Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study was to determine the clinicopathological features, surgical management, and prognosis of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms (SPNs) of the pancreas.
Methods
This study conducted a retrospective analysis of 97 patients who underwent surgery for a pathologically confirmed SPN in five hospitals between January 1996 and December 2014.
Results
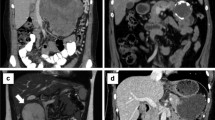
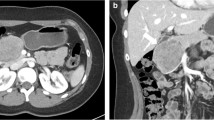
The 97 cases included 93 female and 4 male patients, and the average age was 31.2 years. The tumor was located in the body or tail (70.1 %), the head (20.6 %), and the neck (9.3 %). All patients underwent surgical exploration, including distal pancreatectomy (63.9 %), pancreaticoduodenectomy (20.6 %) (partial portal vein or superior mesenteric vein resection and artificial vascular graft reconstruction performed in 4.1 % of the patients), central pancreatectomy (10.3 %), enucleation (5.2 %), and liver resection (1.0 %). 16.5 % of the patients had malignant tumors. The positive rate of Ki-67 was 66.7 % in patients diagnosed with a malignant neoplasm and was comparable to 8.4 % of the patients diagnosed to have a benign neoplasm (p < 0.001). After a median follow-up of 70.1 months, three patients had recurrence and one patient died of liver metastasis.
Conclusions
SPN is a rare neoplasm with low malignant potential. Surgical resection is warranted even in the presence of local invasion or metastases as patients demonstrate excellent long-term survival. Positive immunoreactivity for Ki-67 may predict the malignant potential and poor outcome of SPNs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang F, Jin C, Long J, Yu XJ, Xu J, Di Y, Li J, Fu de L, Ni QX. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a case series of 26 consecutive patients. Am J Surg 2009;198:210–5.
Wang XG, Ni QF, Fei JG, Zhong ZX, Yu PF. Clinicopathologic features and surgical outcome of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: analysis of 17 cases. World J Surg Oncol 2013;11:38.
Franz, VK. Papillary tumors of the pancreas: benign or malignant? In: Franz VK (ed.) Tumors of the Pancreas. Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Washington, DC: US Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, 1959: 32–33.
Klöppel G, Hruban RH, Klimstra DS, Maitra A, Morohoshi T, Notohara K, Shimizu M, Terris B. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of pancreas. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC 2010; pp: 327–330.
Cai H, Zhou M, Hu Y, He H, Chen J, Tian W, Deng Y. Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical and pathological features of 33 cases. Surg Today 2013;43:148–54.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 2004;240:205–13.
Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G, Fingerhut A, Yeo C, Izbicki J, Neoptolemos J, Sarr M, Traverso W, Buchler M; International Study Group on Pancreatic Fistula Definition. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery 2005;138:8–13.
Yu PF, Hu ZH, Wang XB, Guo JM, Cheng XD, Zhang YL, Xu Q. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a review of 553 cases in Chinese literature. World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:1209–14.
Hu S, Huang W, Lin X, Wang Y, Chen KM, Chai W. Solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas: distinct patterns of computed tomography manifestation for male versus female patients. Radiol Med 2014;119:83–9.
Kim MJ, Choi DW, Choi SH, Heo JS, Sung JY. Surgical treatment of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas and risk factors for malignancy. Br J Surg 2014;101:1266–71.
Sun GQ, Chen CQ, Yao JY, Shi HP, He YL, Zhan WH. Diagnosis and treatment of solid pseudopapillary tumor of pancreas: a report of 8 cases with review of domestic literature. Chin J Gen Surg 2008; 17: 902–7
Ren Z, Zhang P, Zhang X, Liu B. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas: clinicopathologic features and surgical treatment of 19 cases. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:6889–97.
Jung WS, Kim JK, Yu JS, Kim JH, Cho ES, Chung JJ. Comparison of abdominal ultrasonographic findings with endoscopic ultrasonographic findings of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas. Ultrasound Q 2014;30:173–8.
Yin Q, Wang M, Wang C, Wu Z, Yuan F, Chen K, Tang Y, Zhao X, Miao F. Differentiation between benign and malignant solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas by MDCT. Eur J Radiol 2012;81:3010–8.
Kawamoto S, Scudiere J, Hruban RH, Wolfgang CL, Cameron JL, Fishman EK. Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: spectrum of findings on multidetector CT. Clin Imaging 2011;35:21–8.
Ventriglia A, Manfredi R, Mehrabi S, Boninsegna E, Negrelli R, Pedrinolla B, Pozzi Mucelli R. MRI features of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas. Abdom Imaging. 2014;39:1213–20.
Law JK, Stoita A, Wever W, Gleeson FC, Dries AM, Blackford A, Kiswani V, Shin EJ, Khashab MA, Canto MI, Singh VK, Lennon AM. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration improves the pre-operative diagnostic yield of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: an international multicenter case series (with video). Surg Endosc 2014;28:2592–8.
Virgilio E, Mercantini P, Ferri M, Cunsolo G, Tarantino G, Cavallini M, Ziparo V. Is EUS-FNA of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas as a preoperative procedure really necessary and free of acceptable risks? Pancreatology 2014;14:536–8.
Lee JK, Tyan YS. Detection of a solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas with F-18 FDG positron emission tomography. Clin Nucl Med 2005;30:187–8.
Nguyen NQ, Johns AL, Gill AJ, Ring N, Chang DK, Clarkson A, Merrett ND, Kench JG, Colvin EK, Scarlett CJ, Biankin AV. Clinical and immunohistochemical features of 34 solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;26:267–74.
Morikawa T, Onogawa T, Maeda S, Takadate T, Shirasaki K, Yoshida H, Ishida K, Motoi F, Naitoh T, Rikiyama T, Katayose Y, Egawa S, Unno M. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas: an 18-year experience at a single Japanese Institution. Surg Today 2013;43:26–32.
Cavallini A, Butturini G, Daskalaki D, Salvia R, Melotti G, Piccoli M, Bassi C, Pederzoli P. Laparoscopic pancreatectomy for solid pseudo-papillary tumors of the pancreas is a suitable technique; our experience with long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Ann Surg Oncol 2011;18:352–7.
Estrella JS, Li L, Rashid A, Wang H, Katz MH, Fleming JB, Abbruzzese JL, Wang H. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: clinicopathologic and survival analyses of 64 cases from a single institution. Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:147–57.
Lee JS, Han HJ, Choi SB, Jung CW, Song TJ, Choi SY. Surgical outcomes of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: a single institution’s experience for the last ten years. Am Surg 2012;78:216–9.
Cai Y, Ran X, Xie S, Wang X, Peng B, Mai G, Liu X. Surgical management and long-term follow-up of solid pseudopapillary tumor of pancreas: a large series from a single institution. J Gastrointest Surg 2014;18:935–40.
Cheng K, Shen B, Peng C, Yuan F, Yin Q. Synchronous portal-superior mesenteric vein or adjacent organ resection for solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas: a single-institution experience. Am Surg 2013;79:534–9.
Reddy S, Cameron JL, Scudiere J, Hruban RH, Fishman EK, Ahuja N, Pawlik TM, Edil BH, Schulick RD, Wolfgang CL. Surgical management of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas (Franz or Hamoudi tumors): a large single-institutional series. J Am Coll Surg 2009;208:950–9.
Kang CM, Kim KS, Choi JS, Kim H, Lee WJ, Kim BR. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas suggesting malignant potential. Pancreas 2006;32:276–80.
Machado MC, Machado MA, Bacchella T, Jukemura J, Almeida JL, Cunha JE. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: distinct patterns of onset, diagnosis, and prognosis for male versus female patients. Surgery 2008; 143: 29–34.
Lee SE, Jang JY, Hwang DW, Park KW, Kim SW. Clinical features and outcome of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm: differences between adults and children. Arch Surg 2008;143:1218–21.
Park JK, Cho EJ, Ryu JK, Kim YT, Yoon YB. Natural history and malignant risk factors of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas. Postgrad Med 2013;125:92–9.
Ho HK, Sang Y, Jung CK, Eun KP, Jin SS, Young HH, Koh YS, Cho CK, Shin SS, Kweon SS, Kim HS, Kim HJ. Clinical features and surgical outcome of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: 30 consecutive clinical cases. Hepatogastroenterology 2011;58:1002–8.
Yagcı A, Yakan S, Coskun A, Erkan N, Yıldırım M, Yalcın E, Postacı H. Diagnosis and treatment of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: experience of one single institution from Turkey. World J Surg Oncol 2013;11:308.
Yang F, Fu DL, Jin C, Long J, Yu XJ, Xu J, Ni QX. Clinical experiences of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas in China. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;23:1847–51.
Suzuki S, Hatori T, Furukawa T, Shiratori K, Yamamoto M. Clinical and pathological features of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas at a single institution. Dig Surg 2014;31:143–50.
Li L, Li J, Hao C, Zhang C, Mu K, Wang Y, Zhang T. Immunohistochemical evaluation of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: the expression pattern of CD99 is highly unique. Cancer Lett 2011;310:9–14.
Laje P, Bhatti TR, Adzick NS. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in children: a 15-year experience and the identification of a unique immunohistochemical marker. J Pediatr Surg 2013;48:2054–60.
Geers C, Moulin P, Gigot JF, Weynand B, Deprez P, Rahier J, Sempoux C. Solid and pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas—review and new insights into pathogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30:1243–49.
Kim CW, Han DJ, Kim J, Kim YH, Park JB, Kim SC. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: can malignancy be predicted? Surgery 2011; 149: 625–34.
Papavramidis T, Papavramidis S. Solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: review of 718 patients reported in English literature. J Am Coll Surg 2005; 200: 965–72.
Acknowledgments
We express our appreciation to Dr. Thomas Aloia (Surgical Oncology, MD Anderson) who has offered many valuable comments and suggestions. This study is supported by the Department of Health of Zhejiang Province (2013KYB043).
Conflict of Interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, P., Cheng, X., Du, Y. et al. Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasms of the Pancreas: a 19-Year Multicenter Experience in China. J Gastrointest Surg 19, 1433–1440 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2862-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2862-8