Abstract
Purpose
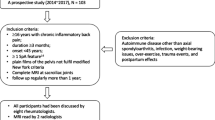
The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of radiomics based on T1-weighted images (T1WI) for assessing sacroiliac joint (SIJ) structural lesions in patients with suspected axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
Materials and methods
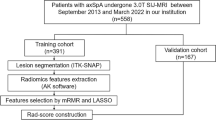
A total of 266 patients with clinical suspicion of axSpA between December 2016 and January 2022 were enrolled. Structural lesions were assessed on low-dose CT (ldCT) and MRI, respectively. Radiomic features, extracted from SIJ T1WI, were included to generate the radiomics model. The performance of the radiomics model was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Furthermore, point-biserial correlation analysis was used to interpret the associations between the radiomic feature and structural lesions.
Results
Using ldCT as the reference standard, the radiomics model showed favorable performance for detecting positive global structural lesions in the training cohort (AUC, 0.82 [95% CI: 0.76, 0.88]) and validation cohort (AUC, 0.82 [95% CI: 0.72, 0.91]. Experienced MRI raters yielded predictive AUCs of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.67, 0.79), and 0.74 (95% CI: 0.66, 0.83) in the training and validation cohort, respectively. The seven radiomic features included in the radiomics model showed significant correlation with different kinds of structural lesions (P all < 0.05). Among them, Wavelet.LHL_firstorder_90Percentile showed the strongest association with fat lesion (r = 0.48, P < 0.05).
Conclusion
The radiomics analysis with T1WI could effectively detect SIJ structural lesions and achieved expert-level performance. Each radiomic feature was correlated with different structural lesions significantly, which might inform radiomic-based applications for axSpA intelligent diagnosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780270401
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J et al (2009) The development of assessment of SpondyloArthritis international society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68:777–783. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.108233
Lambert RG, Bakker PA, van der Heijde D, Weber U, Rudwaleit M, Hermann KG et al (2016) Defining active sacroiliitis on MRI for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: update by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1958–1963. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208642
Maksymowych WP, Lambert RG, Ostergaard M, Pedersen SJ, Machado PM, Weber U et al (2019) MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joints of patients with spondyloarthritis: an update of definitions and validation by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann Rheum Dis 78:1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215589
Mandl P, Navarro-Compan V, Terslev L, Aegerter P, van der Heijde D, D’Agostino MA et al (2015) EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in the diagnosis and management of spondyloarthritis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1327–1339. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206971
Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Braun J, Burgos-Vargas R et al (2009) The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(Suppl 2):ii1–ii44. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.104018
Eshed I, Diekhoff T, Hermann KGA (2023) Is it time to move on from pelvic radiography as the first-line imaging modality for suspected sacroiliitis? Curr Opin Rheumatol 35:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000925
Diekhoff T, Eshed I, Radny F, Ziegeler K, Proft F, Greese J et al (2022) Choose wisely: imaging for diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 81:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220136
Bakker PA, van den Berg R, Lenczner G, Thevenin F, Reijnierse M, Claudepierre P et al (2017) Can we use structural lesions seen on MRI of the sacroiliac joints reliably for the classification of patients according to the ASAS axial spondyloarthritis criteria? Data from the DESIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 76:392–398. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209405
Poddubnyy D, Gaydukova I, Hermann KG, Song IH, Haibel H, Braun J et al (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging compared to conventional radiographs for detection of chronic structural changes in sacroiliac joints in axial spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol 40:1557–1565. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.130141
Ye L, Liu Y, Xiao Q, Dong L, Wen C, Zhang Z et al (2020) MRI compared with low-dose CT scanning in the diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 39:1295–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04824-7
Diekhoff T, Hermann KG, Greese J, Schwenke C, Poddubnyy D, Hamm B et al (2017) Comparison of MRI with radiography for detecting structural lesions of the sacroiliac joint using CT as standard of reference: results from the SIMACT study. Ann Rheum Dis 76:1502–1508. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210640
Bressem KK, Adams LC, Proft F, Hermann KGA, Diekhoff T, Spiller L et al (2022) Deep learning detects changes indicative of axial spondyloarthritis at MRI of sacroiliac joints. Radiology 305:655–665. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.212526
Jiang J, Wei J, Zhu Y, Wei L, Wei X, Tian H et al (2023) Clot-based radiomics model for cardioembolic stroke prediction with CT imaging before recanalization: a multicenter study. Eur Radiol 33:970–980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-09116-4
Alvarez-Jimenez C, Sandino AA, Prasanna P, Gupta A, Viswanath SE, Romero E (2020) Identifying cross-scale associations between radiomic and pathomic signatures of non-small cell lung cancer subtypes: preliminary results. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123663
Chaddad A, Kucharczyk MJ, Niazi T (2018) Multimodal radiomic features for the predicting gleason score of prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10080249
Bitencourt AGV, Gibbs P, Rossi Saccarelli C, Daimiel I, Lo Gullo R, Fox MJ et al (2020) MRI-based machine learning radiomics can predict HER2 expression level and pathologic response after neoadjuvant therapy in HER2 overexpressing breast cancer. EbioMedicine 61:103042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103042
van Voorst H, Bruggeman AAE, Yang W, Andriessen J, Welberg E, Dutra BG et al (2022) Thrombus radiomics in patients with anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke undergoing endovascular treatment. J Neurointerv Surg. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnis-2022-019085
Ye L, Miao S, Xiao Q, Liu Y, Tang H, Li B et al (2022) A predictive clinical-radiomics nomogram for diagnosing of axial spondyloarthritis using MRI and clinical risk factors. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61:1440–1447. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab542
Tenorio APM, Faleiros MC, Junior JRF, Dalto VF, Assad RL, Louzada-Junior P et al (2020) A study of MRI-based radiomics biomarkers for sacroiliitis and spondyloarthritis. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 15:1737–1748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-020-02219-7
Tenorio APM, Ferreira-Junior JR, Dalto VF, Faleiros MC, Assad RL, Louzada-Junior P et al (2022) Radiomic quantification for MRI assessment of sacroiliac joints of patients with spondyloarthritis. J Digit Imaging 35:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00559-7
Ziegeler K, Kreutzinger V, Diekhoff T, Roehle R, Poddubnyy D, Pumberger M et al (2021) Impact of age, sex, and joint form on degenerative lesions of the sacroiliac joints on CT in the normal population. Sci Rep 11:5903. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85303-5
Zwanenburg A, Vallieres M, Abdalah MA, Aerts H, Andrearczyk V, Apte A et al (2020) The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology 295:328–338. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020191145
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Maksymowych WP, Pedersen SJ, Weber U, Baraliakos X, Machado PM, Eshed I et al (2020) Central reader evaluation of MRI scans of the sacroiliac joints from the ASAS classification cohort: discrepancies with local readers and impact on the performance of the ASAS criteria. Ann Rheum Dis 79:935–942. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217232
Bi WL, Hosny A, Schabath MB, Giger ML, Birkbak NJ, Mehrtash A et al (2019) Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J Clin 69:127–157. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21552
Faleiros MC, Nogueira-Barbosa MH, Dalto VF, Junior JRF, Tenorio APM, Luppino-Assad R et al (2020) Machine learning techniques for computer-aided classification of active inflammatory sacroiliitis in magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Rheumatol 60:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-020-00126-8
Joo YB, Baek IW, Park YJ, Park KS, Kim KJ (2020) Machine learning-based prediction of radiographic progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 39:983–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04803-y
Bressem KK, Vahldiek JL, Adams L, Niehues SM, Haibel H, Rodriguez VR et al (2021) Deep learning for detection of radiographic sacroiliitis: achieving expert-level performance. Arthritis Res Ther 23:106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-021-02484-0
Lee KH, Choi ST, Lee GY, Ha YJ, Choi SI (2021) Method for diagnosing the bone marrow edema of sacroiliac joint in patients with axial spondyloarthritis using magnetic resonance image analysis based on deep learning. Diagnostics (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071156
Lin KYY, Peng C, Lee KH, Chan SCW, Chung HY (2022) Deep learning algorithms for magnetic resonance imaging of inflammatory sacroiliitis in axial spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61:4198–4206. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keac059
Devauchelle-Pensec V, D’Agostino MA, Marion J, Lapierre M, Jousse-Joulin S, Colin D et al (2012) Computed tomography scanning facilitates the diagnosis of sacroiliitis in patients with suspected spondylarthritis: results of a prospective multicenter French cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 64:1412–1419. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.33466
Orlhac F, Lecler A, Savatovski J, Goya-Outi J, Nioche C, Charbonneau F et al (2021) How can we combat multicenter variability in MR radiomics? Validation of a correction procedure. Eur Radiol 31:2272–2280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07284-9
Bressem KK, Adams LC, Proft F, Hermann KGA, Diekhoff T, Spiller L et al (2023) Deep learning detects changes indicative of axial spondyloarthritis at MRI of sacroiliac joints. Radiology 307:239007. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.239007
Zhang YP, Zhang XY, Cheng YT, Li B, Teng XZ, Zhang J et al (2023) Artificial intelligence-driven radiomics study in cancer: the role of feature engineering and modeling. Mil Med Res 10:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-023-00458-8
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr Yunjun Yang and Mr Xiang Guo for assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Wenzhou Basic Research Project (Grant No. Y2020163) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82201997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by SM, LY, GZ, DC, QX, TL, CY, CP and MZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MZ, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (YS2020-239). The informed consent was waived due to the retrospective design.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, M., Zhu, G., Chen, D. et al. T1-weighted images-based radiomics for structural lesions evaluation in patients with suspected axial spondyloarthritis. Radiol med 128, 1398–1406 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01717-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01717-3