Abstract
Objective
To study the effect of Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pill (STDP) on angiogenesis in diabetic cardiomyopathy mice with coronary microcirculation dysfunction (CMD).
Methods
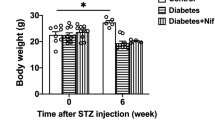
According to a random number table, 6 of 36 SPF male C57BL/6 mice were randomly selected as the control group, and the remaining 30 mice were injected with streptozotocin intraperitoneally to replicate the type 1 diabetes model. Mice successfully copied the diabetes model were randomly divided into the model group, STDP low-dose group [15 mg/(kg·d)], medium-dose group [30 mg/(kg·d)], high-dose group [60 mg/(kg·d)], and nicorandil group [15 mg/(kg·d)], 6 in each group. The drug was given by continuous gavage for 12 weeks. The cardiac function of mice in each group was detected at the end of the experiment, and coronary flow reserve (CFR) was detected by chest Doppler technique. Pathological changes of myocardium were observed by hematoxylin-eosin staining, collagen fiber deposition was detected by masson staining, the number of myocardial capillaries was detected by platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 staining, and the degree of myocardial hypertrophy was detected by wheat germ agglutinin staining. The expression of the vascular endothlial growth factor (VEGF)/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) signaling pathway-related proteins in myocardial tissue was detected by Western blot.
Results
Compared with the model group, medium- and high-dose STDP significantly increased the left ventricular ejection fraction and left ventricular fraction shortening (P<0.01), obviously repaired the disordered cardiac muscle structure, reduced myocardial fibrosis, reduced myocardial cell area, increased capillary density, and increased CFR level (all P<0.01). Western blot showed that high-dose STDP could significantly increase the expression of VEGF and promote the phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, protein kinase B, and eNOS (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusion
STDP has a definite therapeutic effect on diabetic CMD, and its mechanism may be related to promoting angiogenesis through the VEGF/eNOS signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia G, Hill MA, Sowers JR. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: an update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circ Res 2018;122:624–638.
Bajaj NS, Osborne MT, Gupta A, Tavakkoli A, Bravo PE, Vita T, et al. Coronary microvascular dysfunction and cardiovascular risk in obese patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;72:707–717.
Camici PG, d’Amati G, Rimoldi O. Coronary microvascular dysfunction: mechanisms and functional assessment. Nat Rev Cardiol 2015;12:48–62.
Broyd CJ, Hernández-Pérez F, Segovia J, Echavarría-Pinto M, Quirós-Carretero A, Salas C, et al. Identification of capillary rarefaction using intracoronary wave intensity analysis with resultant prognostic implications for cardiac allograft patients. Eur Heart J 2018;39:1807–1814.
Zhang MD, Cui XY, Yuan YY, Zhang YT, Yu X, Wu Y. Mechanism of Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pills in improving cardiac function in diabetic rat with myocardial infarction by promoting angiogensis. Tianjin J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2022;39:1043–1051.
Cui XY, Bai YL, Wu Y. Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pills improve cardiac function in type 2 diabetic rats by promoting angiogenesis. China J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2022;47:6476–6484.
Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato E, Funck-Brentano C, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2020;41:407–477.
Weldy CS, Ashley EA. Towards precision medicine in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021;18:745–762.
Zhao J, Zhou Y, Liu H, Zheng Z, Liu S, Peng J, et al. Effect of Musk Tongxin Dropping Pill on myocardial remodeling and microcirculation dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021;2021:6620564.
Tesic M, Beleslin B, Giga V, Jovanovic I, Marinkovic J, Trifunovic D, et al. Prognostic value of transthoracic doppler echocardiography coronary flow velocity reserve in patients with asymmetric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Heart Assoc 2021;10:e021936.
Yang SS. The study on the mechanism of promoting angiogenesis of Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pills (Dissertation). Harbin: Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
Ma HW, Liu PY, Zhang YQ. Ginsenoside-induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell intervention can affec healing and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rats with diabetic skin ulcer. Chin J Tissue Eng Res (Chin) 2019;23:5300–5306.
Yan WH, Zhang CX, Xing T, Gong X, Yang YX, Li YN, et al. Nicorandil improves cognitive dysfunction in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J South Med Univ 2018;38:384–389.
Ye Z, Gao Y, Xie E, Li Y, Guo Z, Li P, et al. Evaluating the predictive value of diabetes mellitus diagnosed according to the Chinese guidelines (2020 edition) for cardiovascular events. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2022;14:138.
Aronson D, Edelman ER. Coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus. Heart Fail Clin 2016;12:117–133.
American Diabetes Association. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019;42:S103–S123.
Lu Y, Chu X, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Jin C, Zhu J, et al. Effect of Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pill on stable coronary artery disease patients with normal fractional flow reserve and coronary microvascular disease: a study protocol. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22126.
Lu X, Yao J, Li C, Cui L, Liu Y, Liu X, et al. Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pills promote macrophage polarization-induced angiogenesis against coronary microvascular dysfunction via PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway. Front Pharmacol 2022;13:840521.
Cui L, Liu Y, Hu Y, Dong J, Deng Q, Jiao B, et al. Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pill alleviates M1 macrophage polarization-induced inflammation and endothelial dysfunction to reduce coronary microvascular dysfunction via the Dectin-1/Syk/IRF5 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 2023;316:116742.
Lu C, Sun W. Prevalence of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 2014;311:199–200.
Paolillo S, Marsico F, Prastaro M, Renga F, Esposito L, De Martino F, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: definition, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications. Heart Fail Clin 2019;15:341–347.
Westermeier F, Riquelme JA, Pavez M, Garrido V, Díaz A, Verdejo HE, et al. New molecular insights of insulin in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front Physiol 2016;7:125.
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: a hyperglycaemia- and insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia 2018;61:21–28.
Evangelista I, Nuti R, Picchioni T, Dotta F, Palazzuoli A. Molecular dysfunction and phenotypic derangement in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:3264.
Kelshiker MA, Seligman H, Howard JP, Rahman H, Foley M, Nowbar AN, et al. Coronary flow reserve and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 2022;43:1582–1593.
Barrett EJ, Liu Z, Khamaisi M, King GL, Klein R, Klein BEK, et al. Diabetic microvascular disease: an endocrine society scientific statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;102:4343–4410.
Levelt E, Piechnik SK, Liu A, Wijesurendra RS, Mahmod M, Ariga R, et al. Adenosine stress CMR T1-mapping detects early microvascular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus without obstructive coronary artery disease. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2017;19:81.
Meimoun P, Clerc J, Ardourel D, Djou U, Martis S, Botoro T, et al. Assessment of left anterior descending artery stenosis of intermediate severity by fractional flow reserve, instantaneous wave-free ratio, and non-invasive coronary flow reserve. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2017;33:999–1007.
Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato, E, Funck-Brentano C, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2020;41:407–477.
Wang SH, Chu L, Xu Z, Zhou HL, Chen JF, Ning HF. Effect of Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pills on the immediate blood flow of patients with coronary slow flow. Chin J Integr Med 2019;25:360–365.
Zhao JJ, Zhou Y, Liu HH, Zheng ZH, Liu SQ, Peng JH, et al. Effect of Musk Tongxin Dropping Pill on myocardial remodeling and microcirculation dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2021;2021:6620564.
Elgendy IY, Pepine CJ. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: is ischemia due to coronary microvascular dysfunction a mechanistic factor? Am J Med 2019;132:692–697.
Uchida Y, Ichimiya S, Ishii H, Kanashiro M, Watanabe J, Yoshikawa D, et al. Impact of metabolic syndrome on various aspects of microcirculation and major adverse cardiac events in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Circ J 2012;76:1972–1979.
Lai J, Chen F, Chen J, Ruan G, He M, Chen C, et al. Overexpression of decorin promoted angiogenesis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via IGF1R-AKT-VEGF signaling. Sci Rep 2017;7:44473.
Spoladore R, Fisicaro A, Faccini A, Camici PG. Coronary microvascular dysfunction in primary cardiomyopathies. Heart 2014;100:806–813.
Xue C, Chen K, Gao Z, Bao T, Dong L, Zhao L, et al. Common mechanisms underlying diabetic vascular complications: focus on the interaction of metabolic disorders, immuno-inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. Cell Commun Signal 2023;21:298.
Fadini GP, Albiero M, Bonora BM, Avogaro A. Angiogenic abnormalities in diabetes mellitus: mechanistic and clinical aspects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019;104:5431–5444.
Kariuki D, Aouizerat BE, Asam K, Kanaya AM, Zhang L, Florez JC, et al. MicroRNA biomarkers target genes and pathways associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023;203:110868.
Li CL, Liu B, Wang ZY, Xie F, Qiao W, Cheng J, et al. Salvianolic acid B improves myocardial function in diabetic cardiomyopathy by suppressing IGFBP3. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2020;139:98–112.
Kuppuswamy S, Annex BH, Ganta VC. Targeting anti-angiogenic VEGF165b-VEGFR1 signaling promotes nitric oxide independent therapeutic angiogenesis in preclinical peripheral artery disease models. Cells 2022;11:2676.
Ambasta RK, Adeshara K, Yadav S, Kumar P. VEGF/CDK2 are involved in diabetic organ regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020;529:1094–1100.
Lungu CN, Mehedinti MC. Molecular motifs in vascular morphogenesis: vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) as the leading promoter of angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:12169.
Zhou Y, Zhu X, Cui H, Shi J, Yuan G, Shi S, et al. The role of the VEGF family in coronary heart disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021;8:738325.
Zhai S, Zhang XF, Lu F, Chen WG, He X, Zhang CF, et al. Chinese medicine Gegen-Danshen extract protects from myocardial ischemic injury through promoting angiogenesis via up-regulation of VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 2021;267:113475.
Karaman S, Leppänen VM, Alitalo K. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in development and disease. Development 2018;145:dev151019.
Wang J, Zhang Y, Liu YM, Guo LL, Wu P, Dong Y, et al. Huoxue Anxin Recipe promotes myocardium angiogenesis of acute myocardial infarction rats by up-regulating miR-210 and vascular endothelial growth factor. Chin J Integr Med 2016;22:685–90.
Huang F, Liu Y, Yang X, Che D, Qiu K, Hammock BD, et al. Shexiang Baoxin Pills promotes angiogenesis in myocardial infarction rats via up-regulation of 20-HETE-mediated endothelial progenitor cells mobilization. Atherosclerosis 2017;263:184–191.
Pan D, Xu L, Chen P, Miao L, Tian Y, Shi D, et al. Panax Quinquefolium Saponins enhances angiogenesis in rats with diabetes and myocardial infarction. J Ethnopharmacol 2024;319:117252.
Abhinand CS, Galipon J, Mori M, Ramesh P, Prasad TSK, Raju R, et al. Temporal phosphoproteomic analysis of VEGF-A signaling in HUVECs: an insight into early signaling events associated with angiogenesis. J Cell Commun Signal 2023;17:1067–1079.
Kuo HM, Lin CY, Lam HC, Lin PR, Chan HH, Tseng JC, et al. PTEN overexpression attenuates angiogenic processes of endothelial cells by blockade of endothelin-1/endothelin B receptor signaling. Atherosclerosis 2012;221:341–349.
Park JB, Kwon SK, Nagar H, Jung SB, Jeon BH, Kim CS, et al. Rg3-enriched Korean Red Ginseng improves vascular function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Ginseng Res 2014;38:244–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cui XY and Bai YL performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Liu TH supervised this study. Zhang MD and Li GD analyzed data in this study. Zhang YT and Yuan YY provided technical support. Zhang YW, Yu LS and Han LN contributed to writing assistance and proofreading the manuscript. Wu Y made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81930113)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Xy., Liu, Th., Bai, Yl. et al. Shexiang Tongxin Dropping Pill Promotes Angiogenesis through VEGF/eNOS Signaling Pathway on Diabetic Coronary Microcirculation Dysfunction. Chin. J. Integr. Med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3658-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3658-z