Abstract
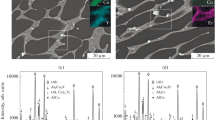
Studies were carried out systematically on a series of Al-8.5 wt pct Zn-xMg-yCu alloys (x is about 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5 wt pct, and y is about 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, and 2.9 wt pct). The effects of alloying elements Mg and Cu on the microstructures of as-cast and homogenized alloys were investigated using the computational/experimental approach. It shows that Mg(Zn,Al,Cu)2 (σ) phase can exist in all the as-cast alloys without any observable Mg32(Al,Zn)49/Al2Mg3Zn3 (T) or Al2CuMg (S) phase, whereas Al2Cu (θ) phase is prone to exist in the alloys with low Mg and high Cu contents. Thermodynamic calculation shows that the real solidification paths of the designed alloys fall in between the Scheil and the equilibrium conditions, and close to the former. After the long-time homogenization [733 K (460 °C)/168 hours] and the two-step homogenization [733 K (460 °C)/24 hours + 748 K (475 °C)/24 hours], the phase components of the designed alloys are generally consistent with the calculated phase diagrams. At 733 K (460 °C), the phase components in the thermodynamic equilibrium state are greatly influenced by Mg content, and the alloys with low Mg content are more likely to be in single-Al phase field even if the alloys contain high Cu content. At 748 K (475 °C), the dissolution of the second phases is more effective, and the phase components in the thermodynamic equilibrium state are dominated primarily by (Mg + Cu) content, except the alloys with (Mg + Cu) ≳ 4.35 wt pct, all designed alloys are in single-Al phase field.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.A. Starke and J.T. Staley: Prog. Aerosp. Sci., 1996, vol. 32, pp. 131–72.
J. Liu: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2006, vols. 519–521, pp. 1233–38.
W.G. Roeseler, B. Sarh, and M.U. Kismarton: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Composite Materials, 2007.
A.S. Warren: Mater. Forum, 2004, vol. 28, pp. 24-31.
T. Marlaud, A. Deschamps, F. Bley, W. Lefebvre, and B. Baroux: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 248–60.
V. Raghavan (2007) J. Phase Equilib. Diff. 28(2):211–12.
[7] N.A. Belov: Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2012, vol. 53, nos. 9–10, pp. 420-27.
[8] Aluminum Association: International Alloy Designations and Chemical Composition Limits for Wrought Aluminum and Wrought Aluminum Alloys, The Aluminum Association, Arlington, VA, 2009.
[9] D. Dumont, A. Deschamps, and Y. Brechet: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 356, no. 1, pp. 326-36.
[10] Y. Deng, Z.M. Yin, and F.G. Cong: Intermetallics, 2012, vol. 26, pp. 114-21.
[11] D.K. Xu, N. Birbilis, D. Lashansky, P.A. Rometsch, and B.C. Muddle: Corros. Sci., 2011, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 217-25.
[12] F.Y. Xie, X.Y. Yan, L. Ding, F. Zhang, S.L. Chen, M.G. Chu, and Y.A. Chang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 355, pp. 144-53.
[13] F.H. Gao, G. Zhao, W.M. Bian, and N. Tian: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, vols. 638–642, pp. 384-89.
[14] S.T. Lim, Y.Y. Lee, and I.S. Eun: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vols. 475–479, pp. 369-72.
[15] S.T. Lim, I.S. Eun, and S.W. Nam: Mater. Trans., 2003, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 181-87.
[16] X.M. Li and M.J. Starink: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2000, vols. 331–337, pp. 1071-6.
H.Y. Liang: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1998.
[18] X.G. Fan, D.M. Jiang, Q.C. Meng, and Z. Li: Mater. Lett., 2006, vol. 60, pp. 1475-79.
[19] L.J. Wang, D.K. Xu, P.A. Rometsch, S.X. Gao, Y. Zhang, Z.B. He, M.J. Couper, and B.C. Muddle: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2011, vol. 693, pp. 276-81.
[20] C. Mondal and A.K. Mukhopadhyay: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 391, pp. 367-76.
[21] Z.A. Wang, M.P. Wang, W.C. Yang, Q. Zhang, X.F. Sheng, and Z. Li: J. Mater. Eng., 2010, vol. 5, pp. 56-63.
[22] C. Zhang, H.B. Cao, G.P. Cao, S. Kou, and Y.A. Chang: JOM, 2008, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 48-51.
[23] H.B. Cao, C. Zhang, J. Zhu, G.P. Cao, S. Kou, R. Schmid-Fetzer, and Y.A. Chang: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 58, no. 5, pp. 397-400.
[24] W. Cao, S.L. Chen, F. Zhang, K. Wu, Y. Yang, Y.A. Chang, R. Schmid-Fetzer, and W.A. Oates: CALPHAD, 2009, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 328-42.
[25] W.X. Shu, J.C. Liu, L.G. Hou, H. Cui, J.T. Liu, and J.S. Zhang: Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2014, vol. 21, no. 12, pp. 1215-21.
[26] J.D. Robson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 382, pp. 112-21.
[27] R. Ghiaasiaan, X. Zeng, and S. Shankar: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 594, pp. 260–77.
[28] X.G. Fan, D.M. Jiang, Q.C. Meng, B.Y. Zhang, and T. Wang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2006, vol. 16, pp. 577–81.
A.K. Mukhopadhyay, G.M. Reddy, K.S. Prasad, V.K. Varma, and C. Mondal: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, 2004.
[30] A.K. Mukhopadhyay: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2012, vol. 710, pp. 50-65.
[31] H. Möller and G. Govender: Sol. St. Phen., 2013, vol. 192, pp. 173-78.
[32] M. Gazizov, V. Teleshov, V. Zakharov, and R. Kaibyshev: J. Alloy. Compd., 2011, vol. 509, no. 39, pp. 9497–9507.
[33] A.F. Norman, K. Hyde, F. Costello, S. Thompson, S. Birley, and P.B. Prangnell: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 354, no. 1, pp. 188-98.
B.H. Zhu: Ph.D. Thesis, General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, 2011.
[35] Y.A. Chang, S.L. Chen, F. Zhang, X.Y. Yan, F.Y. Xie, R. Schmid-Fetzer, and W.A. Oates: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 313-45.
[36] R. Deiasi and P.N. Adler: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 1177-83.
[37] X.J. Jiang, B. Noble, V. Hansen, and J. Tafto: Met. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32, pp. 1063-73.
[38] Y.A. Chang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 7-39.
[39] T. Kraft and Y.A. Chang: JOM, 1997, vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 20-28.
[40] S.L. Chen, F. Zhang, S. Daniel, F.Y. Xie, X.Y. Yan, Y.A. Chang, R. Schmid-Fetzer, and W.A. Oates: JOM, 2003, vol. 55, no. 12, pp. 48-51.
[41] D.K. Xu, P.A. Rometscha, and N. Birbilis: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 534, pp. 234-43.
[42] N.K. Li and J.Z. Cui: Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2008, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 769–73.
[43] F.H. Gao, N.K. Li, N. Tian, Q. Sun, X.D. Liu, and G. Zhao: Trans. Noferrous Met. Soc. China, 2008, vol. 18, pp. 321-26.
[44] X.L. Han, B.Q. Xiong, Y.A. Zhang, Z.H. Li, B.H. Zhu, and F. Wang: Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. (China), 2010, vol. 31, no. 11, pp. 104-08.
[45] Y.L. Deng, L. Wan, L.H. Wu, Y.Y. Zhang, and X.M. Zhang: J. Mater. Sci., 2011, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 875-81.
[46] W.B. Li, Q.L. Pan, Y.P. Xiao, Y.B. He, and X.Y. Liu: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2011, vol. 21, pp. 2127-33.
[47] Y. Liu, B.H. Zhu, Y.A. Zhang, X.W. Li, H.W. Liu, and B.Q. Xiong: Chinese J. Rare Met., 2012, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 529-34.
[48] Y. Han, L. Li, S.Z. Mu, Z.Z. Deng, Y.K. Le, and X.M. Zhang: Special Cast. Nonferr. Alloy., 2010, vol. 30, no. 10, pp. 891-93.
[49] Y.T. Zuo, F. Wang, B.Q. Xiong, Y.A. Zhang, B.H. Zhu, H.W. Liu, and Z.H. Li: Chinese J. Nonferr. Met., 2010, vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 820-26.
[50] Y. Du, Y.A. Chang, B.Y. Huang, W.P. Gong, Z.P. Jin, H.H. Xu, Z.H. Yuan, Y. Liu, Y.H. He, and F.Y. Xie: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 363, pp. 140-51.
[51] W.D. Callister and D.G. Rethwisch: Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 7th ed., Wiley, New York, NY, 2007.
[52] E.A. Brandes and G.B. Brook: Smithells Metals Reference Book, 7th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, London, U.K., 1992.
[53] N.A. Belov, D.G. Eskin, and A.A. Aksenov: Multicomponent Phase Diagrams: Applications for Commercial Aluminum Alloys, Elsevier, Oxford, U.K., 2005.
[54] J.A. Wagner and R.N. Shenoy: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2809-18.
D.K. Xu, N. Birbilis, and P.A. Rometsch: Corros. J. Sci. Eng., 2012, vol. 68 (3), pp. 035001-1–10.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TD-12-001) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2013AA032403). The funds from Beijing Municipal Commission of Education for Common Construction Projects and from State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials of China are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 31, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, W.X., Hou, L.G., Liu, J.C. et al. Solidification Paths and Phase Components at High Temperatures of High-Zn Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys with Different Mg and Cu Contents. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 5375–5392 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3050-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3050-x