Abstract
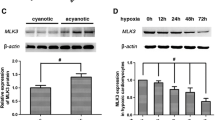
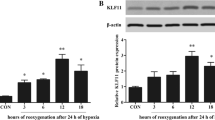
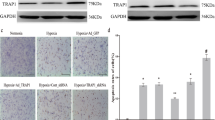
Hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis is one major pathological change of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), but the underlying mechanism remains unexplored. CDC-like kinase 3 (CLK3) plays crucial roles in cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and nucleotide metabolism, however, the role of CLK3 in AMI, especially hypoxia-induced apoptosis, is largely unknown. The expression of CLK3 was elevated in mouse myocardial infarction (MI) models and neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) under hypoxia. Furthermore, CLK3 knockdown significantly promoted apoptosis and inhibited NRVM survival, while CLK3 overexpression promoted NRVM survival and inhibited apoptosis under hypoxic conditions. Mechanistically, CLK3 regulated the phosphorylation status of AKT, a key player in the regulation of apoptosis. Furthermore, overexpression of AKT rescued hypoxia-induced apoptosis in NRVMs caused by CLK3 deficiency. Taken together, CLK3 deficiency promotes hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AKT signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Borer JS, Truter S, Herrold EM, Falcone DJ, Pena M, Carter JN, Dumlao TF, Lee JA, Supino PG (2002) Myocardial fibrosis in chronic aortic regurgitation: molecular and cellular responses to volume overload. Circulation 105:1837–1842
Bullock AN, Das S, Debreczeni JE, Rellos P, Fedorov O, Niesen FH, Guo K, Papagrigoriou E, Amos AL, Cho S, Turk BE, Ghosh G, Knapp S (2009) Kinase domain insertions define distinct roles of CLK kinases in SR protein phosphorylation. Structure 17:352–362
Cesana M, Guo MH, Cacchiarelli D, Wahlster L, Barragan J, Doulatov S, Vo LT, Salvatori B, Trapnell C, Clement K, Cahan P, Tsanov KM, Sousa PM, Tazon-Vega B, Bolondi A, Giorgi FM, Califano A, Rinn JL, Meissner A, Hirschhorn JN, Daley GQ (2018) A CLK3-HMGA2 alternative splicing axis impacts human hematopoietic stem cell molecular identity throughout development. Cell Stem Cell 22:575-588.e577
Chen Y, Li X, Li B, Wang H, Li M, Huang S, Sun Y, Chen G, Si X, Huang C, Liao W, Liao Y, Bin J (2019) Long non-coding RNA ECRAR triggers post-natal myocardial regeneration by activating ERK1/2 signaling. Mol Ther 27:29–45
Cheng Y, Shen A, Wu X, Shen Z, Chen X, Li J, Liu L, Lin X, Wu M, Chen Y, Chu J, Peng J (2021) Qingda granule attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis and modulates the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 133:111022
Damluji AA, van Diepen S, Katz JN, Menon V, Tamis-Holland JE, Bakitas M, Cohen MG, Balsam LB, Chikwe J (2021) Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation 144:e16–e35
Fan M, Yang K, Wang X, Chen L, Gill PS, Ha T, Liu L, Lewis NH, Williams DL, Li C (2023) Lactate promotes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Snail1 lactylation after myocardial infarction. Sci Adv 9:eadc9465
Gong FF, Vaitenas I, Malaisrie SC, Maganti K (2021) Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction: a review. JAMA Cardiol 6:341–349
Hu X, Liu H, Li M, Zhu J, Yu Z (2021) Transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of a peptide derived from CRYAB on the CoCl(2)-induced hypoxic HL-1 cardiomyocytes. J Thromb Thrombolysis 51:265–276
Hu Y, Lu H, Li H, Ge J (2022) Molecular basis and clinical implications of HIFs in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Mol Med 28:916–938
Jellis C, Martin J, Narula J, Marwick TH (2010) Assessment of nonischemic myocardial fibrosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 56:89–97
Knutson AK, Williams AL, Boisvert WA, Shohet RV (2021) HIF in the heart: development, metabolism, ischemia, and atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 131:e137557
Li J, Lin X, Chu J, Wu X, Chen X, Liu L, Shen A, Wu M, Peng J, Shen ZJB, Biomedecine p, pharmacotherapie (2021) Qingda granule attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis and modulates the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 133:111022
Liu M, Liu P, Zheng B, Liu Y, Li L, Han X, Liu Y, Chu L (2022) Cardioprotective effects of alantolactone on isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury and cobalt chloride-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 36:1–18
Mackman N, Bergmeier W, Stouffer GA, Weitz JI (2020) Therapeutic strategies for thrombosis: new targets and approaches. Nat Rev Drug Discov 19:333–352
Martín Moyano P, Němec V, Paruch K (2020) Cdc-Like Kinases (CLKs): biology, chemical probes, and therapeutic potential. Int J Mol Sci 21:7549
Mohammad DK, Ali RH, Turunen JJ, Nore BF, Smith CI (2016) B cell receptor activation predominantly regulates AKT-mTORC1/2 substrates functionally related to RNA processing. PLoS One 11:e0160255
Nam SY, Seo HH, Park HS, An S, Kim JY, Yang KH, Kim CS, Jeong M, Jin YW (2010) Phosphorylation of CLK2 at serine 34 and threonine 127 by AKT controls cell survival after ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 285:31157–31163
Pan F, Xu X, Zhan Z, Xu Q (2021) 6-Gingerol protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced injury by regulating the KCNQ1OT1/miR-340-5p/PI3K/AKT pathway. Panminerva Med 63:482–490
Ruan W, Ma X, Bang IH, Liang Y, Muehlschlegel JD, Tsai KL, Mills TW, Yuan X, Eltzschig HK (2022) The hypoxia-adenosine link during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomedicines 10:1939
Sabatine MS, Braunwald E (2021) Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group: JACC Focus Seminar 2/8. J Am Coll Cardiol 77:2822–2845
Schäfer A, König T, Bauersachs J, Akin M (2022) Novel therapeutic strategies to reduce reperfusion injury after acute myocardial infarction. Curr Probl Cardiol 47:101398
Sun XH, Wang X, Zhang Y, Hui J (2019) Exosomes of bone-marrow stromal cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis under ischemic and hypoxic conditions via miR-486-5p targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Thromb Res 177:23–32
Virgirinia RP, Nakamura M, Takebayashi-Suzuki K, Fatchiyah F, Suzuki A (2021) The dual-specificity protein kinase Clk3 is essential for Xenopus neural development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 567:99–105
Wei L, Zhou Q, Tian H, Su Y, Fu GH, Sun T (2020) Integrin β3 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis via regulating the PTEN/Akt/mTOR and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Biol Sci 16:644–654
Wen Z, Mai Z, Zhu X, Wu T, Chen Y, Geng D, Wang J (2020) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate cardiomyocyte apoptosis in hypoxic conditions through microRNA144 by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:36
Yu H, Chen B, Ren Q (2019) Baicalin relieves hypoxia-aroused H9c2 cell apoptosis by activating Nrf2/HO-1-mediated HIF1α/BNIP3 pathway. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3657–3663
Zhang Q, Wang L, Wang S, Cheng H, Xu L, Pei G, Wang Y, Fu C, Jiang Y, He C, Wei Q (2022a) Signaling pathways and targeted therapy for myocardial infarction. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:78
Zhang Y, Liu S, Ma J-L, Chen C, Huang P, Ji J-H, Wu D, Ren L-Q (2022b) Apocynum venetum leaf extract alleviated doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through the AKT/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 94:153815
Zhou Q, Lin M, Feng X, Ma F, Zhu Y, Liu X, Qu C, Sui H, Sun B, Zhu A, Zhang H, Huang H, Gao Z, Zhao Y, Sun J, Bai Y, Jin J, Hong X, Zou C, Zhang Z (2020) Targeting CLK3 inhibits the progression of cholangiocarcinoma by reprogramming nucleotide metabolism. J Exp Med 217:e20191779
Funding
This research was funded by Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Program of Shandong Province (202103010947), the Scientific Research Foundation of Shandong Provincial Third Hospital (Q2023001), Key R&D Program of Shandong Province, China (2019GSF108249), and Jiangxi Province Municipal Health Commission Science Technology Grant (202210097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lixiao Zhen, Bowen Lin, and Tianyou Yuan conceived and designed experiments. Xiue Ma, Liming Gao and and Rucun Ge performed experiments, analyzed data, and prepared figures. Xiue Ma made the original draft preparation. Bowen Lin revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Gao, L., Ge, R. et al. CDC-like kinase 3 deficiency aggravates hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AKT signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-024-00886-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-024-00886-3