Abstract
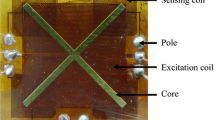
In this paper, based on the sensitivity empirical formula, the microsolenoid fluxgate sensor is designed in reverse by making use of optimized parameters. The fabricated microsolenoid fluxgate sensor with a Co-based amorphous ribbon core presents a best sensitivity of 3587 V/T, a power consumption of 20.35 mW, and a linear range of 0–100 μT. The test results show that the sensitivity of the sensor is in good agreement with the theoretical expectation, with an error lower than 4%. The improvement of the core material makes a major contribution to the high sensitivity. The noise power density of the sensor is 0.14 nT/√Hz@1 Hz at the frequency of 100 kHz and the noise rms level is 2.2 nT in the frequency range of 0.1–10 Hz. Reverse design provides a simple and rapid way to optimize the performance of the existing fluxgate sensor for different applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.A. Robertson, Electron. Lett. 36, 331 (2000).
A. Baschirotto, E. Dallago, P. Malcovati, M. Marchesi, E. Melissano, M. Morelli, P. Siciliano, and G. Venchi, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 58, 3269 (2009).
G. Velasco-Quesada, M. Roman-Lumbreras, A. Conesa-Roca, and F. Jerez, IEEE Sens. J. 11, 280 (2011).
S. Choi, Y.K. Yoon, S.H. Kim, and M.G. Allen, J. Micromech. Microeng. 21, 045004 (2011).
W.Y. Choi and J.O. Kim, Microsyst. Technol. 12, 350 (2006).
P.M. Wu and C.H. Ahn, IEEE Sens. J. 8, 308 (2008).
A. Baschirotto, F. Borghetti, E. Dallago, P. Malcovati, M. Marchesi, E. Melissano, P. Siciliano, and G. Venchi, Sens. Actuators A 132, 90 (2006).
P. Ripka, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215, 735 (2000).
M.H. Acuna, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 3717 (2002).
Y.M. Zhang, M. Steiger, A.D. Hibbs, R.E. Grimm, and T.A. Sprott, J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 15, 51 (2010).
M.R. Kirchhoff and S. Buttgenbach, Microsyst. Technol. 16, 787 (2010).
F. Ludwig, E. Heim, and M. Schilling, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1644 (2009).
O. Zorlu, P. Kejik, and R.S. Popovic, Sens. Actuators A 135, 43 (2007).
C.C. Lu, Y.T. Liu, F.Y. Jhao, and J.T. Jeng, Sens. Actuators A 179, 39 (2012).
H. Joisten, B. Guilhamat, M. Audoin, J.M. Leger, R. Cuchet, G. Barrois, J.B. Albertini, P. Gaud, P. Renaux, D. Bloch, and B. Viala, IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 4356 (2005).
M. Janosek and P. Ripka, Sens. Actuators A 151, 141 (2009).
P. Ripka and W.G. Hurley, Sens. Actuators A 129, 75 (2006).
J. Lei, C. Lei, and Y. Zhou, Measurement 46, 710 (2013).
C. Lei, J. Lei, Z. Yang, and Y. Zhou, Microsyst. Technol. 19, 167 (2013).
A. Garcia and C. Moron, IEEE Trans. Magn. 38, 3312 (2002).
C. Hinnrichs, J. Stahl, K. Kuchenbrandt, and M. Schilling, IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 1983 (2001).
D.X. Chen, E. Pardo, and A. Sanchez, IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 2077 (2005).
C. Lei, L. Chen, J. Lei, X.H. Yang, and Y. Zhou, Sens. Lett. 9, 1689 (2011).
W.Y. Choi, J.S. Hwang, and S.O. Choi, IEEE Sens. J. 4, 768 (2004).
C. Lei, Y. Liu, X.C. Sun, T. Wang, Z. Yang, and Y. Zhou, IEEE Sens. J. 15, 5010 (2015).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61273065), National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAK08B05), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (13ZR1420800), the Support Fund of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (AgriX2015005),the Support Fund of the Joint Research Center for Advanced Aerospace Technology of Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology-Shanghai Jiao Tong University (USCAST2015-2), the Support Fund of Aerospace Technology (15GFZ-JJ02-05), the Analytical and Testing Center in Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and the Center for Advanced Electronic Materials and Devices in Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, C., Sun, XC. & Zhou, Y. Reverse Optimization of an Integrated Solenoid Fluxgate Sensor Based on Co-based Amorphous Soft Magnetic Ribbon. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 5356–5361 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4764-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4764-2