Abstract
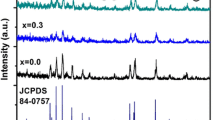
In this study, the boron-doped barium-stabilized bismuth cobalt oxide thermoelectric nanocrystalline ceramic powders were produced by the polymeric precursor technique. The powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and the physical properties measurement system. The X-ray diffraction results showed that these patterns have mixture of two phases as face-centered cubic and body-centered cubic. Values of the crystallite size, the dislocation density, and the microstrain were calculated by the Scherrer equation. According to these values, the crystallite size decreased from 60 to 51 nm with the boron addition in the boron-undoped and boron-doped samples, respectively. The scanning electron microscope results showed that nanograins are rarely seen in the boron-undoped samples, but nanograins turn into needle-like and layered structures with boron addition. The diameters distribution of nanofibers was calculated. The average diameter of the boron-doped sample is smaller than the boron-undoped sample. The physical properties measurement system values showed that the electrical and thermal conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and the figure of merit increased with the temperature rise for both samples. The boron-doping effect increased the electrical and thermal conductivity, decreased the Seebeck coefficient, and decreased the figure of merit.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Funahashi, I. Matsubara, K. Ueno, S. Sodeoka, and H. Yamada: Chem. Mater., 2000, vol. 12, pp. 2424-7.
A. Maignan, S. Hébert, M. Hervieu, C. Michel, D. Pelloquin, and D. Khomskii: J. Phys. Condens. Matter., 2003, vol. 15, pp. 2711-23.
V. Zlati and A.C. Hewson: Properties and Applications of Thermoelectric Materials, Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008.
M.A. Kamarudin, S.R. Sahamir, R.S. Datta, B.D. Long, M.F.M. Sabri, and S.M. Said: Sci. World J., 2013, vol. 2013, art. id 713640. doi:10.1155/2013/713640.
F. Ma, Y. Ou, Y. Yang, Y. Liu, S. Xie, J.F. Li, G. Cao, R. Proksch, and J. Li: J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, vol. 114, pp. 22038-43.
D.K. Taggart, Y. Yang, S.C. Kung, T.M. McIntire, and R.M. Penner: Nano Lett., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 125-31.
W.E. Teo and S. Ramakrishna: Nanotechnol., 2006, vol. 17, pp. R89-106.
I. Uslu, S.S. Cetin, A. Aytimur, S. Yuceyurt, and M.O. Erdal: J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym., 2012, vol. 22, pp. 766-71.
H. Wu, W. Pan, D. Lin, and H. Li: J. Adv. Ceram., 2012, vol. 1, pp. 2-23.
M.A. Senaris-Rodriguez and J.B. Goodenough: J. Solid State Chem., 1995, vol. 118, pp. 323-36.
J. Sunarso: Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Queensland, 2010.
J. Okamoto, G. Shimizu, S. Kubo, Y. Yamada, H. Kitagawa, A. Matsushita, Y. Yamada, and F. Ishikawa: J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2009, vol. 176, p. 012042.
T. Tunc, I. Uslu, S. Durmusoglu, S. Keskin, A. Aytimur, and A. Akdemir: J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym., 2012, vol. 22, pp. 105–11.
C.Y. Hsu, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, and T.T. Shun: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35, pp. 1465-9.
D. Chen, D. Yang, Q. Wang, and Z. Jiang: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2006, vol. 45, pp. 4110-6.
A. Aytimur, İ. Uslu, E. Çınar, S. Koçyiğit, F. Özcan, and A. Akdemir: Ceram. Int., 2013, vol. 39, pp. 911-6.
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, and C.T. Liu: J. Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 109, p. 103505.
C.J. Tong, Y.L. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.J. Lin, and S.Y. Chang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36, pp. 881-93.
C.W. Tsai, M.H. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, and C.C. Yang: J. Alloys Compd., 2010, vol. 490, pp. 160-5.
F.J. Wang, Y. Zhang, and G.L. Chen: J. Alloys Compd., 2009, vol. 478, pp. 321-4.
C. Suryanarayana and M.G. Norton: X-Ray Diffraction a Practical Approach, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1998.
B. Karunagaran, R.T.R. Kumar, D. Mangalaraj, S.K. Narayandass, and G.M. Rao: Cryst. Res. Technol., 2002, vol. 37, pp. 1285-92.
P.H. Klug and L.E. Alexander: X-Ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials, Wiley, New York, NY, 1974.
N.S. Prasad and K.B.R. Varma: Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Adv., 2002, vol. 90, pp. 246-53.
E. Alvarado, L.M. Torres-Martinez, A.F. Fuentes, and P. Quintana: Polyhedron, 2000, vol. 19, pp. 2345-51.
Y. Ding, G.T. Zhang, H. Wu, B. Hai, L.B. Wang, and Y.T. Qian: Chem. Mater., 2001, vol. 13, pp. 435-40.
H. Katsura, T. Hashimoto, and Y. Suemune: J. Jpn. Appl. Phys., 1991, vol. 30, pp. 274-9.
S.Y. Wua and H.N. Dong: Z. Naturforsch., 2004, vol. 59A, pp. 563-7.
S. Ramakrishna, K. Fujihara, W.E. Teo, T.C. Lim, and Z. Ma: An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers, World Scientific, Hackensack, NJ, 2005.
S.L. Shenoy, W.D. Bates, H.L. Frisch, and G.E. Wnek, Polymer, 2005, vol. 46, pp. 3372-84.
C. Song, X. Wang, R. Huang, J. Song, and Y. Guo: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2013, vol. 142, pp. 292-6.
R. Funahashi, I. Matsubara, and S. Sodeoka: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2000, vol. 76, pp. 2385-7.
S. Li, R. Funahashi, I. Matsubara, H. Yamada, K. Ueno, and S. Sodeoka: Ceram. Int., 2001, vol. 27, pp. 321-4.
D. Wang, L. Chen, Q. Yao, and J. Li: Solid State Commun., 2004, vol. 129, pp. 615-8.
T. Yin, D. Liu, Y. Ou, F. Ma, S. Xie, J.F. Li, and J. Li: J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, vol. 114, pp. 10061-5.
W. Xie, S. Zhu, X. Tang, J. He, Y. Yan, V. Ponnambalam, Q. Zhang, S.J. Poon, and T. Tritt: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2009, vol. 42, p. 235407.
K. Zabrocki, P. Ziolkowski, T. Dasgupta, J. De Boor, and E. Muller: J. Electron. Maters., 2013, vol. 42, pp. 2402-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 26, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çinar, E., Koçyiğit, S., Aytimur, A. et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermoelectric Properties of Electrospun Boron-Doped Barium-Stabilized Bismuth-Cobalt Oxide Nanoceramics. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 3929–3937 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2343-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2343-9