2010).
F. Wang, M. Xu, Y. Tang, T. Wang, and W. Shi, Phys. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 1955 (2012).
R. Cheng, Z. Xu, R. Chu, J. Hao, J. Du, and G. Li, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 489 (2016).
L. Li, J. Hao, Z. Xu, R. Chu, W. Li, and G. Li, Ceram. Int. 42, 14886 (2016).
L. Li, J. Hao, Z. Xu, W. Li, and R. Chu, Ceram. Int. 42, 9419 (2016).
K. Wang, A. Hussain, and W. Jo, et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 2241 (2012).
P. Kantha, K. Pengpat, and P. Jarupoom, et al., Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 460 (2009).
C. Xu, D. Lin, and K. Kwok, Solid State Sci. 10, 934 (2008).
Q. Xu, and X.-L. Chen, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 130, 94 (2006).
K. Ramam and M. Lopez, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 4466 (2006).
J. Hao, B. Shen, J. Zhai, C. Liu, X. Li, and X. Gao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 3133 (2013).
F.Z. Yao, and K. Wang, et al., Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 1217 (2016).
M.H. Zhang, and K. Wang, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 3889 (2017).
J. Hao, Z. Xu, R. Chu, W. Li, and J. Du, J. Alloys Compd. 647, 857 (2015).
G. Fan, W. Lu, X. Wang, F. Liang, and J. Xiao, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 035403 (2008).
D. Lin, K.W. Kwok, and H.L.W. Chan, Solid State Ion. 178, 1930 (2008).
D. Lin, K.W. Kwok, and H.L.W. Chan, J. Alloys Compd. 481, 310 (2009).
C. Xu, D. Lin, and K.W. Kwok, Solid State Sci. 10, 934 (2008).
A. Maqbool, A. Hussain, and J. Ur Rahman, et al., Ceram. Int. 40, 11905 (2014).
J. Hao, B. Shen, J. Zhai, and H. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 034101 (2014).
J. Hao, Z. Xu, R. Chu, W. Li, P. Fu, and J. Du, J. Alloys Compd. 677, 96 (2016).
B.S. Kang, S.K. Chol, and C.H. Park, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 1904 (2003).
S. Steinsvik, R. Bugge, J. Gjonnes, J. Tafto, and T. Norby, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 58, 969 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFB0402701), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51372110, 51402144 and 51502127), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (ZR2016EMM02), Independent innovation and achievement transformation in Shandong Province special, China (No. 2014CGZH0904), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (ZR2014JL030), The Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (Nos. J14LA11, J14LA10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Hao, J., Xu, Z. et al. Electric Field-Induced Large Strain in Ni/Sb-co Doped (Bi0.5Na0.5) TiO3-Based Lead-Free Ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 1512–1518 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5935-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5935-5