Abstract
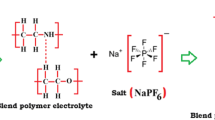
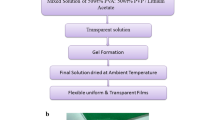
Blended solid polymer electrolytes (BSPE) were prepared by mixing different molecular weight polymers PEO6 (Mw = 1 × 106 g/mol), PEO5 (Mw = 1 × 105 g/mol), and PVDF (Mw = 5.25 × 105 g/mol) complexed with lithium salt. Conductivity and dielectric studies at different temperatures were carried out on these BSPE systems by varying the wt% of PEO5 and PVDF with respect to PEO6, keeping the wt% of lithium salt constant. The electrical characterizations of BSPE systems have been investigated using impedance spectroscopy in the frequency range 0.1–106 Hz. The conductivity data shows that inclusion of PEO5 and PVDF into the PEO6 matrix improved the overall lithium-ion dynamics in the polymer matrix. The composition, PEO6 (94 wt%)-PEO5 (3 wt%)/PVDF (3 wt%)-LiClO4, exhibited maximum conductivity of 6.44 × 10−4 Scm−1 at 303 K. The DC conductivity variation with temperature of BSPE systems follows Arrhenius relation and variation of AC conductivities with frequency obeys Jonscher’s power law. The real and imaginary part of dielectric constant and the dielectric relaxation were also investigated.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable
References
Mallaiah Y, Jeedi VR, Swarnalatha R et al (2021) Impact of polymer blending on ionic conduction mechanism and dielectric properties of sodium based PEO-PVdF solid polymer electrolyte systems. J Phys Chem Solids 155:110096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110096
Sundar M, Selladurai S (2006) Effect of fillers on magnesium-poly(ethylene oxide) solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics (Kiel) 12:281–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-006-0048-9
Wang J, Fan L, Du Q, Jiao K (2022) Lithium ion transport in solid polymer electrolyte filled with alumina nanoparticles. Energy Adv 1:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ya00025c
Basappa M, Ganesha H, Veeresh S et al (2022) Preparation, characterization, and electrochemical properties of PEO/PVDF blend films. Chem Phys Lett 799:139609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2022.139609
Li J, Zhu K, Yao Z et al (2020) A promising composite solid electrolyte incorporating LLZO into PEO/PVDF matrix for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Ionics (Kiel) 26:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03320-x
Sundaramahalingam K, Muthuvinayagam M, Nallamuthu N (2019) AC impedance analysis of lithium ion based PEO:PVP solid polymer blend electrolytes. Polym Sci - Ser A 61:565–576. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X19050171
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N et al (2006) ac impedance, DSC and FT-IR investigations on (x)PVAc-(1 - x)PVdF blends with LiClO4. Mater Chem Phys 98:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.08.063
Natarajan R, Subramanian S, Moni P, Karthikeyan Shunmugavel S (2013) Lithium ion conducting solid polymer blend electrolyte based on bio-degradable polymers. Bull Mater Sci 36:333–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-013-0463-2
Sengwa RJ, Choudhary S, Dhatarwal P (2019) Investigation of alumina nanofiller impact on the structural and dielectric properties of PEO/PMMA blend matrix-based polymer nanocomposites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2:162–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-019-00078-8
Yu X, Manthiram A (2020) A long cycle life, all-solid-state lithium battery with a ceramic-polymer composite electrolyte. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b02547
Caradant L, Lepage D, Nicolle P et al (2020) Blend of polymers as new solid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. ECS Meet Abstr MA2020-02:896–896. https://doi.org/10.1149/ma2020-025896mtgabs
Otsugu S, Kimura Y, Nakajima H, Loos K (2020) Enhancement of Tg of poly(l-lactide) by incorporation of biobased mandelic-acid-derived phenyl groups by polymerization and polymer blending. Macromol Chem Phys 221:1900392. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201900392
Dhatarwal P, Sengwa RJ (2019) Polymer compositional ratio-dependent morphology, crystallinity, dielectric dispersion, structural dynamics, and electrical conductivity of PVDF/PEO blend films. Macromol Res 27:1009–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-019-7142-0
Dhatarwal P, Sengwa RJ (2019) Impact of PVDF/PEO blend composition on the β-phase crystallization and dielectric properties of silica nanoparticles incorporated polymer nanocomposites. J Polym Res 26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1859-5
Mahendran O, Chen SY, Chen-Yang YW et al (2005) Investigations on PMMA-PVdF polymer blend electrolyte with esters of dibenzoic acids as plasticizers. Ionics (Kiel) 11:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02430385
Ngai KS, Ramesh S, Ramesh K, Juan JC (2016) A review of polymer electrolytes: fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics (Kiel) 22:1259–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1756-4
Rajendran S, Sivakumar P (2008) An investigation of PVdF/PVC-based blend electrolytes with EC/PC as plasticizers in lithium battery applications. Phys B Condens Matter 403:509–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2007.06.012
Ndruru STCL, Wahyuningrum D, Bundjali B, Arcana IM (2020) Preparation and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte membranes based on liclo4-complexed methyl cellulose as lithium-ion battery separator. J Eng Technol Sci 52:28–50. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2020.52.1.3
Hirankumar G, Mehta N (2018) Effect of incorporation of different plasticizers on structural and ion transport properties of PVA-LiClO4 based electrolytes. Heliyon 4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00992
Stephan AM (2006) Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur Polym J 42:21–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2005.09.017
Xu J, Liu Y, Cao Q et al (2019) A high-performance gel polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinylidene fluoride)/thermoplastic polyurethane/poly(propylene carbonate) for lithium-ion batteries. J Chem Sci 131:49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-019-1627-4
Ueno M, Imanishi N, Hirano A et al (2009) Effect of molecular weight in composite polymer electrolyte for all solid lithium polymer battery. ECS Meet Abstr MA2009-02:574–574. https://doi.org/10.1149/MA2009-02/8/574
Abutalib MM, Rajeh A (2020) Influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the optical, magnetic and electrical properties of PMMA/PEO composites: Combined FT-IR/DFT for electrochemical applications. J Organomet Chem 920:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2020.121348
Prasanth R, Shubha N, Hng HH, Srinivasan M (2013) Effect of nano-clay on ionic conductivity and electrochemical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) based nanocomposite porous polymer membranes and their application as polymer electrolyte in lithium ion batteries. Eur Polym J 307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2012.10.033
Sunitha VR, Radhakrishnan S (2016) Impedance and dielectric studies of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte systems using MMT and ferroelectric fillers. Ionics (Kiel) 22:2437–2446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1784-0
Zhao J, Wang L, He X et al (2008) Determination of lithium-ion transference numbers in LiPF[sub 6]–PC solutions based on electrochemical polarization and NMR measurements. J Electrochem Soc 155:A292. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2837832
Zugmann S, Fleischmann M, Amereller M et al (2011) Measurement of transference numbers for lithium ion electrolytes via four different methods, a comparative study. Electrochim Acta 56:3926–3933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.02.025
Son CY, Wang Z-GG (2020) Ion transport in small-molecule and polymer electrolytes. J Chem Phys 153:100903. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0016163
Chen P, Liang X, Wang J et al (2017) PEO/PVDF-based gel polymer electrolyte by incorporating nano-TiO2 for electrochromic glass. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 81:850–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4235-5
Maheshwaran C, Mishra K, Kanchan DK, Kumar D (2020) Mg2+ conducting polymer gel electrolytes: physical and electrochemical investigations. Ionics (Kiel) 26:2969–2980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03459-y
Elashmawi IS, Ismail AM (2022) Study of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and electrical behavior of PVDF/PEO blend incorporated with nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04139-9
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2017) Effects of different inorganic nanoparticles on the structural, dielectric and ion transportation properties of polymers blend based nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 247:924–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.07.051
Kuila T, Acharya H, Srivastava SK et al (2007) Enhancing the ionic conductivity of PEO based plasticized composite polymer electrolyte by LaMnO3 nanofiller. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol 137:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2006.11.023
Sunitha VR, Radhakrishnan S (2015) Field enhanced Li ion conduction in nanoferroelectric modified polymer electrolyte systems. Ionics (Kiel) 21:949–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1252-7
Ranjana PAB, Sundaresan B (2020) A study on the complex formation of poly(methyl methacrylate), poly(vinyl chloride) and their blend with lithium perchlorate using FTIR spectroscopy. Macromol Symp 392:3–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.202000172
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ion transport and ion-filler-polymer interaction in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195:5101–5108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.02.026
Kumar KK, Ravi M, Pavani Y et al (2012) Electrical conduction mechanism in NaCl complexed PEO/PVP polymer blend electrolytes. J Non Cryst Solids 358:3205–3211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.08.022
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ (2013) Electrical conduction mechanism in solid polymer electrolytes: new concepts to Arrhenius equation. J Soft Matter 2013:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/323868
Sengwa RJ, Sankhla S, Choudhary S (2010) Effect of melt compounding temperature on dielectric relaxation and ionic conduction in PEO-NaClO4-MMT nanocomposite electrolytes. Ionics (Kiel) 16:697–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0453-y
Shanmukaraj D, Wang GX, Murugan R, Liu HK (2008) Ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability of poly(methylmethacrylate)-poly(ethylene oxide) blend-ceramic fillers composites. J Phys Chem Solids 69:243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.08.072
Dannoun EMA, Aziz SB, Brza MA et al (2022) Electrochemical and Ion transport studies of Li+ ion-conducting MC-based biopolymer blend electrolytes. Int J Mol Sci 23:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169152
Sunitha VR, Radhakrishnan S (2020) Gamma irradiation effects on conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PEO-based nano-composite polymer electrolyte systems. Polym Bull 77:655–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02770-7
Wang W, Alexandridis P (2016) Composite polymer electrolytes: nanoparticles affect structure and properties. Polymers (Basel) 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8110387
Money BK, Hariharan K (2010) Phase dependent heterogeneous dynamics of Li+ Ion in LiPO 3 based systems. Integr Ferroelectr 120:75–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2010.491729
Ahmad MM, Al-Jaafari A (2015) Concentration and mobility of mobile Li+ ions in Li6BaLa2Ta2O12 and Li5La3Ta2O12 garnet lithium ion conductors. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26:8136–8142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3473-6
Money BK, Hariharan K, Swenson J (2012) Glass transition and relaxation processes of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 116:7762–7770. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3036499
Sindhu KP, Abdul Majeed SSM, Shahitha Parveen J (2021) PEO/PMMA solid nanocomposite polyelectrolyte with enhanced ionic conductivity and promising dielectric properties. J Electron Mater 50:6654–6666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09205-y
Liang B, Tang S, Jiang Q et al (2015) Preparation and characterization of PEO-PMMA polymer composite electrolytes doped with nano-Al2O3. Electrochim Acta 169:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.039
Yap YL, You AH, Teo LL (2019) Preparation and characterization studies of PMMA–PEO-blend solid polymer electrolytes with SiO2 filler and plasticizer for lithium ion battery. Ionics (Kiel) 25:3087–3098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02842-8
Teran AA, Tang MH, Mullin SA, Balsara NP (2011) Effect of molecular weight on conductivity of polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 203:18–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2011.09.021
Knoglinger H, Schausberger A, Janeschitz-Kriegl H (1987) The role of short chain molecules for the rheology of polystyrene melts. - I. Molar mass dependent shift factors. Rheol Acta 26:460–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01333847
Singh KP, Gupta PN (1998) Study of dielectric relaxation in polymer electrolytes. Eur Polym J 34:1023–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-3057(97)00207-3
Choudhary S (2017) Structural and dielectric properties of (PEO–PMMA)–SnO2 nanocomposites. Compos Commun 5:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2017.07.004
Perera K, Vidanapathirana K (2017) Impedance spectroscopy, DC polarization, XRD and SEM studies on an ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte to be used for dye sensitized solar cells. Mater Discov 7:30–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.md.2017.07.002
Dutta P, Biswas S, De Kumar S (2002) Dielectric relaxation in polyaniline-polyvinyl alcohol composites. Mater Res Bull 37:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(01)00813-3
Aziz BM, Brza et al (2019) Employing of Trukhan model to estimate ion transport parameters in PVA based solid polymer electrolyte. Polymers (Basel) 11:1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101694
Jayathilaka PARD, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander BE (2003) Dielectric relaxation, ionic conductivity and thermal studies of the gel polymer electrolyte system PAN/EC/PC/LiTFSI. Solid State Ionics 156:179–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00616-1
Alegria A, Colmenero J (2016) Dielectric relaxation of polymers: segmental dynamics under structural constraints. Soft Matter 12:7709–7725. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6sm01298a
Chu L, Xu K, Graf R et al (2021) Dynamic heterogeneity in homogeneous polymer melts. Soft Matter 17:6081–6087. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1sm00017a
Metin B, Blum FD (2006) Segmental dynamics in poly(methyl acrylate) on silica: molecular-mass effects. J Chem Phys 125. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2219739
Acknowledgements
The author C. Revathy sincerely thanks PES University and Department of Science & Humanities (Physics) where the present research work was carried out.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: Sunitha V R. Formal analysis and investigation: Sunitha V R, S. Radhakrishnan, and Rex Joseph. Material preparation and data collection: C Revathy. Data analysis: C Revathy, Sunitha V R, and Benson K Money. Original draft preparation: C Revathy. Review and editing: Sunitha V R, Benson K Money, and S. Radhakrishnan. Supervision: S. Radhakrishnan and Sunitha V R. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
No experiments about human or animals were conducted.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Revathy, C., Sunitha, V.R., Money, B.K. et al. Role of mixed molecular weight PEO-PVDF polymers in improving the ionic conductivity of blended solid polymer electrolytes. Ionics 29, 4025–4035 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05141-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05141-5