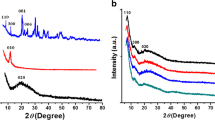
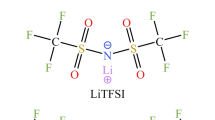
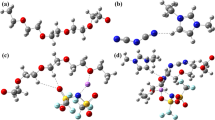
Abstract
In this study, the structure and ionic conductivity behavior of a polymer nanocomposite electrolyte system consisting of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), metal–organic framework 5 (MOF-5), and lithium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) were investigated by using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Based on ionic conductivity data from MD simulations, the mobility of Li cations increases in PEO:LiTFSI electrolyte system with the addition of MOF-5. Zn atoms of MOF-5 hold almost three TFSI anions per Zn atom. In addition, when Zn atoms of MOFs and oxygen atoms of PEO interact, four oxygen atoms are saturated per Zn atom. Furthermore, Li cations are stuck among oxygen atoms of PEO as a result of their ionic interactions with O atoms. Positive charges of MOF-5 leads to the separation of Li cations from TFSI anions in PEO:LiTFSI:MOF-5 electrolyte system. In addition, positively charged atoms of MOF-5 interact with oxygen atoms of PEO chains. MOF-5 exhibits acidic surface properties through Zn atoms located close to its surface, and Zn atoms interact with partially negatively charged oxygen atoms of PEO chains and fully negatively charged TFSI anions. Therefore, lithium cations are released. The mobility of Li cations increases due to favorable interactions of MOF-5 with PEO and TFSI anions. The ionic conductivity results verify that nanoparticles like MOF-5 consisting of positively charged atoms can be used to improve the ionic mobility in electrolyte systems which include PEO-like polymers consisting of partially negative charged atoms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiang Y, Li J, Lei J, Liu D, Xie Z, Qu D, Li K, Deng T, Tang H (2016) Advanced separators for lithium-ion and lithium–sulfur batteries: a review of recent progress. Chemsuschem 9:3023–3039. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201600943
Barghamadi M, Kapoor A, Wen C (2013) A review on Li-S batteries as a high efficiency rechargeable lithium battery. J Electrochem Soc 160:A1256–A1263. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.096308jes
Park M, Zhang X, Chung M, Less GB, Sastry AM (2010) A review of conduction phenomena in Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:7904–7929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.06.060
Zhang H, Li C, Piszcz M, Coya E, Rojo T, Rodriguez-Martinez LM, Armand M, Zhou Z (2017) Single lithium-ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes: advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 46:797–815. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00491a
Arya A, Sharma AL (2017) Insights into the use of polyethylene oxide in energy storage/conversion devices: a critical review. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:443002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa8675
Zhao CZ, Duan H, Huang JQ, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Guo YG, Wan LJ (2019) Designing solid-state interfaces on lithium-metal anodes: a review. Sci China Chem 62:1286–1299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-019-9519-9
Ye F, Liao K, Ran R, Shao Z (2020) Recent advances in filler engineering of polymer electrolytes for solid-state Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Fuels 34:9189–9207. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c02111
Manthiram A (2017) An outlook on lithium ion battery technology. ACS Cent Sci 3:1063–1069. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00288
Erickson EM, Ghanty C, Aurbach D (2014) New horizons for conventional lithium ion battery technology. J Phys Chem Lett 5:3313–3324. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz501387m
Appetecchi GB, Croce F, Persi L, Ronci F, Scrosati B (2000) Transport and interfacial properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 45:1481–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(99)00363-1
Zubi G, Dufo-López R, Carvalho M, Pasaoglu G (2018) The lithium-ion battery: state of the art and future perspectives. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 89:292–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.002
Zhou G, Li F, Cheng HM (2014) Progress in flexible lithium batteries and future prospects. Energy Environ Sci 7:1307–1338. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee43182g
Fergus JW (2010) Ceramic and polymeric solid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:4554–4569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.01.076
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 394:456–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/28818
Yao P, Yu H, Ding Z, Liu Y, Lu J, Lavorgna M, Wu J, Liu X (2019) Review on polymer-based composite electrolytes for lithium batteries. Front Chem 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00522
Bekaert E, Buannic L, Lassi U, Llordés A, Salminen J (2017) Electrolytes for Li- and Na-ion batteries: concepts, candidates, and the role of nanotechnology. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-42977-1.00001-7
Quartarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A (1998) PEO-based composite polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 110:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2738(98)00114-3
Wang H, Sheng L, Yasin G, Wang L, Xu H, He X (2020) Reviewing the current status and development of polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries. Energy Storage Mater 33:188–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2020.08.014
Fenton DE, Parker JM, Wright PV (1973) Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer (Guildf) 14:589. https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(73)90146-8
Ye L, Feng Z (2010) Polymer electrolytes as solid solvents and their applications. Polym Electrolytes Fundam Appl 550–582. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845699772.2.550
Tarascon JM, Gozdz AS, Schmutz C, Shokoohi F, Warren PC (1996) Performance of Bellcore’s plastic rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 86–88:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(96)00330-X
Ramesh S, Wen LC (2010) Investigation on the effects of addition of SiO2 nanoparticles on ionic conductivity, FTIR, and thermal properties of nanocomposite PMMA-LiCF3SO3-SiO2. Ionics (Kiel) 16:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0388-3
Krawiec W, Scanlon LG, Fellner JP, Vaia RA, Vasudevan S, Giannelis EP (1995) Polymer nanocomposites: a new strategy for synthesizing solid electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Power Sources 54:310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7753(94)02090-P
Yue L, Ma J, Zhang J, Zhao J, Dong S, Liu Z, Cui G, Chen L (2016) All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater 5:139–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2016.07.003
Wieczorek W, Raducha D, Zalewska A, Stevens JR (1998) Effect of salt concentration on the conductivity of PEO-based composite polymeric electrolytes. J Phys Chem B 102:8725–8731. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp982403f
Wang W, Alexandridis P (2016) Composite polymer electrolytes: nanoparticles affect structure and properties. Polymers (Basel). 8:387. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8110387
Hallinan DT, Balsara NP (2013) Polymer electrolytes. Annu Rev Mater Res 43:503–525. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-071312-121705
Gupta H, Singh SK, Singh VK, Tripathi AK, Srivastava N, Tiwari RK, Mishra R, Meghnani D, Singh RK (2019) Development of polymer electrolyte and cathode material for Li-batteries. J Electrochem Soc 166:A5187–A5192. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0331903jes
Berthier C, Gorecki W, Minier M, Armand MB, Chabagno JM, Rigaud P (1983) Microscopic investigation of ionic conductivity in alkali metal salts-poly(ethylene oxide) adducts. Solid State Ionics 11:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(83)90068-1
Long L, Wang S, Xiao M, Meng Y (2016) Polymer electrolytes for lithium polymer batteries. J Mater Chem A 4:10038–10039. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta02621d
Singh SK, Shalu L, Balo H, Gupta VK, Singh AK, Tripathi YL, Verma RK (2018) Singh, Improved electrochemical performance of EMIMFSI ionic liquid based gel polymer electrolyte with temperature for rechargeable lithium battery. Energy 150:890–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.024
Choo Y, Halat DM, Villaluenga I, Timachova K, Balsara NP (2020) Diffusion and migration in polymer electrolytes. Prog Polym Sci 103:101220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2020.101220
Wu X, Chen K, Yao Z, Hu J, Huang M, Meng J, Ma S, Wu T, Cui Y, Li C (2021) Metal organic framework reinforced polymer electrolyte with high cation transference number to enable dendrite-free solid state Li metal conversion batteries. J Power Sources 501:229946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.229946
Gorecki W, Andreani R, Berthier C, Armand M, Mali M, Roos J, Brinkmann D (1986) NMR, DSC, and conductivity study of a poly(ethylene oxide) complex electrolyte: PEO(LiClO4)x. Solid State Ionics 18–19:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(86)90130-X
Gorecki W, Jeannin M, Belorizky E, Roux C, Armand M (1995) Physical properties of solid polymer electrolyte PEO(LiTFSI) complexes. J Phys Condens Matter 7:6823–6832. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/7/34/007
Li X, Wang Z, Lin H, Liu Y, Min Y, Pan F (2019) Composite electrolytes of pyrrolidone-derivatives-PEO enable to enhance performance of all solid state lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 293:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.10.023
Liu D, Purewal JJ, Yang J, Sudik A, Maurer S, Mueller U, Ni J, Siegel DJ (2012) MOF-5 composites exhibiting improved thermal conductivity. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:6109–6117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.12.129
Polu AR, Rhee HW, Jeevan Kumar Reddy M, Shanmugharaj AM, Ryu SH, Kim DK (2017) Effect of POSS-PEG hybrid nanoparticles on cycling performance of polyether-LiDFOB based solid polymer electrolytes for all solid-state Li-ion battery applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 45:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.09.004
Xue Z, He D, Xie X (2015) Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:19218–19253. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta03471j
Gadjourova Z, Andreev YG, Tunstall DP, Bruce PG (2001) Ionic conductivity in crystalline polymer electrolytes. Nature 412:520–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/35087538
Shin JH, Henderson WA, Passerini S (2003) Ionic liquids to the rescue? Overcoming the ionic conductivity limitations of polymer electrolytes. Electrochem Commun 5:1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2003.09.017
Wang X, Zhai H, Qie B, Cheng Q, Li A, Borovilas J, Xu B, Shi C, Jin T, Liao X, Li Y, He X, Du S, Fu Y, Dontigny M, Zaghib K, Yang Y (2019) Rechargeable solid-state lithium metal batteries with vertically aligned ceramic nanoparticle/polymer composite electrolyte. Nano Energy 60:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.03.051
Zhou Q, Ma J, Dong S, Li X, Cui G (2019) Intermolecular chemistry in solid polymer electrolytes for high-energy-density lithium batteries. Adv Mater 31:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902029
Xu Z, Yang T, Chu X, Su H, Wang Z, Chen N, Gu B, Zhang H, Deng W, Zhang H, Yang W (2020) Strong Lewis acid-base and weak hydrogen bond synergistically enhancing ionic conductivity of poly(ethylene oxide)@SiO2 electrolytes for a high rate capability Li-metal battery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:10341–10349. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b20128
Dirican M, Yan C, Zhu P, Zhang X (2019) Composite solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 136:27–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2018.10.004
Wang S, McGuirk CM, d’Aquino A, Mason JA, Mirkin CA (2018) Metal–organic framework nanoparticles. Adv Mater 30:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201800202
Liang F, Wen Z (2021) MOF/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Composite polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium battery. Wuji Cailiao Xuebao/J Inorg Mater 36:332–336. https://doi.org/10.15541/jim20200206
Choi JS, Son WJ, Kim J, Ahn WS (2008) Metal-organic framework MOF-5 prepared by microwave heating: factors to be considered. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 116:727–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.04.033
Zhang Z, Huang Y, Gao H, Li C, Hang J, Liu P (2021) MOF-derived multifunctional filler reinforced polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium batteries. J Energy Chem 60:259–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2021.01.013
Moosavi SM, Nandy A, Jablonka KM, Ongari D, Janet JP, Boyd PG, Lee Y, Smit B, Kulik HJ (2020) Understanding the diversity of the metal-organic framework ecosystem. Nat Commun 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17755-8
Kong L, Zhong M, Shuang W, Xu Y, Bu XH (2020) Electrochemically active sites inside crystalline porous materials for energy storage and conversion. Chem Soc Rev 49:2378–2407. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00880b
Burgaz E, Erciyes A, Andac M, Andac O (2019) Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized metal organic framework-5 (MOF-5) by using consecutive combination of ultrasound and microwave irradiation methods. Inorganica Chim Acta 485:118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2018.10.014
Kuppler RJ, Timmons DJ, Fang QR, Li JR, Makal TA, Young MD, Yuan D, Zhao D, Zhuang W, Zhou HC (2009) Potential applications of metal-organic frameworks. Coord Chem Rev 253:3042–3066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.05.019
Gerbaldi C, Nair JR, Kulandainathan MA, Kumar RS, Ferrara C, Mustarelli P, Stephan AM (2014) Innovative high performing metal organic framework (MOF)-laden nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J Mater Chem A 2:9948–9954. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta01856g
Angulakshmi N, Zhou Y, Suriyakumar S, Dhanalakshmi RB, Satishrajan M, Alwarappan S, Alkordi MH, Stephan AM (2020) Microporous metal-organic framework (MOF)-based composite polymer electrolyte (CPE) mitigating lithium dendrite formation in all-solid-state-lithium batteries. ACS Omega 5:7885–7894. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04133
Yuan C, Li J, Han P, Lai Y, Zhang Z, Liu J (2013) Enhanced electrochemical performance of poly(ethylene oxide) based composite polymer electrolyte by incorporation of nano-sized metal-organic framework. J Power Sources 240:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.05.030
Yaghi OM, O’Keeffe M, Ockwig NW, Chae HK, Eddaoudi M, Kim J (2003) Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 423:705–714. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01650
Millward AR, Yaghi OM (2005) Metal–organic frameworks with exceptionally high capacity for storage of carbon dioxide at room temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127:17998–17999. https://doi.org/10.1021/JA0570032
Diddens D, Paillard E, Heuer A (2017) Improving the lithium ion transport in polymer electrolytes by functionalized ionic-liquid additives: simulations and modeling. J Electrochem Soc 164:E3225–E3231. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0271711jes
Ebadi M, Costa LT, Araujo CM, Brandell D (2017) Modelling the polymer electrolyte/Li-metal interface by molecular dynamics simulations. Electrochim Acta 234:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.030
Molinari N, Mailoa JP, Kozinsky B (2018) Effect of salt concentration on ion clustering and transport in polymer solid electrolytes: a molecular dynamics study of PEO-LiTFSI. Chem Mater 30:6298–6306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b01955
Brooks DJ, Merinov BV, Goddard WA, Kozinsky B, Mailoa J (2018) Atomistic description of ionic diffusion in PEO-LiTFSI: effect of temperature, molecular weight, and ionic concentration. Macromolecules 51:8987–8995. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.8b01753
Costa LT, Sun B, Jeschull F, Brandell D (2015) Polymer-ionic liquid ternary systems for Li-battery electrolytes: molecular dynamics studies of LiTFSI in a EMIm-TFSI and PEO blend. J Chem Phys 143:9. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4926470
Singh VK, Shalu L, Balo H, Gupta SK, Singh RK (2017) Singh, Solid polymer electrolytes based on Li+/ionic liquid for lithium secondary batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 21:1713–1723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3529-z
Xue Y, Zheng S, Xue H, Pang H (2019) Metal-organic framework composites and their electrochemical applications. J Mater Chem A 7:7301–7327. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA12178H
Angulakshmi N, Kumar RS, Kulandainathan MA, Stephan AM (2014) Composite polymer electrolytes encompassing metal organic frame works: a new strategy for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J Phys Chem C 118:24240–24247. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp506464v
Angulakshmi N, Nahm KS, Nair JR, Gerbaldi C, Bongiovanni R, Penazzi N, Stephan AM (2013) Cycling profile of MgAl2O4-incorporated composite electrolytes composed of PEO and LiPF6 for lithium polymer batteries. Electrochim Acta 90:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.12.003
Richard MN, Dahn JR (1999) Accelerating rate calorimetry study on the thermal stability of lithium intercalated graphite in electrolyte. II. Modeling the results and predicting differential scanning calorimeter curves. J Electrochem Soc 146:2078–2084. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1391894
Richard MN, Dahn JR (1999) Accelerating rate calorimetry studies of the effect of binder type on the thermal stability of a lithiated mesocarbon microbead material in electrolyte. J Power Sources 83:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(99)00260-8
Senthil Kumar R, Raja M, AnbuKulandainathan M, Manuel Stephan A (2014) Metal organic framework-laden composite polymer electrolytes for efficient and durable all-solid-state-lithium batteries. RSC Adv 4:26171–26175. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA03147D
Zhang Z, You JH, Zhang SJ, Wang CW, Zhou Y, Li JT, Huang L, Sun SG (2020) Metal organic framework nanorod doped solid polymer electrolyte with decreased crystallinity for high-performance all-solid-state lithium batteries. ChemElectroChem 7:1125–1134. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201901987
Dutta R, Kumar A (2016) Structural and dielectric properties of ionic liquid doped metal organic framework based polymer electrolyte nanocomposites. J Phys Conf Ser 765. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/765/1/012020
Qing X, Li J, Wang Z, Chen M, Lin J, Lin X (2020) A functionalized metal organic framework-laden nanoporous polymer electrolyte for exceptionally stable lithium electrodeposition. Chem Commun 56:15533–15536. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cc06265k
Ataei F, Dorranian D, Motakef-Kazemi N (2021) Synthesis of MOF-5 nanostructures by laser ablation method in liquid and evaluation of its properties. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:3819–3833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05126-4
Sun H, Jin Z, Yang C, Akkermans RLC, Robertson SH, Spenley NA, Miller S, Todd SM (2016) COMPASS II: extended coverage for polymer and drug-like molecule databases. J Mol Model 22:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-2909-0
Peng Z, Ewig CS, Hwang MJ, Waldman M, Hagler AT (1997) Derivation of class II force fields. 4. Van der waals parameters of alkali metal cations and halide anions. J Phys Chem A 101:7243–7252. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp964080y
Ennari J (2008) Modelling of transport properties and state of water of polyelectrolytes containing various amounts of water. Polymer (Guildf) 49:2373–2380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.03.019
Zwanzig R (1961) Memory effects in irreversible thermodynamics. Phys Rev 124:983–992. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.124.983
Green MS (1952) Markoff random processes and the statistical mechanics of time-dependent phenomena. J Chem Phys 20:1281–1295. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1700722
Kubo R (1957) Statistical mechanical theory of irreversible processes. I. General theory and simple applications to magnetic and conduction problems. J Phys Soc Japan 12:570–586. https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.12.570
Srinophakun T, Martkumchan S (2012) Ionic conductivity in a chitosan membrane for a PEM fuel cell using molecular dynamics simulation. Carbohydr Polym 88:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.11.094
Pozuelo J, Riande E, Saiz E, Compañ V (2006) Molecular dynamics simulations of proton conduction in sulfonated poly(phenyl sulfone)s. Macromolecules 39:8862–8866. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma062070h
Wood WW, Parker FR (1957) Monte Carlo equation of state of molecules interacting with the Lennard-Jones potential. I. A supercritical isotherm at about twice the critical temperature. J Chem Phys 27:720–733. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1743822
Brooks CL (1989) Computer simulation of liquids. J Solution Chem 18:99–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00646086
Wang Z, Zhou H, Meng C, Xiong W, Cai Y, Hu P, Pang H, Yuan A (2020) Enhancing ion transport: function of ionic liquid decorated MOFs in polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:4265–4274. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b02543
Scipioni R, Stixrude L, Desjarlais MP (2017) Electrical conductivity of SiO2 at extreme conditions and planetary dynamos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:9009–9013. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1704762114
Acknowledgements
The use of facilities in the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering at Ondokuz Mayis University is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The following files are available free of charge.
The configurations of optimized geometries in electrolyte systems, the configurations for interactions between MOF-5:PEO:LiTFSI and MSD graphs of PEO:LiTFSI:MOF-5 systems.
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozlek, M., Burgaz, E., Inanc, I. et al. The structural and ionic conductivity analysis of poly(ethylene oxide)/LiTFSI/MOF-5 nanocomposite electrolytes by using molecular dynamics simulations. Ionics 28, 3255–3268 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04580-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04580-w