Abstract
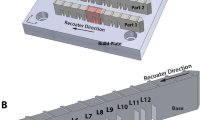
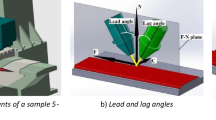
Path planning in additive manufacturing (AM) processes has an impact on the thermal histories experienced at discrete locations in simple and complex AM structures. One component of path planning in directed energy deposition is the time required for the laser or heat source to return to a given location to add another layer of material. As structures become larger and more complex, the length of this interlayer dwell time can significantly impact the resulting thermal histories. The impact of varying dwell times between 0 and 40 seconds on the microstructural and mechanical properties of Inconel® 625 and Ti-6Al-4V builds has been characterized. Even though these materials display different microstructures and solid-state phase transformations, the addition of an interlayer dwell generally led to a finer microstructure in both materials that impacted the resulting mechanical properties. With the addition of interlayer dwell times up to 40 seconds in the Inconel® 625 builds, finer secondary dendrite arm spacing values, produced by changes in the thermal history, correspond to increased yield and tensile strengths. These mechanical properties did not appear to change significantly, however, for dwell times greater than 20 seconds in the Inconel® 625 builds, indicating that longer dwell times have a minimal impact. The addition of interlayer dwell times in Ti-6Al-4V builds resulted in a slight decrease in the measured alpha lath widths and a much more noticeable decrease in the width of prior beta grains. In addition, the yield and tensile values continued to increase, nearly reaching the values observed in the rolled plate substrate material with dwell times up to 40 seconds.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.G. Conley and H.L. Marcus, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 1997, vol. 119, pp. 811-816.
D.D. Gu, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach and R. Poprawe, Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, vol. 57, pp. 133-164.
N. Guo and M.C. Leu, Front. Mech. Eng. 2013, vol. 8, pp. 215-243.
V. Shankar, K.B.S. Rao and S.L. Mannan, J. Nucl. Mater. 2001, vol. 288, pp. 222-232.
G. Lütjering, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 1998, vol. 243, pp. 32-45.
B. Dutta and F.H. Froes, Adv. Mater. Processes 2014, vol. 172, pp. 18-23.
B. Dutta, S. Palaniswamy, J. Choi, L.J. Song, J. Mazumder and Fasm, Adv. Mater. Processes 2011, vol. 169, pp. 33-36.
W.E. Frazier, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, vol. 23, pp. 1917-1928.
J.J. Lewandowski and M. Seifi, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, vol. 46, pp. 151-186.
G.P. Dinda, A.K. Dasgupta and J. Mazumder, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2009, vol. 509, pp. 98-104.
S.M. Kelly and S.L. Kampe, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 1861-1867.
V. Manvatkar, A. De and T. Debroy, J. Appl. Phys. 2014, vol. 116., p. 124905
P.A. Kobryn and S.L. Semiatin, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2003, vol. 135, pp. 330-339.
A.H. Nickel, D.M. Barnett and F.B. Prinz, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2001, vol. 317, pp. 59-64.
L. Costa, R. Vilar, T. Reti and A.M. Deus, Acta Mater. 2005, vol. 53, pp. 3987-3999.
P.A. Kobryn and S.L. Semiatin: Laser forming of Ti–6Al–4V: Research overview, Solid Freeform Fabrication Proceedings, University of Texas, Austin, TX, 2000, pp. 58–65.
A.R. Nassar, J.S. Keist, E.W. Reutzel and T.J. Spurgeon, Additive Manufacturing 2015, vol. 6, pp. 39-52.
J.R. Fessler, R. Merz, A.H. Nickel, F.B. Prinz and L.E. Weiss: Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, 1996, pp. 117–24.
E.R. Denlinger, J.C. Heigel, P. Michaleris and T.A. Palmer, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2015, vol. 215, pp. 123-131.
Z.Q. Wang, E. Denlinger, P. Michaleris, A.D. Stoica, D. Ma and A.M. Beese, Mater. Design 2017, vol. 113, pp. 169-177.
C.C. Silva, H.C. de Miranda, M.F. Motta, J.P. Farias, C.R.M. Afonso and A.J. Ramirez, J. Mat. Res. Tech. 2013, vol. 2, pp. 228-237.
J.N. DuPont, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1996, vol. 27, pp. 3612-3620.
J. Tinoco and H. Fredriksson, High Temp. Mater. Processes 2004, vol. 23, pp. 13-24.
S. Roy, R. Madhavan and S. Suwas, Philos. Mag. 2014, vol. 94, pp. 358-380.
S. Kelly, S. Kampe and C. Crowe: in Microstructural Study of Laser Formed Ti-6Al-4V, MRS Proceedings, Cambridge University Press, 2000, p. 3.
P.Q. Xu, L.J. Li and C.B. Zhang, Mater. Charact. 2014, vol. 87, pp. 179-185.
G. Tapia and A. Elwany: J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, vol. 136.
M. Cieslak, T. Headley, A. Romig and T. Kollie, Metallurgical Transactions A 1988, vol. 19, pp. 2319-2331.
J. Tiley, T. Searles, E. Lee, S. Kar, R. Banerjee, J.C. Russ and H.L. Fraser, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2004, vol. 372, pp. 191-198.
H.J.G. Gundersen, T.B. Jensen and R. Osterby, J. Microsc. 1978, vol. 113, pp. 27-43.
J.S. Keist and T.A. Palmer, Mater. Design 2016, vol. 106, pp. 482-494.
ASTM standard E112-12: Standard test methods for determining average grain size, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2012, p. 27.
ASTM standard E8-08: Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2008.
Z.Q. Wang, T.A. Palmer and A.M. Beese, Acta Mater. 2016, vol. 110, pp. 226-235.
B.E. Carroll, T.A. Palmer and A.M. Beese, Acta Mater. 2015, vol. 87, pp. 309-320.
J.C. Heigel, P. Michaleris and T.A. Palmer: Proc. IMechE Part B: J. Engineering Manufacture. 2016. vol. 230. pp. 1295–1308.
M.F. Gouge, J.C. Heigel, P. Michaleris and T.A. Palmer, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2015, vol. 79, pp. 307-320.
Acknowledgments
The material is based upon work supported by the Office of Naval Research through the Naval Sea Systems Command under Contract No. N00024-02-D-6604 Delivery order No. 0611, and Contract No. N00024-12-D-6404 Delivery order No. 0001. Special thanks to Dr. William Frazier, Dr. Madan Kittur, Ms. Malinda Pagett, Mr. Anthony Zaita, and Dr. Edward Reutzel for their helpful discussions and recommendations. We also acknowledge Mr. Jay Tressler and Mr. Griffin Jones for fabrication of the wall structures, Ms. Beth Carroll for assistance with initial tensile tests, Mr. Ed Good for use of his metallurgical laboratory, and Dr. Abdalla Nassar for developing the code for measuring microstructural features.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 24, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, B.K., Beese, A.M., Keist, J.S. et al. Impact of Interlayer Dwell Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nickel and Titanium Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 4411–4422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4164-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4164-0