Abstract
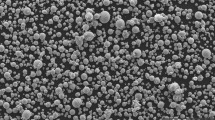
The effect of particle size on the cold compaction behavior of rapidly solidified hypereutectic Al-27 wt pct Si alloy powder was studied by double action axial pressing at room temperature. The geometrical characteristics (morphology, size, shape, and distribution of Si reinforcing phase) and hardness of the powder as a function of the particle size were investigated. The result shows that finer powder particle size showed smaller primary Si particles and achieved a lower density at a given pressure. Whereas, the microhardness of Al matrix increases while the particle size decreases, which indicates that the supersaturation due to the high solidification rate increases the deformation resistance of the alloy powder. Furthermore, the geometrical characteristics of Si phases strongly depend on the particle size due to the suppressed growth of Si phases during atomization. This microstructural characteristic evidently affects the powder compactibility at high applied pressures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.P. Martin, A.M. Hodge, and G.H. Campbell: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 229-232.
K.N. Ramakrishnan, R. Nagarajan, G.V. RamaRao, and S. Venkadesan: Mater. Lett., 1997, vol. 33, pp. 191-194.
F. Delie and D. Bouvard: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 3905-3913.
W. Wu, G. Jiang, R.H. Wagoner, and G.S. Daehn: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 4323-4330.
P.J. Denny: Powder Technol., 2002, vol. 127, pp. 162-172.
O. Dominguez, M. Phillippot, and J. Bigot: Scripta Mater., 1995, vol. 32, pp. 13-17.
X.Y. Liu, L.X. Hu, and E.D. Wang: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 551, pp. 682-687.
M.F. Moreno and C.J.R.G. Oliver: Powder Technol., 2011, vol. 206, pp. 297-305.
O. Skrinjar and P.L. Larsson: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 1871-1884.
S.S. Razavi-Tousi, R. Yazdani-Rad, and S.A. Manafi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 1105-1110.
H. Abdoli, E. Salahi, H. Farnoush, and K. Pourazrang: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 461, pp. 166-172.
J.B. Fogagnolo, E.M. Ruiz-Navas, M.H. Robert, and J. M. Torralba: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 355, pp. 50-55.
Z. Razavi Hesabi, H.R. Hafizpour, and A. Simchi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 454–455, pp. 89–98.
H.S. Kin, H.R. Lee, C.W. Won, S.S. Cho, B.S. Chun, and S.J. Kim: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 1715-1719.
H.S. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 251, pp. 100-105.
Y.Q. Liu, S.H. Wei, J.Z. Fan, Z.L. Ma, and T. Zuo: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 30, pp. 417-422.
P.J. Ward, H.V. Atkinson, P.R.G. Anderson, L.G. Elias, B. Garcia, L. Kahlen, and J.M. Rodriguez-ibabe: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 1717-1727.
M.R. Akbarpour, E. Salahi, F.A. Hesari, A. Simchi, and H.S. Kim: Ceram. Int., 2014, vol. 40, pp. 951-960.
M. Rajabi, A. Simchi, M. Vahidi, and P. Davami: J. Alloys Compd., 2008, vol. 466, pp. 111-118.
M. Moazami-Goudarzi and F. Akhlaghi: Powder Technol., 2013, vol. 245, pp. 126-133.
Y.E. Kalay, L.S. Chumbley, I.E. Anderson, and R.E. Napolitano: Metall. Mater. Trans., 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 1452-1457.
Soon-Jik Hong: Mater. Trans., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 1055-1058.
H.R. Hafizpour, A. Simchi, and S. Parvizi: Adv. Powder Technol., 2010, vol. 21, pp. 273-278.
M.W. Ullah and T. Carlberg: J. Cryst. Growth, 2011, vol. 318, pp. 212-218.
C.L. Xu and Q.C. Jiang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 437, pp. 451-455.
P. Dong, W.L. Hou, X.C. Chang, M.X. Quan, and J.Q. Wang: J. Alloys Compd., 2007, vol. 436, pp. 118-123.
S. He, Y. Liu, S. Guo: Rare Metal mat. Eng. 2009, vol. 38, pp. 353-356.
J.L. Estrada and J. Duszczyk: J. Mater. Sci. 1990, vol. 25 pp.1381-1391.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge for the financial support from the National Key Fundamental Research Project of China (JPPT-125-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 14, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Wang, R., Peng, C. et al. Effect of Particle Size on Microstructure and Cold Compaction of Gas-Atomized Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloy Powder. Metall Mater Trans B 46, 824–830 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-014-0253-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-014-0253-2