Abstract
Objective
To investigate the potential alleviating effects of acupuncture on maternal separation (MS)-induced changes in plasma pro-inflammatory cytokine levels of rat pups.
Methods
On postnatal day 15, rat pups were randomly assigned to 4 groups (n=6 per group) using a random number table: normal, MS, MS with acupuncture stimulation at Shenmen (HT 7) acupoint (MS+HT 7), and MS with acupuncture stimulation at Chengshan (BL 57) acupoint (MS+BL 57) groups. Rat pups in the normal group were housed with their mothers under standard conditions; those in the MS, MS+HT 7 and MS+BL 57 groups were maternally separated and individually maintained. Acupuncture stimulation was performed at HT 7 or BL 57 acupoints once a day for 7 consecutive days. A tail suspension test was performed to measure immobility time of rats and the plasma was collected on postnatal day 21, then levels of corticosterone (CORT), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in plasma were measured.
Results
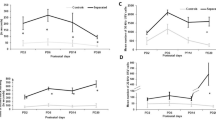
Compared with the normal group, the immobility time and the plasma levels of CORT, IL-1β, IL-6 and GDNF in the MS group were significantly increased (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with the MS group, the immobility time and the plasma levels of CORT, IL-1β, IL-6 and GDNF were significantly reduced in the MS+HT 7 group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Moreover, the immobility time and plasma levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in the MS+HT 7 group were significantly lower than those in the MS+BL 57 group (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Acupuncture stimulation at HT 7 can alleviate the behavioral impairment and changes of the cytokines by MS, indicating that acupuncture can help to relieve MS-induced depression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Felger JC, Lotrich FE. Inflammatory cytokines in depression: neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuroscience 2013;246:199–229.
Bae CH, Kim DS, Jun YL, Kwon S, Park HJ, Hahm DH, et al. Proteomic analysis of the effect of acupuncture on the suppression of kainic acid-induced neuronal destruction in mouse hippocampus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013;2013:436315.
Wang WD, Lu XY, Ng SM, Hong L, Zhao Y, Lin YN, et al. Effects of electro-acupuncture on personality traits in depression: a randomized controlled study. Chin J Integr Med 2013;19:777–782.
Park HJ, Chae Y, Jang J, Shim I, Lee H, Lim S. The effect of acupuncture on anxiety and neuropeptide Y expression in the basolateral amygdala of maternally separated rats. Neurosci Letters 2005;377:179–184.
Park HJ, Lim S, Lee HS, Lee HJ, Yoo YM, Kim SA, et al. Acupuncture enhances cell proliferation in dentate gyrus of maternally-separated rats. Neurosci Letters 2002;319:153–156.
Park HJ, Chae Y, Kim JW, Lee H, Chung JH. Effect of acupuncture on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system in maternal separation rats. Cellul Molecul Neurobiol 2011;31:1123–1127.
Kwon S, Kim D, Park H, Yoo D, Park HJ, Hahm DH, et al. Prefrontal-limbic change in dopamine turnover by acupuncture in maternally separated rat pups. Neurochem Res 2012;37:2092–2098.
Park H, Yoo D, Kwon S, Yoo TW, Park HJ, Hahm DH, et al. Acupuncture stimulation at HT7 alleviates depressioninduced behavioral changes via regulation of the serotonin system in the prefrontal cortex of maternally-separated rat pups. J Physiolog Sci 2012;62:351–357.
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P. The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 1985;85:367–370.
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A. The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2005;29:571–625.
Hache G, Guiard BP, Le Dantec Y, Orvoen S, David DJ, Gardier AM, et al. Antinociceptive effects of fluoxetine in a mouse model of anxiety/depression. Neuroreport 2012;23:525–529.
Bulbul M, Babygirija R, Cerjak D, Yoshimoto S, Ludwig K, Takahashi T. Impaired adaptation of gastrointestinal motility following chronic stress in maternally separated rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;302:G702–G711.
Wuppen K, Oesterle D, Lewicka S, Kopitz J, Plaschke K. A subchronic application period of glucocorticoids leads to rat cognitive dysfunction whereas physostigmine induces a mild neuroprotection. J Neural Transmiss 2010;117:1055–1065.
Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ben-Menachem-Zidon O, Licht T, Weidenfeld J, Ben-Hur T, et al. Brain interleukin-1 mediates chronic stress-induced depression in mice via adrenocortical activation and hippocampal neurogenesis suppression. Molecul Psychiatry 2008;13:717–728.
Monje FJ, Cabatic M, Divisch I, Kim EJ, Herkner KR, Binder BR, et al. Constant darkness induces IL-6-dependent depression-like behavior through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Neurosci 2011;31:9075–9083.
Hocaoglu C, Kural B, Aliyazicioglu R, Deger O, Cengiz S. IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha and its relationship with lipid parameters in patients with major depression. Metabol Brain Dis 2012;27:425–430.
Sukoff Rizzo SJ, Neal SJ, Hughes ZA, Beyna M, Rosenzweig-Lipson S, Moss SJ, et al. Evidence for sustained elevation of IL-6 in the CNS as a key contributor of depressive-like phenotypes. Translat Psychiatry 2012;2:e199.
Jiang SH, Tu WZ, Zou EM, Hu J, Wang S, Li JR, et al. Neuroprotective effects of different modalities of acupuncture on traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014;2014:431580.
Sun H, Zhao H, Zhang J, Bao F, Wei J, Wang DH, et al. Effect of acupuncture at Baihui (GV 20) and Zusanli (ST 36) on the level of serum inflammatory cytokines in patients with depression. Chin Acupunct Moxibust (Chin) 2010;30:195–199.
Ducray A, Krebs SH, Schaller B, Seiler RW, Meyer M, Widmer HR. GDNF family ligands display distinct action profiles on cultured GABAergic and serotonergic neurons of rat ventral mesencephalon. Brain Res 2006;1069:104–112.
Gratacos E, Perez-Navarro E, Tolosa E, Arenas E, Alberch J. Neuroprotection of striatal neurons against kainate excitotoxicity by neurotrophins and GDNF family members. J Neurochem 2001;78:1287–1296.
Rosa AR, Frey BN, Andreazza AC, Cereser KM, Cunha AB, Quevedo J, et al. Increased serum glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor immunocontent during manic and depressive episodes in individuals with bipolar disorder. Neurosci Letters 2006;407:146–150.
Takebayashi M, Hisaoka K, Nishida A, Tsuchioka M, Miyoshi I, Kozuru T, et al. Decreased levels of whole blood glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in remitted patients with mood disorders. Internat J Neuropsychopharmacol 2006;9:607–612.
Otsuki K, Uchida S, Hobara T, Yamagata H, Watanabe Y. Epigenetic regulation in depression. Jpn J Psychopharmacol 2012;32:181–186.
Jiang P, Dang RL, Li HD, Zhang LH, Zhu WY, Xue Y, et al. The impacts of swimming exercise on hippocampal expression of neurotrophic factors in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014;2014:729827.
Liu Q, Zhu HY, Li B, Wang YQ, Yu J, Wu GC. Chronic clomipramine treatment restores hippocampal expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in a rat model of depression. J Affect Disorders 2012;141:367–372.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. NRF- 2014R1A5A2009936)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Bae, CH., Jun, Y.L. et al. Acupuncture alters pro-inflammatory cytokines in the plasma of maternally separated rat pups. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 943–947 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2827-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2827-8