Abstract
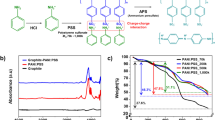
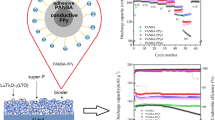
In this study, water-soluble polymer electrolytes were synthesized, and their potential as binders for negative electrode active materials was evaluated. Poly(isobutylene-alt-maleic anhydride) was used as a base material, and it was turned water-soluble via reaction with an excess of LiOH in the presence of maleic anhydride. In the next step, a BF3-THF complex was introduced into the lithium carboxylate group, and the ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolyte was improved proportionately by the amount of Lewis acid incorporation. The synthesized water-soluble polymer electrolyte was mixed with SBR and used as a binder for an anode active material. Although the peel strength decreased as the content of the polymer electrolyte binder increased, the lithium-ion battery composed of Li/electrolyte/graphite showed relatively high formation efficiency. In particular, the improvement in cell performances was observed because the resistance of the negative electrode interface was reduced by the ion conductive polymer binder.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dias F, Polomp L, Veldhuis J (2000) Trend in polymer electrolytes for secondary lithium batteries. J Power Sources 88:169–191
Tarascon J, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Lee J, Lee Y, Bhattacharya B, Nho Y, Park J (2009) Separator grafted with siloxane by electron beam irradiation for lithium secondary batteries. Electrochim Acta 54:4312–4315
Jung S, Jeong H (2017) Extended Kalman filter-based state of charge and state of power estimation algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle Li-Po battery packs. Energies 10:1237
Hollinger AS, McAnallen DR, Brockett MT, DeLaney SC, Ma J, Rahn CD (2020) Cylindrical lithium-ion structural batteries for drones. Int J Energy Res 44:560–566
König A, Nicoletti L, Schröder D, Wolff S, Waclaw A, Lienkamp M (2021) An overview of parameter and cost for battery electric vehicles. World Electr Veh J 12:21
Liu Y, Zhang R, Wang J, Wang Y (2021) Current and future lithium-ion battery manufacturing. IScience 24:102332
Van Schalkwijk W, Scrosati B (2002) Advances in lithium-ion batteries. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York
Pender J, Jha G, Youn D, Ziegler J, Andoni I, Choi E, Heller A, Dunn B, Weiss P, Penner R, Mullins C (2020) Electrode degradation in lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 14:1243–1295
Landesfeind J, Eldiven A, Gasteiger H (2018) Influence of the binder on lithium ion battery electrode tortuosity and performance. J Electrochem Soc 165:A1122–A1128
Shi Y, Zhou X, Yu G (2017) Material and structural design of novel binder systems for high energy, high-power lithium-ion batteries. Acc Chem Res 50:2642–2652
Jiang M, Mu P, Zhang H, Dong T, Tang B, Qiu H, Chen Z, Cui G (2022) An endotenon sheath-inspired double-network binder enables superior cycling performance of silicon electrodes. Nano-Micro Lett 14:87
Mu P, Zhang H, Jiang H, Dong T, Zhang S, Wang C, Li J, Ma Y, Dong S, Cui G (2021) Bioinspired antiaging binder additive addressing the challenge of chemical degradation of electrolyte at cathode/electrolyte interphase. J Am Chem Soc 143:18041
Yao Y, McDowell T, Ryu I, Wu H, Liu N, Hu L, Nix D, Cui Y (2011) Interconnected silicon hollow nanospheres for lithium-ion battery anodes with long cycle life. J Am Chem Soc 11:2949–2954
Buqa H, Holzapfel M, Krumeich F, Veit C, Novák P (2006) Study of styrene butadiene rubber and sodium methyl cellulose as binder for negative electrodes in lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 161:617–622
Chen Y, Zeng S, Qian J, Wang Y, Cao Y, Yang H, Ai X (2014) Li+ conductive polymer-embedded nano-Si particles as anode material for advanced Li-ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc 6:3508–3512
Markevich E, Salitra G, Aurbach D (2005) Influence of the PVDF binder on the stability of LiCoO2 electrodes. Electrochem Commun 7:1298–1304
Yen J, Chang C, Lin Y, Shen S, Hong J (2013) Effects of styrene-butadiene rubber/carboxymethylcellulose (SBR/CMC) and polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) binders on low temperature lithium ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 160:1811–1818
Liu Z, Dong T, Mu P, Zhang H, Liu W, Cui G (2022) Interfacial chemistry of vinylphenol-grafted PVDF binder ensuring compatible cathode interphase for lithium batteries. Chem Eng J 446:136798
Wei L, Chen C, Hou Z, Wei H (2016) Poly(acrylic acid sodium) grafted carboxymethyl cellulose as a high performance polymer binder for silicon anode in lithium ion batteries. Sci Rep 6:19583
Jeena M, Lee J, Kim S, Kim C, Kim J, Park S, Ryu J (2014) Multifunctional molecular design as an efficient polymeric binder for silicon anodes in lithium-ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc 6:18001–18007
Zhao H, Zhou X, Park S-J, Shi F, Fu Y, Ling M, Yuca N, Battaglia V, Liu G (2014) A polymerized vinylene carbonate anode binder enhances performance of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 263:288–295
Grygiel K, Lee J, Sakaushi K, Antonietti M, Yuan J (2015) Thiazolium poly(ionic liquid)s: synthesis and application as binder for lithium-ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc 4:1312–1316
Tsao C, Hsu C, Kuo P (2016) Ionic conducting and surface active binder of poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(acrylonitrile) for high power lithium-ion battery. Electrochim Acta 196:41–47
Nguyen V, Kuss C (2020) Review—conducting polymer-based binders for lithium-ion batteries and beyond. J Electrochem Soc 167:065501
Zhu Y, Wang X, Hou Y, Gao X, Liu L, Wu Y, Shimizu M (2013) A new single-ion polymer electrolyte based on polyvinyl alcohol for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 87:113–118
Cao C, Li Y, Feng Y, Peng C, Li Z, Feng W (2019) A solid-state single-ion polymer electrolyte with ultrahigh ionic conductivity for dendrite-free lithium metal batteries. Energy Storage Materials 19:401–407
Zhang J, Wang S, Han D, Xiao M, Sun L, Meng Y (2020) Lithium (4-styrenesulfonyl) (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide based single-ion polymer electrolyte with superior battery performance. Energy Storage Mater 24:579–587
Dong T, Zhang H, Ma Y, Zhang J, Du X, Lu C, Shangguan X, Li J, Zhang M, Yang J, Zhou X, Cui G (2019) A well-designed water-soluble binder enlightening the 5 V-class LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes. Mater Chem A 7:24594–24601
Hergenrother P, Smith J (1994) Chemistry and properties of imide oligomers end-capped with phenylethynylphthalic anhydrides. Polymer 35:4857–4864
Ku J, Hwang S, Ham D, Song M, Shon J, Ji S, Choi J, Doo S (2015) Poly(isobutylene-alt-maleic anhydride) binders containing lithium for high-performance Li-ion batteries. J of Power Sources 287:36–42
Ryu S, Trapa P, Olugebefola S, Gonzalez-Leon J, Sadoway D, Mayes A (2005) Effect of counter ion placement on conductivity in single-ion conducting block copolymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 152:A158–A163
Kwon N, Ryu S (2021) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of self-doped solid polymer electrolyte based on lithium 4-styrene sulfonate with BF3-THF. Solid State Ionics 361:115563
Kelly J, Fafilek G, Besenhard O, Kronberger H, Nauer E (2005) Contaminant absorption and conductivity in polymer electrolyte membranes. J of Power Sources 145:249–252
Altava B, Compañ V, Andrio A, Castillo L, Mollá S, Burguete M, García-Verdugo E, Luis S (2015) Conductive films based on composite polymers containing ionic liquids absorbed on crosslinked polymeric ionic-like liquids (SILLPs). Polymer 72:69–81
Stoeva Z, Martin-Litas I, Staunton E, Andreev Y, Bruce P (2003) Ionic conductivity in the crystalline polymer electrolytes PEO6:LiXF6, X = P, As. Sb J Am Chem Soc 125:4619–4626
Zhou D, Shanmukaraj D, Tkacheva A, Armand M, Wang G (2019) Polymer electrolytes for lithium-based batteries: advances and prospects. Chem 5:2326–2352
He J, Wang J, Zhong H, Ding J, Zhang L (2015) Cyanoethylated carboxymethyl chitosan as water soluble binder with enhanced adhesion capability and electrochemical performances for LiFePO4 cathode. Electrochim Acta 182:900–907
Hwang C, Cho Y, Kang N, Ko Y, Lee U, Ahn D, Kim J, Kim Y, Song H (2015) Selectively accelerated lithium ion transport to silicon anodes via an organogel binder. J of Power Sources 298:8–13
Nie M, Lucht B (2014) Role of lithium salt on solid electrolyte interface (SEI) formation and structure in lithium ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 161:A1001–A1006
Wang A, Kadam S, Li H, Shi S, Qi Y (2018) Review on modeling of the anode solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) for lithium-ion batteries. Comput Mater 4:15
An S, Li J, Daniel C, Mohanty D, Nagpure S, Wood D III (2016) The state of understanding of the lithium-ion-battery graphite solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and its relationship to formation cycling. Carbon 105:52–76
Pathan T, Rashid M, Walker M, Widanage W, Kendrick E (2019) Active formation of Li-ion batteries and its effect on cycle life. J Phys Energy 1:044003
An S, Li J, Du Z, Daniel C, Wood D III (2017) Fast formation cycling for lithium ion batteries. J of Power Sources 342:846–852
Funding
This research was supported by Chungbuk National University, Korea National University Development Project (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, ST., Jeong, YW., Kim, SS. et al. Synthesis of poly(isobutylene-alt-maleic anhydride)-based water-soluble binders and their electrochemical properties. Ionics 28, 4303–4310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04647-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04647-8