Summary
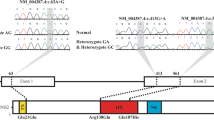
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a common acyanotic congenital cardiac disorder associated with genetic mutations. The objective of this study was to identify the genetic factors in a Chinese family with ASD patients by a whole exome sequencing approach. Causative ASD gene mutations were examined in 16 members from a three-generation family, among which 6 individuals were diagnosed as having ASD. One hundred and eighty-three unrelated healthy Chinese were recruited as a normal control group. Peripheral venous blood was collected from every subject for genetic analysis. Exome sequencing was performed in the ASD patients. Potential causal mutations were detected in non-ASD family members and normal controls by polymerase chain reaction and sequencing analysis. The results showed that all affected family members carried two novel compound mutations, c.1187delT of PCDHGA4 and c.2557insC of SLFN14, and these two mutations were considered to have synergetic function on ASD. In conclusion, the mutations of c.1187delT of PCDHGA4 and c.2557insC of SLFN14 may be pathogenic factors contributing to the development of ASD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Y, Duan W, Huang G, et al. Genome-wide copy number variant analysis for congenital ventricular septal defects in Chinese Han population. BMC Med Genomics, 2016,9:2
Fahed AC, Gelb BD, Seidman JG, et al. Genetics of congenital heart disease: the glass half empty. Circ Res, 2013,112(4):707–720
Zhu X, Deng X, Huang G, et al. A novel mutation of Hyaluronan synthase 2 gene in Chinese children with ventricular septal defect. PLoS One, 2014,9(2):e87437
Su W, Zhu P, Wang R, et al. Congenital heart diseases and their association with the variant distribution features on susceptibility genes. Clin Genet, 2016,91(3):349–354
Liu XY, Wang J, Zheng JH, et al. Involvement of a novel GATA4 mutation in atrial septal defects. Int J Mol Med, 2011,28(1):17–23
Mattapally S, Nizamuddin S, Murthy KS, et al. c.620C>T mutation in GATA4 is associated with congenital heart disease in South India. BMC Med Genet, 2015,16:7
Yang YQ, Wang J, Liu XY, et al. Mutation spectrum of GATA4 associated with congenital atrial septal defects. Arch Med Sci, 2013,9(6):976–983
Silvestry FE, Cohen MS, Armsby LB, et al. Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect and Patent Foramen Ovale: From the American Society of Echocardiography and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2015,28(8):910–958
Yang YQ, Wang J, Liu XY, et al. Novel GATA4 mutations in patients with congenital ventricular septal defects. Med Sci Monit, 2012, 18(6):CR344–CR350
Zhang KK, Xiang M, Zhou L, et al. Gene network and familial analyses uncover a gene network involving Tbx5/Osr1/Pcsk6 interaction in the second heart field for atrial septation. Hum Mol Genet, 2016,25(6):1140–1151
Wang J, Mao JH, Ding KK, et al. A novel NKX2. 6 mutation associated with congenital ventricular septal defect. Pediatr Cardiol, 2015,36(3):646–656
Sun YM, Wang J, Qiu XB, et al. A HAND2 Loss-of-Function Mutation Causes Familial Ventricular Septal Defect and Pulmonary Stenosis. G3 (Bethesda, Md.), 2016,6(4):987–992
Grimberg J, Nawoschik S, Belluscio L, et al. A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res, 1989,17(20):8390
Hirabayashi T, Yagi T. Protocadherins in neurological diseases. Adv Neurobiol, 2014,8:293–314
de la Casa-Esperon E. From mammals to viruses: the Schlafen genes in developmental, proliferative and immune processes. Biomol Concepts, 2011,2(3):159–169
Marconi C, Di Buduo CA, Barozzi S, et al. SLFN14-related thrombocytopenia: identification within a large series of patients with inherited thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost, 2016,115(5):1076–1079
Fletcher SJ, Johnson B, Lowe GC, et al. SLFN14 mutations underlie thrombocytopenia with excessive bleeding and platelet secretion defects. J Clin Investig, 2015,125(9):3600–3605
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to all the family members for their participation in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Health and Family Planning Commission of Hubei Province of China (No. WJ2017M053).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, W., Wang, Rc., Lohano, M.K. et al. Identification of Two Mutations in PCDHGA4 and SLFN14 Genes in an Atrial Septal Defect Family. CURR MED SCI 38, 989–996 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1974-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1974-2