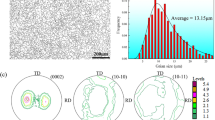
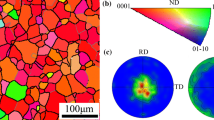
Abstract
Magnesium alloy AZ31B plastically deforms via twinning and slip. Corresponding to the unidirectional nature of twinning, the activity of twinning/detwinning is directly related to loading history and materials texture. Using the elastic viscoplastic self-consistent model implementing with the twinning and detwinning model (EVPSC–TDT), we revisited experimental data of AZ31B sheets under four different strain paths: (1) tension–compression–tension along rolling direction, (2) tension–compression–tension along transverse direction, (3) compression–tension–compression along rolling direction, and (4) compression–tension–compression along transverse direction, and identified the dominant deformation mechanisms with respect to the strain path. We captured plastic deformation behaviors observed in experiments and quantitatively interpreted experimental observations in terms of the activities of different deformation mechanisms and the evolution of texture. It is found that the in-plane pre-tension has slight effect on the subsequent deformation, and the pre-compression and the reverse tension after compression have significant effect on the subsequent deformation. The inelastic behavior under compressive unloading is found to be insignificant at a small strain level but pronounced at a large strain level. Such significant effect is mainly ascribed to the activity of twinning and detwinning.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Gharghouri, G.C. Weatherly, J.D. Embury, and J. Root: Phil. Mag., 1999, vol. A79, p. 1671–95.
X.Y. Lou, M. Li, R.K. Boger, S.R. Agnew, and R.H. Wagoner: Int. J. Plast, 2007, vol. 23, p. 44–86.
L. Wu, S.R. Agnew, Y. Ren, D.W. Brown, B. Clausen, G.M. Stoica, H.R. Wenk, and P.K. Liaw: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2010, vol., A527, p. 7057–67.
G. Proust, C.N. Tomé, A. Jain, and S.R. Agnew: Int. J. Plast, 2009, vol. 25, p. 861–80.
M. Ghazisaeidi and D.R. Trinkle: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, p. 1287–92.
P.G. Partridge: Metall. Rev., 1973, vol. 12, p. 169–94.
J.X. Zhang, Q. Yu, Y.Y. Jiang, and Q.Z. Li: Int. J. Plast, 2011, vol. 27, p. 768–87.
Q. Yu, J.X. Zhang, and Y.Y. Jiang: Phil. Mag. Lett., 2011, vol. 91, p. 757–65.
S.H. Park, S.C. Hong, J.H. Lee, and C.S. Lee: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2012, vol. A532, p. 401–06.
C.H. Cáceres, T. Sumitomo, and M. Veidt: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, p. 6211–18.
G. E. Mann, T. Sumitomo, C.H. Cáceres, and J.R. Griffiths: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2007, vol. A456, p. 138–46.
S. Kleiner and P.J. Uggowitzer: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2004, vol. A379, p. 258–63.
G.I. Taylor: J. Inst. Metals., 1938, vol. 62, p. 307–24.
C.S. Barrett and C.T. Haller: Trans. AIME, 1947, vol. 171, p. 246–55.
S. Mahajan and D.F. William: Int. Mater. Rev., 1973, vol. 18, p. 43–61.
L. Wang, P. Eisenlohr, Y. Yang, T.R. Bieler, and M.A. Crimp: Scripta Mater., 2010, vol., 63, p. 827–30.
L. Wang, Y. Yang, P. Eisenlohr, T.R. Bieler, M.A. Crimp, and D.E. Mason: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, p. 421–30.
P.V. Van Houtte: Acta Metall. 1978, vol. 26, p. 591–604.
C.N. Tomé, R.A. Lebensohn, and U.C. Kocks: Acta Metall. Mater. 1991, vol. 39, p. 2667–80.
R.A. Lebensohn and C.N. Tomé: Acta Metall. Mater. 1993, vol. 41, p. 2611–24.
S.R. Kalidindi: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1998, vol. 46, p. 267–90.
A. Staroselsky and L. Anand: Int. J. Plast., 2003, vol. 19, p. 1843–64.
B. Clausen, C.N. Tomé, D.W. Brown, and S.R. Agnew: Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, p. 2456–68.
H. Wang, B. Raeisinia, Wu PD, Agnew SR, Tomé CN, Int J Solids Struct 2010;47:2905–17.
Li M, Lou XY, Kim JH, Wagoner RH, Int J Plast 2010;26:820–58.
Kim JH, Kim D, Lee YS, Lee MG, Chung K, Kim HY, Wagoner RH, Int J Plast 2013;50:66–93.
D. Mohr, M.A. Chevin, and L. Greve: J. App. Mech., 2013, vol. 80, art. id. 061002.
Hama T, Kitamura N, Takuda H, Mater Sci Eng 2013;A583:232–41.
Proust G, Tomé CN, Kaschner GC, Acta Mater 2007;55:2137–48.
Wang H, Wu PD, Tomé CN, Wang J, Mater Sci Eng 2012;A555:93–98.
Wang H, Wu PD, Wang J, Tomé CN, Int J Plast 2013;49:36–52.
Wang H, Wu PD, Tomé CN, Huang Y, J Mech Phys Solids 2010;58:594–612.
Wang H, Wu PD, Wang J, Int J Plast 47;2013:49–64.
Wu W, Qiao H, An K, Guo XQ, Wu PD, Liaw PK, Int J Plast 2014;62:105–20.
Qiao H, Agnew SR, Wu PD, Int J Plast 2015;65:61–84.
Guo XQ, Wu W, Wu PD, Qiao H, An K, Liaw PK, Scripta Mater 2013;69:319–22.
Wang H, Wu PD, Wang J, Comput Mater Sci 2015;96:214–18.
Hama T, Kariyazaki Y, Hosokawa N, Fujimoto H, Takuda H, Mater Sci Eng 2012;A551:209–17.
Hama T, Nagao H, Kuchinomachi Y, Takuda H, Mater Sci Eng 2014;A591:69–77.
Piao K, Chung K, Lee MG, Wagoner RH, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012;43A:3300–13.
Wang H, Wu PD, Gharghouri MA, Mater Sci Eng 2010;A527:3588–94.
Wang H, Wu PD, Boyle KP, Neale KW, Int J Solids Struct 2011;48:1000–10.
Wang H, Wu PD, Tomé CN, Wang J, Int J Solids Struct 2012;49:2155–67.
Wang H, Clausen B, Tomé CN, Wu PD, Acta Mater 2013;61:1179–88.
P.D. Wu, H. Wang, and K.W. Neale: Int. J. App. Mech., 2012, vol. 4, art. id. 1250024.
Lee SY, Wang H, Gharghouri MA, Nayyeri G, Woo W, Shin E, Wu PD, Poole WJ, Wu W, An K, Acta Mater 2014;73:139–48.
Eshelby JD, Proc. R. Soc. London 1957; A241:376–96.
Martin E, Capolungo L, Jiang LA, Jonas JJ, Acta Mater 2010;58:3970–83.
Simmons G and Wang H: Single Crystal Elastic Constants and Calculated Polycrystal Properties. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1971.
Agnew SR, Duygulu O, Int J Plast 2005;21:1161–93.
Khan AS, Pandey A, Gnaupel-Herold T, Mishra RK, Int J Plast 2011;27:688–706.
Hong SG, Park SH, Lee CS, J Mater Res 2010; 25:784–92.
Hama T, Takuda H, Int J Plast 2011; 27:1072–92.
T.W. Duerig, R. Zadno: in Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys, TW Duerig, ed., Butterworth-Heineman, London, 1990, pp. 369–93.
Wagoner RH, Lim H, Lee MG, Int J Plast 2013;45:3–20.
Yu Q, Wang J, Jiang Y, McCabe RJ, Tomé CN. Mater Res Lett 2014;2:82–88.
Yu Q, Wang J, Jiang Y, McCabe RJ, Li N, Tomé CN. Acta Mater 2014;77:28–42.
Beyerlein IJ, Wang J, Barnett MR, Tomé CN, Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012;468:1496–1520.
Q. Yu, Y.Y. Jiang, and J. Wang: Philos. Mag. Lett., 2015. DOI:10.1080/09500839.2015.1022621.
Mu S, Jonas JJ, Gottstein G, Acta Mater 2012;60:2043–53.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and by the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation. HW and JW were supported by the US department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences (Project No: FWP-06SCPE401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 17, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Wu, P. & Wang, J. Numerical Assessment of the Role of Slip and Twinning in Magnesium Alloy AZ31B During Loading Path Reversal. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 3079–3090 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2890-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2890-8