Summary
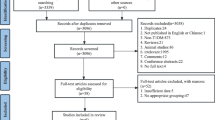
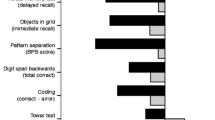
The purpose of this study was to investigate the existence and extent of cognitive impairment in adult diabetes mellitus (DM) patients with episodes of recurrent severe hypoglycemia, by using meta-analysis to synthesize data across studies. PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane library search engines were used to identify studies on cognitive performance in DM patients with recurrent severe hypoglycemia. Random-effects meta-analysis was performed on seven eligible studies using an inverse-variance method. Effect sizes, which are the standardized differences between the experimental group and the control group, were calculated. Of the 853 studies, 7 studies met the inclusion criteria. Compared with control subjects, the adult DM patients with episodes of recurrent severe hypoglycemia demonstrated a significantly lowered performance on memory in both types of DM patients, and poor performance of processing speed in type 2 DM patients. There was no significant difference between adult DM patients with and those without severe hypoglycemia in other cognitive domains such as general intelligence, executive function, processing speed and psychomotor efficiency. Our results seem to confirm the hypothesis that cognitive dysfunction is characterized by worse memory and processing speed in adult DM patients with a history of recurrent severe hypoglycemia, whereas general intelligence, executive function, and psychomotor efficiency are spared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjørgaas M, Gimse R, Vik T, et al. Cognitive function in type 1 diabetic children with and without episodes of severe hypoglycaemia. Acta Paediatr, 1997,86(2):148–153
Bergada I, Suissa S, Dufresne J, et al. Severe hypoglycemia in IDDM children. Diabetes Care, 1989,12(4):239–244
Languren G, Montiel T, Julio-Amilpas A, et al. Neuronal damage and cognitive impairment associated with hypoglycemia: An integrated view. Neurochem Int, 2013,63(4): 331–343
Strachan MW. R D Lawrence Lecture 2010. The brain as a target organ in Type 2 diabetes: exploring the links with cognitive impairment and dementia. Diabet Med, 2011,28(2):141–147
Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. J Pediatr, 1994,125(2): 177–188
Musen G, Jacobson AM, Ryan CM, et al. Impact of diabetes and its treatment on cognitive function among adolescents who participated in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care, 2008,31(10):1933–1938
Egger M, Gschwend S, Smith GD, et al. Increasing incidence of hypoglycemic coma in children with IDDM. Diabetes Care, 1991,14(11):1001–1005
McNay EC, Cotero VE. Mini-review: impact of recurrent hypoglycemia on cognitive and brain function. Physiol Behav, 2010,100(3):234–238
Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. N Engl J Med, 1993,329(14):977–986
Blasetti A, Chiuri RM, Tocco AM, et al. The effect of recurrent severe hypoglycemia on cognitive performance in children with type 1 diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Child Neurol, 2011,26(11):1383–1391
Ho MS, Weller NJ, Ives FJ, et al. Prevalence of structural central nervous system abnormalities in early-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr, 2008,153(3):385–390
Warren RE, Frier BM. Hypoglycaemia and cognitive function. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2005,7(5):493–503
Kramer L, Fasching P, Madl C, et al. Previous episodes of hypoglycemic coma are not associated with permanent cognitive brain dysfunction in IDDM patients on intensive insulin treatment. Diabetes, 1998,47(12):1909–1914
Strachan MW, Deary IJ, Ewing FM, et al. Recovery of cognitive function and mood after severe hypoglycemia in adults with insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetes Care, 2000,23(3):305–312
Brismar T, Maurex L, Cooray G, et al. Predictors of cognitive impairment in type 1 diabetes. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2007,32(8-10):1041–1051
Genuth S, Nathan DM, Zinman B, et al. Long-term effect of diabetes and its treatment on cognitive function: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. N Engl J Med, 2007,356(18): 1842–1852
Aung PP, Strachan MW, Frier BM, et al. Severe hypoglycaemia and late-life cognitive ability in older people with type 2 diabetes: the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabet Med, 2012,29(3):328–336
Yaffe K, Falvey CM, Hamilton N, et al. Association between hypoglycemia and dementia in a biracial cohort of older adults with diabetes mellitus. JAMA Intern Med, 2013,173(14):1300–1306
Feinkohl I, Aung PP, Keller M, et al. Severe hypoglycemia and cognitive decline in older people with type 2 diabetes: the Edinburgh type 2 diabetes study. Diabetes Care, 2014,37(2):507–515
Dickerson BC, Eichenbaum H. The episodic memory system: neurocircuitry and disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2010,35(1):86–104
Auer RN. Hypoglycemic brain damage. Metab Brain Dis, 2004,19(3-4):169–175
Musen G, Simonson DC, Bolo NR, et al. Regional brain activation during hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2008,93(4):1450–1457
Thomas J, Garg ML, Smith DW. Altered expression of histone and synaptic plasticity associated genes in the hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis, 2013,28(4):613–618
Kirchhoff BA, Lugar HM, Smith SE, et al. Hypoglycaemia-induced changes in regional brain volume and memory function. Diabet Med, 2013,30(4):151–156
Maeshima S, Ozaki F, Masuo O, et al. Memory impairment and spatial disorientation following a left retrosplenial lesion. J Clin Neurosci, 2001,8(5):450–451
Sinclair AJ, Girling AJ, Bayer AJ. Cognitive dysfunction in older subjects with diabetes mellitus: impact on diabetes self-management and use of care services. All Wales Research into Elderly (AWARE) Study. Diabetes Res Clin Practic, 2000,50(3):203–212
Brands AM, Biessels GJ, de Haan EH, et al. The effects of type 1 diabetes on cognitiveperformance: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 2005,28(3):726–735
Bauduceau B, Doucet J, Bordier L, et al. Hypoglycaemia and dementia in diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab, 2010,36 (Suppl 3):106–111
Bordier L, Doucet J, Boudet J, et al. Update on cognitive decline and dementia in elderly patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab, 2014,40(5):331–337
Cukierman-Yaffe T. Diabetes, dysglycemia and cognitive dysfunction. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2014,30(5):341–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2016CFB671), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M590696).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yx., Liu, Zr., Yu, Y. et al. Effect of recurrent severe hypoglycemia on cognitive performance in adult patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. CURR MED SCI 37, 642–648 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-017-1784-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-017-1784-y