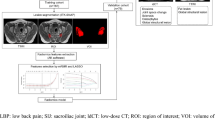
Abstract
Objectives
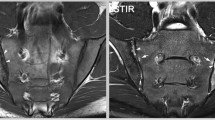
To develop an objective and efficient method based on radiomics to evaluate bone marrow edema (BMO) of sacroiliac joints (SIJs) by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and to compare with the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) scoring system.
Methods
From September 2013 to March 2022, patients with axSpA who underwent 3.0T SIJ-MRI were included and were randomly divided into training and validation cohorts at a ratio of 7:3. The optimal radiomics features selected from the SIJ-MRI in the training cohort were included to generate the radiomics model. The performance of the model was evaluated by ROC analysis and decision curve analysis (DCA). Rad scores were calculated using the radiomics model. The responsiveness was compared for Rad scores and SPARCC scores. We also assessed the correlation between the Rad score and SPARCC score.
Results
A total of 558 patients were finally included. The radiomics model showed favorable discrimination of a SPARCC score <2 or ≥2 both in the training (AUC, 0.90; 95% CI: 0.87–0.93) and validation cohorts (AUC, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.86–0.95). DCA confirmed that the model was clinically useful. Rad score showed higher responsiveness to treatment-related change than SPARCC score. Furthermore, a significant correlation was noted between the Rad score and SPARCC score when scoring the status of BMO (rs=0.80, P < 0.001), and a strong correlation was noted when scoring the change in BMO (r=0.70, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
The study proposed a radiomics model to accurately quantify the BMO of SIJs in patients with axSpA, providing an alternative to the SPARCC scoring system.
Key Points • The Rad score is an index with high validity for the objective and quantitative evaluation of bone marrow edema (BMO) of the sacroiliac joints in axial spondyloarthritis. • The Rad score is a promising tool to monitor the change of BMO upon treatment. |



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lambert RG, Bakker PA, van der Heijde D et al (2016) Defining active sacroiliitis on MRI for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: update by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann Rheum Dis 75(11):1958–1963. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208642
Rudwaleit M, Jurik AG, Hermann KG et al (2009) Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann Rheum Dis 68(10):1520–1527. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.110767
Rudwaleit M, Landewe R, van der Heijde D et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis 68(6):770–776. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.108217
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68(6):777–783. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.108233
Maksymowych WP, Wichuk S, Chiowchanwisawakit P et al (2014) Fat metaplasia and backfill are key intermediaries in the development of sacroiliac joint ankylosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(11):2958–2967. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38792
Sepriano A, Ramiro S, Landewe R et al (2019) Is active sacroiliitis on MRI associated with radiographic damage in axial spondyloarthritis? Real-life data from the ASAS and DESIR cohorts. Rheumatology (Oxford) 58(5):798–802. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key387
Sepriano A, Ramiro S, Landewé R et al (2022) Inflammation of the sacroiliac joints and spine and structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging in axial spondyloarthritis: five-year data from the DESIR cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 74(2):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.24449
Arnbak B, Jensen TS, Schiøttz-Christensen B et al (2019) What level of inflammation leads to structural damage in the sacroiliac joints? A four-year magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study of low back pain patients. Arthritis & Rheumatology 71(12):2027–2033. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41040
Maksymowych WP (2019) The role of imaging in the diagnosis and management of axial spondyloarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 15(11):657–672. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-019-0309-4
MacKay JW, Aboelmagd S, Gaffney JK (2015) Correlation between clinical and MRI disease activity scores in axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34(9):1633–1638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2936-8
Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D et al (2005) Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of sacroiliac joint inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 53(5):703–709. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21445
Maksymowych WP, Dougados M, van der Heijde D et al (2016) Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study. Ann Rheum Dis 75(7):1328–1335. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207596
Pedersen SJ, Poddubnyy D, Sørensen IJ et al (2016) Course of magnetic resonance imaging-detected inflammation and structural lesions in the sacroiliac joints of patients in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled danish multicenter study of adalimumab in spondyloarthritis, as assessed by the Berl. Arthritis & Rheumatology 68(2):418–429. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39434
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278(2):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Li M, Jin YM, Zhang YC et al (2021) Radiomics for predicting perineural invasion status in rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 27(33):5610–5621. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i33.5610
Bitencourt AGV, Gibbs P, Rossi Saccarelli C et al (2020) MRI-based machine learning radiomics can predict HER2 expression level and pathologic response after neoadjuvant therapy in HER2 overexpressing breast cancer. EBioMedicine 61:103042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103042
Sun R, Sundahl N, Hecht M et al (2020) Radiomics to predict outcomes and abscopal response of patients with cancer treated with immunotherapy combined with radiotherapy using a validated signature of CD8 cells. J Immunother Cancer 8(2):e001429. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-001429
Kepp FH, Huber FA, Wurnig MC et al (2021) Differentiation of inflammatory from degenerative changes in the sacroiliac joints by machine learning supported texture analysis. Eur J Radiol 140:109755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109755
Ye L, Miao S, Xiao Q et al (2022) A predictive clinical-radiomics nomogram for diagnosing of axial spondyloarthritis using MRI and clinical risk factors. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61(4):1440–1447. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab542
Lee KH, Choi ST, Lee GY et al (2021) Method for diagnosing the bone marrow edema of sacroiliac joint in patients with axial spondyloarthritis using magnetic resonance image analysis based on deep learning. Diagnostics (Basel) 11(7):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071156
Faleiros MC, Nogueira-Barbosa MH, Dalto VF et al (2020) Machine learning techniques for computer-aided classification of active inflammatory sacroiliitis in magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Rheumatol 60(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-020-00126-8
van den Berg R, de Hooge M, Bakker PA et al (2015) Metric properties of the SPARCC score of the sacroiliac joints - data from baseline, 3-month, and 12-month followup in the SPACE cohort. J Rheumatol 42(7):1186–1193. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.140806
Maksymowych WP, Ostergaard M, Landewe R et al (2021) Impact of filgotinib on sacroiliac joint MRI structural lesions at 12 weeks in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (TORTUGA trial). Rheumatology (Oxford) 61(5):2063–2071. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab543
van der Heijde D, Sieper J, Maksymowych WP et al (2018) Clinical and MRI remission in patients with nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis who received long-term open-label adalimumab treatment: 3-year results of the ABILITY-1 trial. Arthritis Res Ther 20(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1556-5
Zou KH, Warfield SK, Bharatha A et al (2004) Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index. Acad Radiol 11(2):178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1076-6332(03)00671-8
Weiss PF, Maksymowych WP, Xiao R et al (2020) Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac joint inflammation and structural scores: change score reliability and recalibration utility in children. Arthritis Res Ther 22(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-020-02157-4
Hededal P, Ostergaard M, Sorensen IJ et al (2018) Development and validation of MRI sacroiliac joint scoring methods for the semiaxial scan plane corresponding to the berlin and SPARCC MRI scoring methods, and of a new global MRI sacroiliac joint method. J Rheumatol 45(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.161583
Chronaiou I, Thomsen RS, Huuse EM et al (2017) Quantifying bone marrow inflammatory edema in the spine and sacroiliac joints with thresholding. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 18(1):497. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1861-1
Zarco P, Almodovar R, Bueno A et al (2018) Development and validation of SCAISS, a tool for semi-automated quantification of sacroilitis by magnetic resonance in spondyloarthritis. Rheumatol Int 38(10):1919–1926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-018-4104-3
Kucybala I, Tabor Z, Polak J et al (2020) The semi-automated algorithm for the detection of bone marrow oedema lesions in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Rheumatol Int 40(4):625–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04511-w
Puhakka KB, Jurik AG, Schiottz-Christensen B et al (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in early seronegative spondylarthropathy. Abnormalities correlated to clinical and laboratory findings. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(2):234–237. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh008
Rudwaleit M, Schwarzlose S, Hilgert ES et al (2008) MRI in predicting a major clinical response to anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 67(9):1276–1281. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.073098
Van Praet L, Jans L, Carron P et al (2014) Degree of bone marrow oedema in sacroiliac joints of patients with axial spondyloarthritis is linked to gut inflammation and male sex: results from the GIANT cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 73(6):1186–1189. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203854
Jee WH, McCauley TR, Lee SH et al (2004) Sacroiliitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: association of MR findings with disease activity. Magn Reson Imaging 22(2):245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2003.09.002
Funding
This work was supported by Wenzhou Basic Research Project (Y2020163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lusi Ye and Yunjun Yang designed and supervised the study. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Shouliang Miao, Dan Chen, Mo Zheng, Fei Yao, Qinqin Xiao, Guanxia Zhu, Chenqiang Pan, Tao Lei, and Chenhao Ye. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mo Zheng and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, M., Miao, S., Chen, D. et al. Can radiomics replace the SPARCC scoring system in evaluating bone marrow edema of sacroiliac joints in patients with axial spondyloarthritis?. Clin Rheumatol 42, 1675–1682 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06543-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06543-6