Abstract
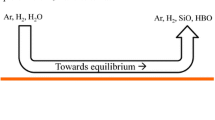
The removal of boron from silicon by top blowing of humidified hydrogen has been studied in the present work through experimental work, thermodynamic calculations, computational fluid dynamic modeling, and quantum chemistry calculations. The effect of process parameters; temperature, lance diameter, lance distance from the melt surface, gas flow rate, and crucible material on the kinetics of boron removal were studied. It has been shown that the rate of boron removal is decreased with increasing temperature due to the competitive reactions between silicon and oxygen as well as boron and oxygen, which can be confirmed with the increases of p SiO/p HBO in the system. The rate of boron removal is increased with increasing the gas flow rate due mainly to the better supply and transport of the gas over the melt surface, as confirmed by the CFD modeling. Moreover, the rate of boron removal in alumina crucible is the highest followed by that in quartz and graphite crucibles, respectively. Faster B removal in quartz crucible than that in graphite crucible can be attributed to more oxygen dissolves in silicon melts. The fastest boron removal in alumina crucible is attributed to the additional boron gasification through aluminum borate (AlBO2) formation on the melt surface. Thermodynamic properties of the AlBO2 species have thus been revised by quantum chemistry calculations, which were more accurate to describe the formation of gaseous AlBO2 than those in the JANAF Thermochemical Tables. The main chemical reactions for boron gasification from silicon melts are proposed as
Based on the obtained results, it has been proposed that boron removal from silicon melt by humidified hydrogen is controlled both by the chemical reaction for boron gasification and mass transport in the adjacent gas phase.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
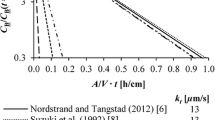
J. Safarian, G. Tranell, M. Tangstad: Energy Procedia, Vol. 20 (2012), pp. 88-97.
S. Tsao and S.S. Lian: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vols. 475–479,pp. 2595–98.
K. Suzuki, K. Sakaguchi, T. Nakagiri, and N. Sano: J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1990, vol. 54, pp. 161–67.
E. Nordstrand and M. Tangstad: Metall. Mat.. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 814–22.
S. Rousseau, M. Benmansour, D. Morvan, and J. Amouroux: Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2007, vol. 91, pp. 1906–15.
T. Ikeda and M. Maeda: Mater. Trans., 1996, vol. 37, pp. 983–87.
C.P. Khattak, D.B. Joyce, and F. Schmid: Report NREL/SR-520-27593, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, 1999.
C.P. Khattak, D.B. Joyce, and F. Schmid: Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2002, vol. 74, pp. 77–89.
N. Yuge, M. Abe, K. Hanazawa, H. Baba, N. Nakamura, Y. Kato, Y. Sakaguchi, S. Hiwasa, and F. Aratani: Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl., 2001, vol. 9, pp. 203–209.
N. Nakamura, H. Baba, Y. Sakaguchi, and Y. Kato: Mater. Trans., 2004, vol. 45 (3), pp. 858–64.
J.J. Wu, W.H. Ma, Y.N. Dai, and K. Morita: Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China, 2009, vol. 19, pp. 463–67.
J. Safarian, K. Tang, K. Hildal, G. Tranell: Metall. Mater. Trans. E, 2014, vol. 1E, pp. 41-47.
C. Alemany, C. Trassy, B. Pateyron, K.-I. Li, and Y. Delannoy: Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2002, vol. 72, pp. 41–48.
E. Fourmond, C. Ndzogha, D. Pelletier, Y. Delannoy, C. Trassy, Y. Caratini, Y. Baluais, and R. Einhaus: 19th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Paris, France. 7–11 June, 2004.
Ø.S. Sortland, M. Tangstad: Metall. Mater. Trans. E, 2014, vol. 1E, pp. 211-25.
K. Tang, S. Andersson, E. Nordstrand, and M. Tangstad: JOM, 2012, vol. 64 (8), pp. 952–56.
V. D. Eisenhüttenleute: Slag Atlas, 2nd ed., Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, Dusseldorf, Germany, 1995.
K. Tang, E.J. Øvrelid, G. Tranell, and M. Tangstad: 12th International Ferroalloys Congress, Helsinki, Finland. 6–9 June 2010, pp. 619–629.
M. Næss, G. Tranell, J.E. Olsen, N. Kamfjord, K. Tang: Oxidation of Metals, Vol. 78 (2012), pp. 239-251.
M.W. Chase: NIST-JANAF Thermochemical Tables, 4th ed., NIST, 1998.
D. Feller, K.A. Peterson, and D.A. Dixon: J. Chem. Phys., 2008, vol. 129, 204105.
K.A. Peterson, D. Feller, and D.A. Dixon: Theor. Chem. Acc., 2012, vol. 131, 1079.
R.A. Kendall, T.H. Dunning, Jr., and R.J. Harrison: J. Chem. Phys., 1992, vol. 96 (9), pp. 6796-6806.
T.H. Dunning, Jr., K.A. Peterson, and A.K. Wilson: J. Chem. Phys., 2001, vol. 114 (21), pp. 9244-9253.
T. Van Mourik, A.K. Wilson, and T.H. Dunning, Jr.: Mol. Phys., 1999, vol. 96 (4), pp. 529-547.
K.A. Peterson and T.H. Dunning, Jr.: J. Chem. Phys., 2002, vol. 117 (23), pp. 10548-10560.
T.H. Dunning, Jr.: J. Chem. Phys., 1989, vol. 90 (2), pp. 1007-1023.
D.E. Woon and T.H. Dunning, Jr.: J. Chem. Phys., 1993, vol. 98 (2), pp. 1358-1371.
W. Klopper, J. Comp. Chem., 1997, vol. 18 (1), pp. 20-7.
S. Stopkowicz and J. Gauss: J. Chem. Phys., 2008, vol. 129, 164119.
CFOUR, Coupled-Cluster techniques for Computational Chemistry, a quantum-chemical program package by J.F. Stanton, J. Gauss, M.E. Harding, P.G. Szalay with contributions from A.A. Auer, R.J. Bartlett, U. Benedikt, C. Berger, D.E. Bernholdt, Y.J. Bomble, L. Cheng, O. Christiansen, M. Heckert, O. Heun, C. Huber, T.-C. Jagau, D. Jonsson, J. Jusélius, K. Klein, W.J. Lauderdale, D.A. Matthews, T. Metzroth, L.A. Mück, D.P. O’Neill, D.R. Price, E. Prochnow, C. Puzzarini, K. Ruud, F. Schiffmann, W. Schwalbach, C. Simmons, S. Stopkowicz, A. Tajti, J. Vázquez, F. Wang, J.D. Watts and the integral packages MOLECULE (J. Almlöf and P.R. Taylor), PROPS (P.R. Taylor), ABACUS (T. Helgaker, H.J.A. Jensen, P. Jørgensen, and J. Olsen), and ECP routines by A. V. Mitin and C. van Wüllen. For the current version, see http://www.cfour.de.
C. E. Hecht: Statistical Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory, W. H. Freeman, New York, 1990.
C.E. Moore: Atomic Energy Levels, Natl. Bur. Stand. Ref. Data Ser., Natl. Bur. of Stand. (U.S), Circ. No. 35 (U.S. GPO, Washington D.C., 1971.
A. Karton and J. M. L. Martin: J. Phys. Chem. A., 2007, vol. 111 (26), pp. 5936-5944.
G. Wang, M. Chen, G. Jiang, H. Zhou, and M. Zhou: Chem. Phys., 2005, vol. 313, pp. 325-329.
D. Feller, K.A. Peterson, and J. G. Hill: J. Chem. Phys., 2011, vol. 135, 044102.
J. Safarian, M. Tangstad: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 1427-1445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 4, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safarian, J., Tang, K., Olsen, J.E. et al. Mechanisms and Kinetics of Boron Removal from Silicon by Humidified Hydrogen. Metall Mater Trans B 47, 1063–1079 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0566-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0566-9