Abstract
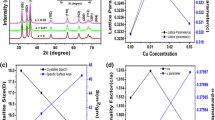
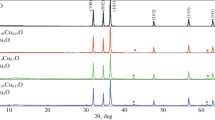
Cu ion–doped Zn0.94Cd0.06−xCuxO (x = 3 and 5 wt%) nanomaterials are prepared via low temperature sol–gel auto-combustion method using citric acid (C6H8O7) as a fuel radical. Tailoring effects of Cu doping concentration on the optical and dielectric relaxation properties of Zn0.94Cd0.06O nanomaterials are investigated using XRD technique, UV–Vis diffuse reflectance, and impedance spectroscopy. XRD analysis reveals that all the prepared nanomaterials are crystallized in wurtzite hexagonal structure with space group P63mc. Rietveld refinement also confirms the single-phase crystalline nature. The average diameters of the synthesized nanomaterials estimated by Debye–Scherrer formula are found as ~ 29.50 nm (Zn0.94Cd0.03Cu0.03O) and 30.21 nm (Zn0.94Cd0.01Cu0.05O) after calcination at 600 °C. Direct band gap increases from 3.04 eV (3 wt% Cu) to 3.10 eV (5 wt% Cu) with increasing Cu concentration. Dielectric behavior is governed by the space charge polarization whereas the electric modulus studies support non-Debye [β < 1 (0.83 at 3 wt% Cu and 0.88 at 5 wt% Cu)] type of dielectric relaxation. The Nyquist plot of 3 wt% Cu ion doping shows small semicircle, which is associated with non-ohmic nature. Sizes of the semicircles are correlated with the grain resistance that points out the electrode nature of prepared nanomaterials. Finally, 3 wt% Cu ion–doped nanomaterials show high value of dielectric constant (~ 1150 at 20 Hz) and minimum loss (~ 1.96 at 20 Hz) that may be suitable for potential application in semiconductor devices.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karimi M, Jahangir V, Ezzati M, Saydi J, Lejbini MB (2014) Zn0.94Cd0.06O nanoparticles with various structures, morphologies and optical properties toward MB optodecolorization. Opt Mater 36:697–703
Nahm C, Shin S, Lee W, Kim JI, Jung DR, Kim J, Nam S, Byun S, Park B (2013) Electronic transport and carrier concentration in conductive ZnO:Ga thin films. Curr Appl Phys 13:415–418
Wang B, Iqbal J, Shan X, Huang G, Fu H, Yu R, Yu D (2009) Effects of Cr-doping on the photoluminescence and ferromagnetism at room temperature in ZnO nanomaterials prepared by soft chemistry route. Mater Chem Phys 113:103–106
Yan X, Itoh T, Dai S, Ozaki Y, Fang Y (2013) Cu, Mn doping effect to optical behavior and electronic structure of ZnO ceramic. J Phys Chem Solids 74:1127–1130
Xu L, Li X (2010) Influence of Fe-doping on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J Crystal Growth 312:851
Wu D, Yang M, Huang Z, Yin G, Liao X, Kang Y, Chen X, Wang H (2009) Preparation and properties of Ni-doped ZnO rod arrays from aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 330:380–385
Gong H, Hu JQ, Wang JH, Ong CH, Zhu FR (2006) Nano-crystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin film gas sensor for CO. Sensors Actuators B 115:247–251
Chen T, Zheng Y, Lin JM, Chena G (2008) Study on the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in water using Ag/ZnO as catalyst by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization ion-trap mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19:997–1003
Sagadevan S, Pal K, Chowdhury ZZ, Hoque ME (2017) Structural, dielectric and optical investigation of chemically synthesized Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles composites. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83:394–404
Wang F, Liu B, Zhao C, Yuan S (2009) Synthesis of Zn1−xCdxO bramble-like nanostructures. Mater Lett 63:1357–1359
Rodl C, Schleife (2014) Photoemission spectra and effective masses of n- and p-type oxide semiconductors from first principles: ZnO, CdO, SnO2, MnO, and NiO. Phys Status Solidi A 211:74
Park MS, Min BI (2003) Ferromagnetism in ZnO codoped with transition metals: Zn1−x(FeCo)xO and Zn1−x(FeCu)xO. Phys Rev B 68:224436
Buchholz DB, Chang RPH, Song JH, Ketterson JB (2005) Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Cu-doped ZnO thin films. Appl Phys Lett 87:082504
Sharma S, Nanda K, Kundu RS, Punia R, Kishore N (2015) Structural properties, conductivity, dielectric studies and modulus formulation of Ni modified ZnO nanoparticles. J Atom Mol Nano Phys 2:15
Das BK, Das T (2017) Structural, optical and dielectric study of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesised by high energy ball milling. Int J Nano Biomaterials 7(2):140
Verma K, Kumar A, Varshney D (2012) Dielectric relaxation behavior of AxCo1−xFe2O4 (A=Zn, Mg) mixed ferrites. J Alloys Compd 526:91–97
Wang F, Liu B, Zhang Z, Yuan S (2009) Synthesis and properties of Cd-doped ZnO nanotubes. Phys E 41:879–882
Varghese N, Panchakarla LS, Hanapi M, Govindaraj A, Rao CNR (2007) Solvothermal synthesis of nanorods of ZnO, N-doped ZnO and CdO. Mater Res Bull 42:2117–2124
Zhou SM, Zhang XH, Meng XM, Wu SK, Lee ST (2006) Fabrication of large-scale ultra-fine Cd-doped ZnO nanowires. Mater Res Bull 41:340–346
Saxena P, Varshney D (2017) Effect of d-block element substitution on structural and dielectric properties on iron cobaltite. J Alloys Compd 705:320–326
Hasnidawani JN, Azlina HN, Norita H, Bonnia NN, Ratim S, Ali ES (2016) Synthesis of ZnO nanostructures using sol-gel method. Procedia Chem 19:211–216
Ravichandran K, Saravanakumar K, Chandramohan R, Nandhakumar V (2012) Influence of simultaneous doping of Cd and F on certain physical properties of ZnO nanopowders synthesized via a simple soft chemical route. Appl Surf Sci 261:405–410
Shannon RD (1976) Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst A32 32:751–767
Albores FP, Delgado FP, Flores WA, Madrid PA, Valdovinos ER, Yoshida MM (2011) Microstructural study of ZnO nanostructures by Rietveld analysis. J Nanomater 643126:1
Morales AE, Mora ES, Pal U (2007) Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Rev Mexicana Ficisa S 53(2):18
Heinemann M, Eifert B, Heiliger C (2013) Band structure and phase stability of the copper oxides Cu2O, CuO, and Cu4O3. Phys Rev B 87:115111
Acharya AD, Moghe S, Panda R, Shrivastava SB, Gangrade M, Shripathi T, Phase DM, Ganesan V (2012) Effect of Cd dopant on electrical and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis route. Thin Solid Films 525:49–55
Wang YS, Thomas PJ, Brien PO (2006) Optical properties of ZnO nanocrystals doped with Cd, Mg, Mn, and Fe ions. J Phys Chem B 110:21412–21415
Kamarulzaman N, Kasim MF, Rusdi R (2015) Band gap narrowing and widening of ZnO nanostructures and doped materials. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:346
Choudhary P, Varshney D (2018) Dielectric relaxation behavior and impedance studies of Cu2+ ion doped Mg – Zn spinel nanoferrites. Solid State Commun 271:89–96
Kamran M, Ullah A, Rahman S, Tahir A, Nadeem K, Rehman MA, Hussain S (2017) Structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of multiferroic Co 1−x Mg x Cr 2 O 4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 433:178–186
Koops CG (1951) On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys Rev 83:121–124
Yadav HK, Sreenivas K, Gupta V, Scott JF, Katiyar RS (2008) Raman spectroscopy and dielectric studies of multiple phase transitions in ZnO:Ni. Appl Phys Lett 92:122908
Ghosh CK, Malkhandi S, Mitra MK, Chattopadhyay KK (2008) Effect of Ni doping on the dielectric constant of ZnO and its frequency dependent exchange interaction. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:245113
Manimuthu P, Murugaraj R, Venkateswaran C (2014) Non-universal dielectric relaxation in SrFeO3−δ. Phys Lett A 378:2725–2728
Pandit R, Sharma KK, Kaur P, Kumar R (2014) Cation distribution controlled dielectric, electrical and magnetic behavior of In 3+ substituted cobalt ferrites synthesized via solid-state reaction technique. Mater Chem Phys 148:988–999
Dar MA, Varshney D (2018) Structures and properties of Mg0.95Mn0.01TM0.04O (TM = Co, Ni, and Cu) nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion technique. RSC Adv 8:14120–14128
Kambale RC, Shaikh PA, Bhosale CH, Rajpure KY, Kolekar YD (2009) Dielectric properties and complex impedance spectroscopy studies of mixed Ni–Co ferrites. Smart Mater Struct 18:085014
Thomas AK, Abraham K, Thomas J, Saban KV (2017) Electrical and dielectric behaviour of Na0.5La0.25Sm0.25Cu3Ti4O12 ceramics investigated by impedance and modulus spectroscopy. J Asian Ceram Soc 5:56–61
Tang R, Jiang C, Qian W, Jian J, Zhang X, Wang H, Yang H (2015) Dielectric relaxation, resonance and scaling behaviors in Sr3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrite. Sci Rep 5:13645
Choudhary P, Varshney D (2018) Elucidation of structural, vibrational and dielectric properties of transition metal (Co 2+ ) doped spinel Mg-Zn chromites. J Magn Magn Mater 454:274–288
Hemalatha KS, Sriprakash G, Prasad MVNA, Damle R, Rukmani K (2015) Temperature dependent dielectric and conductivity studies of polyvinyl alcohol-ZnO nanocomposite films by impedance spectroscopy. J Appl Phys 118:154103
Sharma MK, Gayen RN, Pal AK, Kanjilal D, Chatterjee R (2011) Complex impedance spectroscopy of Mn-doped zinc oxide nanorod films. Solid State Commun 151:1182–1187
Sinclair DC (1995) Characterization of electro-materials using ac impedance spectroscopy. Ceramica Y Vidrio 34:55
Irvine JTS, Sinclair DC, West AR (1990) Electroceramics: characterization by impedance spectroscopy. Adv Mater 2:132–138
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. M. Gupta and Dr. U. P. Deshpande of UGC-DAE CSR, Indore for the fruitful discussions. The authors are also thankful to Late Dr. Dinesh Varshney for his guidance and encouragement. Miss Gagandeep Kaur, School of Chemical Sciences, Indore, is gratefully acknowledged for his support.
Funding
UGC-DAE-CSR, as an institute, extended its facilities and provided financial assistance (Grant No.: CSRIC/BL-22/CRS-119-2014/269) for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, P., Saxena, P., Yadav, A. et al. Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped ZnCdO nanomaterials with improved dielectric and impedance properties for potential applications. Ionics 25, 4991–5001 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03014-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03014-4