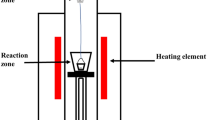
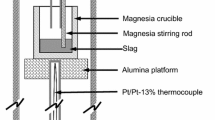
Abstract
The chemical interaction of a typical slag of EAF with three different carbon sources, coke, rubber-derived carbon (RDC), coke-RDC blend, was studied in atmospheric pressure at 1823 K (1550 °C). Using an IR-gas analyzer, off-gases evolved from the sample were monitored. While the coke-RDC blend exhibited the best reducing performance in reaction with molten slag, the RDC sample showed poor interaction with the molten slag. The gasification of the coke, RDC, and coke-RDC blend was also carried out under oxidizing conditions using a gas mixture of CO2 (4 wt pct) and Ar (96 wt pct) and it was shown that the RDC sample had the highest rate of gasification step \( C_{0} \mathop{\longrightarrow}\limits{{k_{3} }}{\text{CO}} + nC_{\text{f}} \) (11.6 site/g s (×6.023 × 1023/2.24 × 104)). This may be attributed to its disordered structure confirmed by Raman spectra and its nano-particle morphology observed by FE-SEM. The high reactivity of RDC with CO2 provided evidence that the Boudouard reaction was fast during the interaction with molten slag. However, low reduction rate of iron oxide from slag with RDC can be attributed to the initial weak contact between RDC and molten slag implying that the contact between carbonaceous matter and slag plays significant roles in the reduction of iron oxide from slag.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Schroeder: Steel Times, 2000, vol. 32, pp. 368–72.
V. Sahajwalla, L. Hong, and C.N. Saha: AISTech, AIST, Association for Iron and Steel Technology, Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005, p. 597.
V. Sahajwalla, R. Khanna, M. Rahman, Z. Huang, E. Tanaka, N.C. Saha, D. Knights, and P. O’Kane: AISTech, Association for Iron and Steel Technology,Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005, p. 547.
M. Rahman, V. Sahajwalla, R. Khanna, N.C. Saha, D. Knights, and P. O’Kane: AISTech, Association for Iron and Steel Technology, Warrendale, PA, USA, (2005), p. 491.
S. Gupta, V. Sahajwalla, and J. Wood: Energy Fuel, 2006, vol. 20, pp. 2557–63.
M. Zaharia, V. Sahajwalla, R. Khanna, P. Koshy, and P. O’Kane: ISIJ Int., 2009, 49 pp. 1513–21.
M. Zaharia, V. Sahajwalla, B-C. Kim, R. Khanna, N.C. Saha, P. O’Kane, J. Dicker, C. Skidmore, and D. Knights: Energy Fuel, 2009, vol. 23 (5), pp. 2467–74.
V. Sahajwalla, M. Zaharia, S. Kongkarat, R. Khanna, N.C. Saha, and P. O’Kane: Energy Fuel, 2010, vol. 24, 379–91.
S. Maroufi, I. Mansuri, P. O’Kane, C. Skidmore, Z. Jin, A. Fontana, M. Zaharia, and V. Sahajwalal: 10th International Conference on Molten Slag, Fluxes and Salts, TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), Seattle, USA, 2016.
M. Ozawa, S. Kitagawa, S. Nakayama, and Y. Takesono: ISIJ, 1986, vol. 26 pp. 621–28.
F.T. Lee and C.H. Lee: Steel Times Int, 1995, pp. 20–25.
F.-Z. Ji, M. Barati, K. Coley, and A.G. Irons: VII International Conference on Molten Slags Fluxes and Salts, The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2004, pp. 399–406.
M. Rahman: PhD thesis, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, 2009.
S.L. Teasdale, and P.C. Hayes: ISI Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 634–41.
T. Nagasaka, M. Hino, and S. Ban-Ya: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2001, vol. 31B(5), pp. 945–55.
V. Sahajwalla, M. Zaharia, S. Kongkarat, R. Khanna, M. Rahman, N.S. Chaudhury, P. O’Kane, J. Dicker, C. Skidmore, and D. Knights: Energy & Fuels, 2012, vol. 26, pp. 58–66.
R.K. Paramguru, R.K. Galgali, and H.S. Ray: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 805–10.
S. Ergun: J. Phys. Chem, 1956, vol. 60, pp. 480–5.
S. Ergun: Ind. Eng. Chem, 1955, vol. 47, pp. 2075–80.
S. Ergun: Chem. Eng. Progr., 1952, vol. 48, pp. 227–36.
S. Ergun: Anal. Chem, 1951, vol. 23, pp. 151–56.
A.E. Reif: J. Phys. Chem, 1952, vol 56, pp. 785–88.
H. Freund: Fuel, 1986, vol. 65, pp. 63–66.
M. Mentser, and S. Ergun: Carbon, 1967, vol. 5 pp. 331–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 7, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maroufi, S., Mayyas, M., Mansuri, I. et al. Study of Reaction Between Slag and Carbonaceous Materials. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 2316–2323 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1020-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1020-y