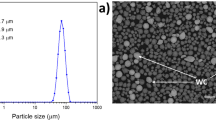
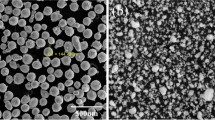
Abstract
Stellite 6 is widely used in high-temperature environments; the evolution of its microstructure and mechanical properties during high-temperature exposure is essential for long-term service. In our work, Stellite 6 claddings were manufactured by plasma arc cladding, followed by a long-term isothermal aging process at 700 °C to imitate high-temperature service. The microstructures were characterized using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD). It was observed that the microstructure of the as-clad coating mainly consisted of γ-Co (cobalt) and carbide eutectics. During isothermal aging at 700 °C, the γ-Co was found to transform to ε-Co. Moreover, fine M23C6 particles were observed to precipitate along the stacking faults of ε-Co. The eutectic carbides also experienced remarkable change; M23C6 grew along the edge of the M7C3 block, indicating the decomposition of M7C3, which might result in the dispersal of eutectic after aging for 500 hours. The microhardness and wear tests indicated that the aging process was beneficial in enhancing the mechanical properties both at room temperature (RT) and 700 °C. According to the morphology of the worn surface, the enhancement of wear performance mainly resulted from the restriction effect of dispersal eutectic carbides and timely removal of oxide. It was also found that the wear mode gradually transformed from adhesive wear to abrasive wear with aging time, which mainly resulted from the increase in the amount of precipitations cut from the matrix, and they acted as the friction pair during the wear test.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.D. Conceição and A.S.C.M. D’Oliveira: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, vol. 288, pp. 69–78.
H.X. Deng, S. Tsuruoka, H.C. Yu, and B. Zhong: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, vol. 204 (23), pp. 3927–34.
H. Kashani, A. Amadeh, and A. Ohadizadeh: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 435, pp. 474–77.
M.M. Ferozhkhan, K.G. Kumar, and R. Ravibharath: Arabian J. Sci. Eng., 2017, vol. 42 (5), pp. 2067–74.
Š. Houdková, Z. Pala, E. Smazalová, M. Vostřák, and Z. Česánek: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, vol. 318, pp. 129–41.
V. Fallah, M. Alimardani, S.F. Corbin, and A. Khajepour: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, vol. 257 (5), pp. 1716–23.
R.R. Bharath, R. Ramanathan, B. Sundararajan, and P.B. Srinivasan: Mater. Des., vol. 29 (9), pp. 1725–31.
S.A.A. Dilawary, A. Motallebzadeh, A.H. Paksoy, M. Afzal, and E. Atar: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, vol. 317, pp. 110–16.
H.F. López and A.J. Saldivar-Garcia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 8–18.
Y. Koizumi, S. Suzuki, K. Yamanaka, B.S. Lee, K. Sato, and Y. Li: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61 (5), pp. 1648–61.
T.L. Achmad, W. Fu, H. Chen, C. Zhang, and Z.G. Yang: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2016, vol. 121, pp. 86–96.
B. Ren, M. Zhang, C. Chen, X. Wang, T. Zou, and Z. Hu: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, vol. 26, pp. 1–10.
S. Zangeneh, H.R. Lashgari, M. Saghafi, and M. Karshenas: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527 (24), pp. 6494–6500.
E.E. Gdoutos: Fracture of Nano and Engineering Materials and Structures, Proc. 16th Eur. Conf. of Fracture (ECF16), Springer Netherlands, 2006, pp. 889–90.
Y. Chen, Y. Li, S. Kurosu, K. Yamanaka, N. Tang, and Y. Koizumi: Wear, 2014, vol. 310 (1–2), pp. 51–62.
K. Wieczerzak, P. Bala, R. Dziurka, T. Tokarski, G. Cios, and T. Koziel: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 698, pp. 673–84.
W.M. Gui, H.Y. Zhang, M. Yang, T. Jin, X.F. Sun, and Q. Zheng: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 695, pp. 1271–78.
V.M. Desai, C.M. Rao, T.H. Kosel, and N.F. Fiore: Wear, 1984, vol. 94 (1), pp. 89–101.
D.Z. Yang, C. Hua, S.Z. Qu, J.J. Xu, J.M. Chen, C. Yu, and H. Lu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, vol. 50A, pp. 1153–61.
C.A. Scheider, W.S. Rasband, and K.W. Eliceiri: Nat. Meth., 2012, vol. 9, pp. 671–75.
A. Boyde, P.G. Howell, and S.J. Jones: J. Microsc., 2011, vol. 101 (3), pp. 261–66.
A.J Saldívar and H.F López: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45 (4), pp. 427–33.
S. Hamar-Thibault, M. Durand-Charre, and B. Andries: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 545–50.
J.R. Lane and N.J. Grant: Trans. ASM, 1952, vol. 44, pp. 113–37.
R.W. Revie: Uhlig’s Corrosion Handbook, 3rd ed, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2011 pp. 747–56.
D.T. Cavanaugh: Grad. Theses Diss., 2015, vol. 14786, pp. 1–86.
M.K. Brun, M. Lee, and F. Gorsler: Wear, 1985, vol. 104 (1), pp. 21–29.
W.S.D. Silva, R.M. Souza, J.D.B. Mello, and H. Goldenstein: Wear, 2011, vol. 271 (9–10), pp. 170–81.
K. Feng, Y. Chen, P. Deng, Y. Li, H. Zhao, and F. Lu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, vol. 243, pp. 170–81.
H. Torres, M. Varga, and M.R. Ripoll: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, vol. 671 pp. 170–81.
B. Kaplan, A. Markström, S. Norgren, and M. Selleby: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45A, pp. 4820–28.
C.C. Viáfara and A. Sinatora: Wear, 2011, vol. 271 (9), pp. 1689–1700.
M.S. Sawant and N.K. Jain: Wear, 2017, vols. 378–379, pp. 155–64.
D. Kesavan and M. Kamaraj: Surf. Coat. Technol., 2010, vol. 204 (24), pp. 4034–43.
B. Briscoe and I.M. Hutchings: Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials, 2nd ed., ScienceDirect, 1992, pp. 79–105.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51875354 and 51575347) and the Shanghai Industrial Strong Foundation Project (Grant No. GYQJ-2018-2-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted December 5, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D., Wang, Q., Wei, X. et al. Effects of Isothermal Aging Process on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Stellite 6 Coatings by Plasma Arc Cladding. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 2807–2816 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05196-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05196-y