Abstract
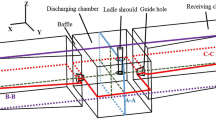
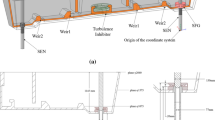
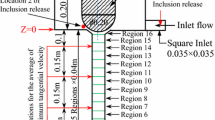
Gas was injected into the upper part of a water model ladle shroud, producing micro-bubbles by the shearing action of the high-speed entry flow of water, combined with subsequent bubble breaking actions of turbulence. An impact pad was used in favor of a standard turbulence inhibitor, to maintain the integrity of the micro-bubbles, and assure their wide distribution within the tundish. The effects of these two systems on removing small inclusions were investigated, and a numerical model was developed to simulate the motion behaviors of bubbles in the tundish, considering bubble coalescence. Both the turbulence inhibitor and the impact pad performed similar on flow improvement, but the impact pad effectively restrained coalescence between bubbles, leading to a 55.3 pct drop in the average bubble size within the tundish, and generating a 53.9 pct reduction in the residual numbers of inclusions below 51 μm diameter, by contrast with the turbulence inhibitor data. The impact pad fits well with gas bubbling for deep cleaning the liquid steel in tundish.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C D :
-
Drag coefficient (–)
- C VM :
-
Virtual mass factor (–)
- C L :
-
Lift coefficient (–)
- d b :
-
Diameter of bubble (m)
- g :
-
Gravity acceleration (m2/s)
- G k :
-
Generation rate of turbulence kinetic energy (–)
- k :
-
Turbulent kinetic energy (m2/s2)
- \(\dot{m}_{{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Dimensionless mean residence time (–)
- m p :
-
Mass of particles (kg)
- n i :
-
Number density of inclusions (number/m3)
- N p :
-
Total number of inclusions (–)
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Q a :
-
Active flow rate (m3/s)
- Q i :
-
Inlet flow rate (m3/s)
- Q s :
-
Volume flow rate of inclusion suspension (m3/s)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number (–)
- r 1, r 2 :
-
Radius of two colliding bubbles (m)
- Δt :
-
Time step (s)
- u, u b :
-
Velocity of fluid flow and bubbles (m/s)
- u rel :
-
Relative velocity between two colliding bubbles (m/s)
- V cell :
-
Volume of the cell (m3)
- V s :
-
Volume of inclusion suspension (m3)
- We :
-
Weber number (–)
- ρ, ρ g, ρ p :
-
Densities of liquid, gas, and particle (kg/m3)
- ε :
-
Turbulent dissipation rate (m2/s3)
- \(\overline{\theta }_{\text{c}}\) :
-
Dimensionless mean residence time (–)
- θ min, θ max :
-
Dimensionless responds time and peak time (–)
- σ ε :
-
Turbulent Prandtl number for turbulent dissipation rate (–)
- μ eff, μ, μ t :
-
Effective viscosity, laminar viscosity, and turbulent viscosity (kg/m-s)
- RTD:
-
Residence time distribution
- SEN:
-
Submerged Entry Nozzle
References
S. Tokuda, I. Muto, Y. Sugawara, and N. Hara: Corros. Sci., 2020, vol. 167, p. 108506.
D. Tang and P.C. Pistorius: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 580–5.
K. Chattopadhyay, R.I.L. Guthrie, and M. Isac: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 331–48.
S. Chang, X.K. Cao, C.H. Hsin, Z.S. Zou, M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guthrie: ISIJ Int., 2016, vol. 56, pp. 1188–97.
D. Mazumdar: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 23–9.
J.H. Park and L.F. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2020, vol. 51B, pp. 2453–82.
A. Cwudzinski: Steel Res. Int., 2015, vol. 86, pp. 972–83.
J.S. Zhang, Q. Liu, S.F. Yang, Z.X. Cheng, J.S. Li, and Z.Y. Jiang: ISIJ Int., 2019, vol. 59, pp. 1167–77.
S.K. Ray, M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2011, vol. 38, pp. 173–80.
M.R.M. Yazdi, A.R.F. Khorasani, and S. Talebi: Can. Metall. Q., 2019, vol. 58, pp. 379–88.
P.Y. Ni, L.T.I. Jonsson, M. Ersson, and P.G. Jonsson: Steel Res. Int., 2016, vol. 87, pp. 1356–65.
S. Lopez-Ramirez, J. D. J. Barreto, Palafox-Ramos, R. D. Morales and D. Zacharias: Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 615–27.
H.J. Yang, S. Vanka, and B.G. Thomas: JOM., 2018, vol. 70, pp. 2148–56.
S. Chang, L.C. Zhong, and Z.Z. Zou: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 837–44.
S. Chang, X.K. Cao, Z.S. Zou, M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 2732–43.
A. Asad, M. Haustein, K. Chattopadhyay, C.G. Aneziris, and R. Schwarze: JOM., 2018, vol. 70, pp. 2927–33.
A. Cwudzinski: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2018, vol. 45, pp. 528–36.
J. Jiang, J.S. Li, H.J. Wu, S.F. Yang, T. Li, and H.Y. Tang: Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 143–8.
L.F. Zhang and S. Taniguchi: Int. Mater. Rev., 2000, vol. 45, pp. 59–82.
S. Chang, Z.S. Zou, J.H. Liu, M. Isac, X.K.E. Cao, X.F. Su, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Powder Technol., 2021, vol. 387, pp. 125–35.
S. Chatterjee and K. Chattopadhyay: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 1416–24.
S. Chatterjee, D.H. Li, and K. Chattopadhyay: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 756–66.
S. Chang, X.K. Cao, Z.S. Zou, M. Isac, and R.I.L. Guthrie: ISIJ Int., 2018, vol. 58, pp. 60–7.
D. Gerlach, G. Biswas, F. Durst, and V. Kolobaric: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer., 2005, vol. 48, pp. 425–38.
S. Chang, W.X. Huang, Z.Z. Zou, B.K. Li, and R.I.L. Guthrie: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 367, pp. 296–304.
P.K. Singh and D. Mazumdar: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 1091–103.
Y. Li, C.G. Cheng, M.L. Yang, Z.X. Dong, and Z.L. Xue: Metals., 2018, vol. 8, p. 590.
R. Liu and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 388–405.
Q.Y. Zhang, L.T. Wang, and Z.R. Xi: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 8, pp. 1177–82.
S. Chang, X.K. Cao, and Z.Z. Zou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 953–7.
Y. Sahai and T. Emi: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. 1166–73.
C. Laborde-Boulet, F. Larachi, N. Dromard, O. Delsart, and D. Schweich: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2009, vol. 64, pp. 4399–413.
A. Tomiyama, H. Tamai, I. Zun, and S. Hosokawa: Chem. Eng. Sci., 2002, vol. 57, pp. 1849–58.
P. J. O’Rourke: Ph.D Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, 1981.
M. Mezhericher, A. Levy, and I. Borde: Int. J. Multiphase Flow., 2012, vol. 43, pp. 22–38.
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51904061).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted July 25, 2021; accepted November 11, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, S., Zou, Z., Li, B. et al. Modeling Inclusion Removal when Using Micro-bubble Swarm in a Full-Scale Tundish with an Impact Pad. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 526–536 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02388-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02388-z