Abstract
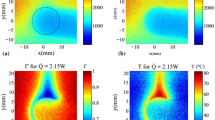
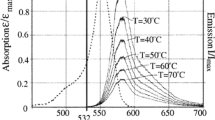
A 1/17th water physical model of a 200-ton steel ladle furnace with a single gas injection was used to simulate bath heating using a single burner to mimic the heat flux due to electric arcs in the industrial steel ladle. Two phases were considered, using water to simulate the molten steel and air to simulate the argon injection at a flow rate of 1.54 NL min−1. The planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence (PLIF) technique was for the first time experimentally implemented to measure temperature fields in a longitudinal plane of the gas-stirred ladle model. PLIF employs a laser source of 532-nm wavelength to light water seeded with rhodamine B, which emits fluorescence depending on its temperature, after a complex calibration is made. Next, the fluorescence is captured by a camera with a 550-nm wavelength filter. The PLIF measurements were validated by local thermocouple measurements at five different locations in the measurement plane. Temperature fields measured by PLIF are in good agreement with those obtained locally by thermocouples, so the PLIF technique can be used to measure temperature fields with the advantage of getting a complete temperature contour field, in contrast to point values of temperatures with thermocouples. Experiments were carried out to study the thermal mixing for two common tuyere positions, i.e., axisymmetric and eccentric (mid-radius) positions. Results on the injection mode show that axisymmetric gas injection is a more efficient heat transfer configuration between the burner and the liquid phase than is the symmetric injection mode for the particular heating configuration studied in this work.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ganguly and S. Chakraborty: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44(3), pp. 573-546.
A. Deodhar, U. Singh, R. Shukla, B. P. Gautham and A. K. Singh: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48(2), pp. 1217-1229.
Y. Pan, C. E. Grip and B. Björkman: Scand. J. Metall., 2003, vol. 32(2), pp. 71-85.
S. Chatterjee and K. Chattopadhyay: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2017, vol. 44(6), pp. 403-412.
[5 Y. Liu, M. Ersson, H. Liu, P. G. Jönsson and Y. Gan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50(1), pp. 555-577.
D. Mazumdar: Steel Res. Int., 2019, vol. 90(4), p. 1800279.
S. Lopez-Ramirez, J. De Barreto, P. Vite-Martinez, J. R. Serrano and C. Duran-Valencia: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35(5), pp. 957-66.
W. Jianjun, D. Chaoshan, Z. Li, Z. Yuzhu, L. Zhenghang and X. Zeqiang: Acta Metall. Sin., 1997, vol. 33(5), pp. 509-514.
AK Sinha, A Vassilicos (1998) Ironmak Steelmak, 25(5):387.
M. L. Lowry and Y. Sahai: Iron & steelmaker, 1992, vol. 19(3), pp. 81-86.
S. X. Liu, X. M. Yang, L. Du, L. Li, and C. Z. Liu: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48(12), pp. 1712-1721.
D. Y. Sheng and L. Jonsson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31(4), pp. 867-875.
J. D. J. Barreto, M. B. Meza and R. D. Morales: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36(5), pp. 543-552.
S. Chatterjee and K. Chattopadhyay: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2017, vol. 44(6), pp. 413-420.
M. Alizadeh, H. Edris and A. Shafyei (2008) J. Iron Steel Res. Int,. 15(2),. 7-13.
A. Vargas-Zamora, J. Palafox-Ramos, R. D. Morales, M. Diaz-Cruz and J. D. J. Barreto-Sandoval: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35(2), pp. 247-257.
B Yang, H Lei, Q Bi, J Jiang, H Zhang, Y Zhao and JA Zhou (2018) Steel Res. Int. vol. 89(10), 1800173.
H. Tang, L. Guo, G. Wu, H. Xiao, H. Yao, J. Zhang (2018) Metals, 8(6), 374.
J. W. Hlinka and T. W. Miller: Iron Steel Eng., 1970, vol. 47(8), pp. 123-133.
Y. Pan and B. Björkman: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42(6), pp. 614-623.
H. Park, J. Park and S. Y. Jung: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2019, vol. 139, pp. 293-302.
S. Grafsrønningen and A. Jensen: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2012, vol. 55(15-16), pp. 4195-4206.
A. S. Nebuchinov, Y. A. Lozhkin, A. V. Bilsky and D. M. Markovich: Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 2017, vol. 80, pp. 139-146.
R. Taher and C. Abid: Heat Mass Transfer, 2018, vol. 54(5), pp. 1453-66.
G. Ascanio: Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 2015, vol. 23(7), pp. 1065-1076.
L. E. Jardón-Pérez, A. M. Amaro-Villeda, C. González-Rivera, G. Trápaga, A. N. Conejo and M. A. Ramírez-Argáez: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50(5), pp. 2121-2133.
A. H. Thaker, S. V. Bhujbal and V. V. Buwa: Chem. Eng. J. (Amsterdam, Neth.), (2019, in press), 122036. (2019).
L. E. Jardón-Pérez, D. R. González-Morales, G. Trápaga, C. González-Rivera, and M. A. Ramírez-Argáez: Metals, 2019, vol. 9(5), pp. 555.
R. Koitzsch, H. J. Odenthal and H. Pfeifer: Steel Res. Int., 2007, vol. 78(6), pp. 473-81.
D. Mazumdar, H. B. Kim and R. I. L. Guthrie: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2000, vol. 27(4), pp. 302-309.
M. Neifer, S. Rödl and D. Sucker: Steel Res., 1993, vol. 64(1), pp. 54-62.
P. Low, N. Takama, B. Kim and C. Bergaud: TRANSDUCERS 2007-2007 International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, 1rs ed., IEEE, Lyon, France, 2007, pp. 1055-1058.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank DGAPA-UNAM for financial support through Project IN115619. Luis Enrique Jardón-Pérez, CVU 624968, is a student registered in Doctoral Program in Chemical Engineering at the UNAM; thanks to CONACYT for Ph. D. scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted March 24, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jardón-Pérez, L.E., Amaro-Villeda, A.M., Trápaga-Martínez, G. et al. Utilization of the Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence Technique (PLIF) to Measure Temperature Fields in a Gas-Stirred Ladle. Metall Mater Trans B 51, 2510–2521 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01944-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01944-3