Abstract
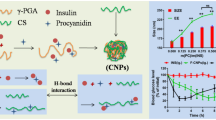
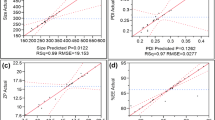
Novel insulin-loaded nanoparticles based on hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin modified carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC-HP-β-CD) were prepared to improve the oral bioavailability of insulin. The CMC-HP-β-CD was characterized by FT-IR spectroscopy and 1H-NMR spectra. The insulin-loaded nanoparticles were prepared through crosslinking with calcium ions, and the morphology and size of the prepared nanoparticles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Cumulative release in vitro study was performed respectively in simulated gastric medium fluid (SGF, pH=1.2), simulated intestinal fluid (SIF, pH=6.8) and simulated colonic fluid (SCF, pH=7.4). The encapsulation efficiency of insulin was up to 87.14 ± 4.32% through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Statistics indicated that only 15% of the encapsulated insulin was released from the CMC-HP-β-CD nanoparticles in 36 h in SGF, and about 50% of the insulin could be released from the nanoparticles in SIF, whereas more than 80% was released in SCF. In addition, the solution containing insulin nanoparticles could effectively reduce the blood glucose level of diabetic mice. The cytotoxicity test showed that the samples had no cytotoxicity. CMC-HP-β-CD nanoparticles are promising candidates as potential carriers in oral insulin delivery systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mansourpour M, Mahjub R, Amini M, et al. Development of Acidresistant Alginate/Trimethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Cationic β-cyclodextrin Polymers for Insulin Oral Delivery[J]. Aaps Pharmscitech., 2015, 16(4): 952–962
De Araújo TM, Teixeira Z, Barbosa-Sampaio HC, et al. Insulin-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanoparticles: Efficient, Sustained and Safe Insulin Delivery System[J]. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol., 2013, 9(6): 1098–1106
Azevedo JR, Sizilio RH, Brito MB, et al. Physical and Chemical Characterization Insulin-loaded Chitosan-TPP Nanoparticles[J]. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2011, 106(3): 685–689
Zhang X, Sun M, Zheng A, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Insulin-loaded Bioadhesive PLGA Nanoparticles for Oral Administration[J]. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 2012, 45(5): 632–638
Al-Qadi S, Grenha A, Carrión-Recio D, et al. Microencapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Protein Delivery: In vivo evaluation of Insulin-loaded Formulations[J]. J. Control. Release., 2012, 157(3): 383–390
Santander-Ortega MJ, Bastos-Gonzalez D, Ortega-Vinuesa JL, et al. Insulin-loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for Oral Administration: An in vitro Physico-chemical Characterization[J]. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol., 2009, 5(1): 45–53
Sarmento B, Ribeiro AJ, Veiga F, et al. Insulin-loaded Nanoparticles are Prepared by Alginate Ionotropic Pre-gelation Followed by Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complexation[J]. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 2007, 7(8): 2833–2841
Cui F, Qian F, Zhao Z, et al. Preparation, Characterization, and Oral Delivery of Insulin Loaded Carboxylated Chitosan Grafted poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Nanoparticles[J]. Biomacromolecules., 2009, 10(5): 1253–1258
Cheng G, Liu T, Dang Y, et al. pH/redox Responsive Core Cross-Linked Nanoparticles from Thiolated Carboxymethyl Chitosan for in Vitro Release study of Methotrexate[J]. Carbohyd Polym., 2014, 111(20): 964–970
Giovino C, Ayensu I, Tetteh J, et al. Development and Characterisation of Chitosan Films Impregnated with Insulin Loaded PEG-b-PLA Nanoparticles (NPs): A Potential Approach for Buccal Delivery of Macromolecules[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2012, 428(1/2): 143–151
Gerweck LE, Seetharaman K. Cellular pH Gradient in Tumor Versus Normal Tissue: Potential Exploitation for the Treatment of Cancer[J]. Cancer. Res., 1996, 56(6): 1194–1198
Liu C, Fan W, Chen X, et al. Self-assembled Nanoparticles Based on Linoleic-acid Modified Carboxymethyl-chitosan as Carrier of Adriamycin (ADR)[J]. Curr. Appl. Phys., 2007, 7: 125–129
Yang J, Sun H, Song C. Preparation, Characterization and in Vivo Evaluation of pH-sensitive Oral Insulin-loaded poly(lactic-coglycolicacid) Nanoparticles[J]. Diabetes. Obes. Metab., 2012, 14(4): 358–364
Elsayed, A, Al-Remawi M, Maghrabi I, et al. Development of Insulin Loaded Mesoporous Silica Injectable Particles Layered by Chitosan as a Controlled Release Delivery System[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2014, 461(1/2): 448–458
Cui FD, Tao AJ, Cun DM, et al. Preparation of Insulin Loaded PLGAHp55 Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery[J]. J. Pharm. Sci., 2007, 96(2): 421–427
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Na L, et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel β-cyclodextrin Derivative for Oral Insulin Delivery and Absorption[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2013, 61: 494–500
Kumar PS, Saini TR, Chandrasekar D, et al. Novel Approach for Delivery of Insulin Loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles Using a Combination of Stabilizers[J]. Drug. Deliv., 2007, 14(8): 517–523
Gould S., Scott R. C. 2-Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD): a Toxicology Review[J]. Food. Chem. Toxicol., 2005, 43(10): 1451–1459
Tao HQ, Meng Q, Li MH, et al. HP-β-CD-PLGA Nanoparticles Improve the Penetration and Bioavailability of Puerarin and Enhance the Therapeutic Effects on Brain Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in Rats[J]. N-S. Arch. Pharmacol., 2013, 386(1): 61–70
Zhang X, Zhang X, Gao X, et al. β-Cyclodextrin Grafting Hyperbranched Polyglycerols as Carriers for Nasal Insulin Delivery[J]. Carbohyd Polym., 2011, 84(4): 1419–1425
Liu M, Wen C, Sun Y, et al. Preparation, Characterization and in vivo Evaluation of Formulation of Repaglinide with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2014, 477(1–2): 159–166
Zhang L, Zhu W, Lin Q, et al. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Functionalized Calcium Carbonate Microparticles as a Potential Carrier for Enhancing Oral Delivery of Water-insoluble Drugs[J]. Int. J. Nanomed., 2015, 10: 3291–3302
Dan W, Li H, Gu J, et al. Ternary System of Dihydroartemisinin with Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and Lecithin: Simultaneous Enhancement of drug Solubility and Stability in Aqueous Solutions[J]. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed., 2013, 83(83): 141–148
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Na L, et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel β-cyclodextrin Derivative for Oral Insulin Delivery and Absorption[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2013, 61: 494–500
Zhang L, Jiang H, Zhu W, et al. Improving the Stability of Insulin Solutions Containing Intestinal Proteases in vitro[J]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2008, 9: 2376–2387
Zhang L, Song L, Zhang C, et al. Improving Intestinal Insulin Absorption Efficiency Through Coadministration of Cell-penetrating Peptide and Hygroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin[J]. Carbohyd Polym., 2012, 87: 1822–1827
Aiassa V, Zoppi A, Albesa I, et al. Inclusion Complexes of Chloramphenicol with β -cyclodextrin and Aminoacids as a Way to Increase drug Solubility and Modulate ROS Production[J]. Carbohyd Polym., 2015, 121: 320–327
Bruno S, Donatella M, Maria C B, et al. Effect of Chitosan Coating in Overcoming the Phagocytosis of Insulin Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by Mononuclear Phagocyte System[J]. Carbohyd Polym., 2011, 84(3): 919–925
Lin CC, Lin CW. Preparation of N, O-carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles as an Insulin Carrier[J]. Drug. Deliv., 2009, 16(8): 458–464
Mayura O, Jagdish S. Chitosan-zinc-insulin Complex Incorporated Thermosensitive Polymerfor Controlled Delivery of Basal Insulin in Vivo[J]. J. Control. Release., 2012(163): 145–153
Jin Y, Song YP, Zhu X, et al. Goblet Cell-targeting Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery and the Influence of Mucus on Insulin Transport[J]. Biomaterials., 2012, 33: 1573–1582
Wan Y, Wu C, Xiong G, et al. Mechanical Properties and Cytotoxicity of Nanoplate-like Hydroxyapatite/polylactide Nanocomposites Prepared by Intercalation Technique[J]. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed., 2015, 47: 29–37
He M, Xue J, Geng H, et al. Fibrous Guided Tissue Regeneration Membrane Loaded with Anti-inflammatory Agent Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning for the Purpose of Controlled Release[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 335: 121–129
Zhan J, Tian X, Zhu Y, et al. Oxygen Plasma Modified P(3HB-4HB) Used as Anticoagulant Materials[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 280(9): 564–571
Anitha A, Divya Rani VV, Krishna R, et al. Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Studies of Chitosan, O-carboxymethyl and N.O-carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles[J]. Carbohyd Polym., 2009, 78(4): 672–677
Xu ZP, Walker TL, Liu K, et al. Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles as Cellular Delivery Vectors of Supercoiled Plasmid DNA [J]. Int. J. Nanomed., 2007, 2:163–174
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
SONG Haoyuan and MA Xiaoling contributed equally to this study
Funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 51273156) and the Open Foundation of Hubei key laboratory of Purification and Application of Plant Anti-cancer Active Ingredients (No. HLPAI2014005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., Ma, X., Xiong, F. et al. Preparation and evaluation of insulin-loaded nanoparticles based on hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin modified carboxymethyl chitosan for oral delivery. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 31, 1394–1400 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1544-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1544-z